1
Slide 1

Slide 2

COMPLIANCE MADE EASY Shawn Wells Director, Innovation Programs 12-JUNE-2013 shawn@redhat.com | @shawndwells 2
Slide 3

50 MINUTES, 3 GOALS 1. Review security compliance tech + initiatives • • • 2. 3. SCAP Security Guide Project Security Technical Implementation Guides (STIGs) FedRAMP / FISMA Moderate
Slide 4

50 MINUTES, 3 GOALS 1. Review security compliance tech + initiatives • • • SCAP Security Guide Project Security Technical Implementation Guides (STIGs) FedRAMP / FISMA Moderate 2. Demonstrate current capabilities • • 3. OpenSCAP + SCAP Security Guide RHN Satellite Audit [ CLI ] [ GUI ]
Slide 5

50 MINUTES, 3 GOALS 1. Review security compliance tech + initiatives • • • SCAP Security Guide Project Security Technical Implementation Guides (STIGs) FedRAMP / FISMA Moderate 2. Demonstrate current capabilities • • OpenSCAP + SCAP Security Guide RHN Satellite Audit [ CLI ] [ GUI ] 3. Discuss compliance content roadmap • Program validation & priority adjustment
Slide 6
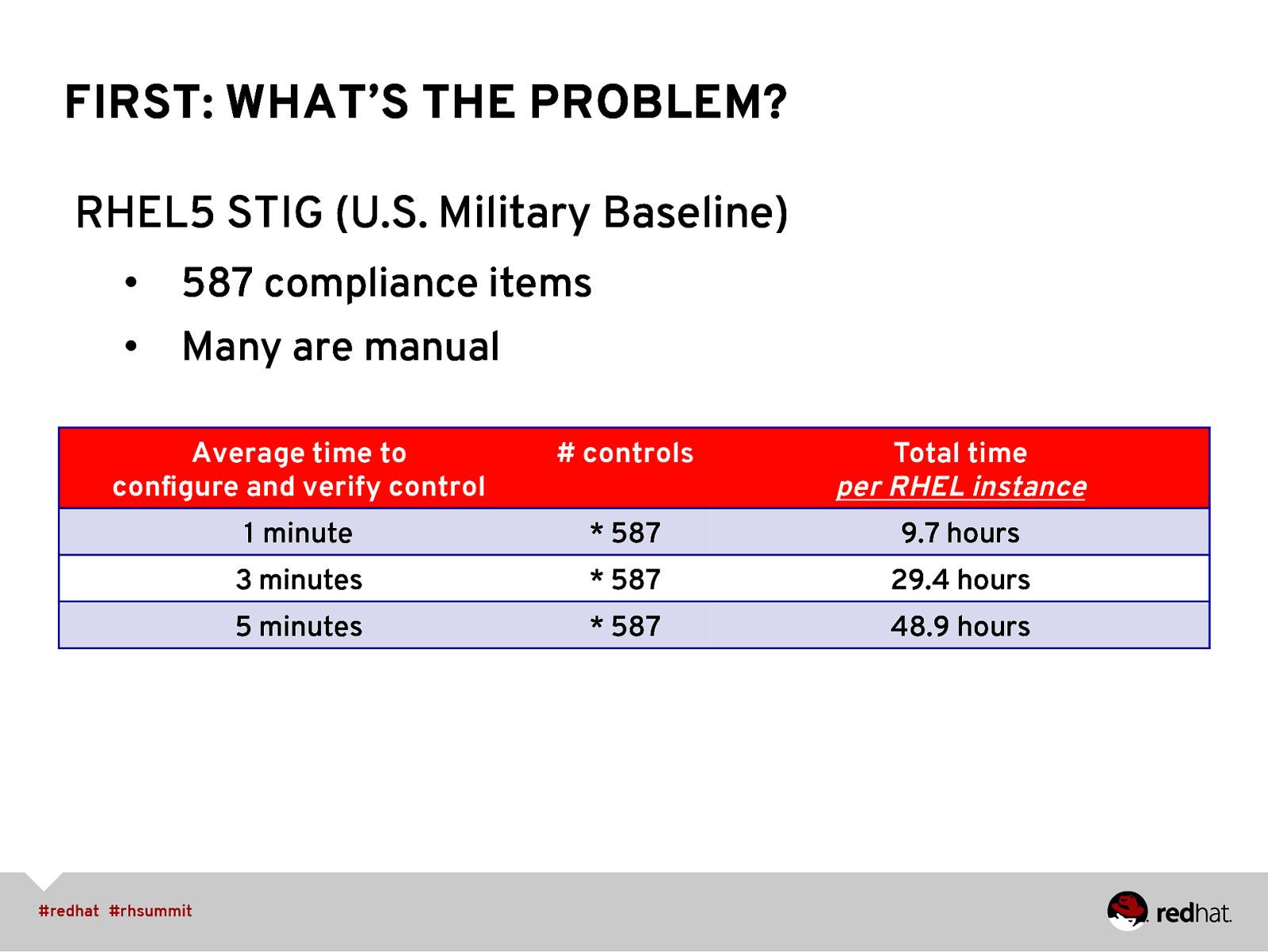
FIRST: WHAT’S THE PROBLEM? RHEL5 STIG (U.S. Military Baseline) • 587 compliance items • Many are manual Average time to configure and verify control
controls
Total time per RHEL instance 1 minute
- 587 9.7 hours 3 minutes
- 587 29.4 hours 5 minutes
- 587 48.9 hours
Slide 7

Common Criteria
Slide 8

Common Criteria != Compliance Policy
Slide 9
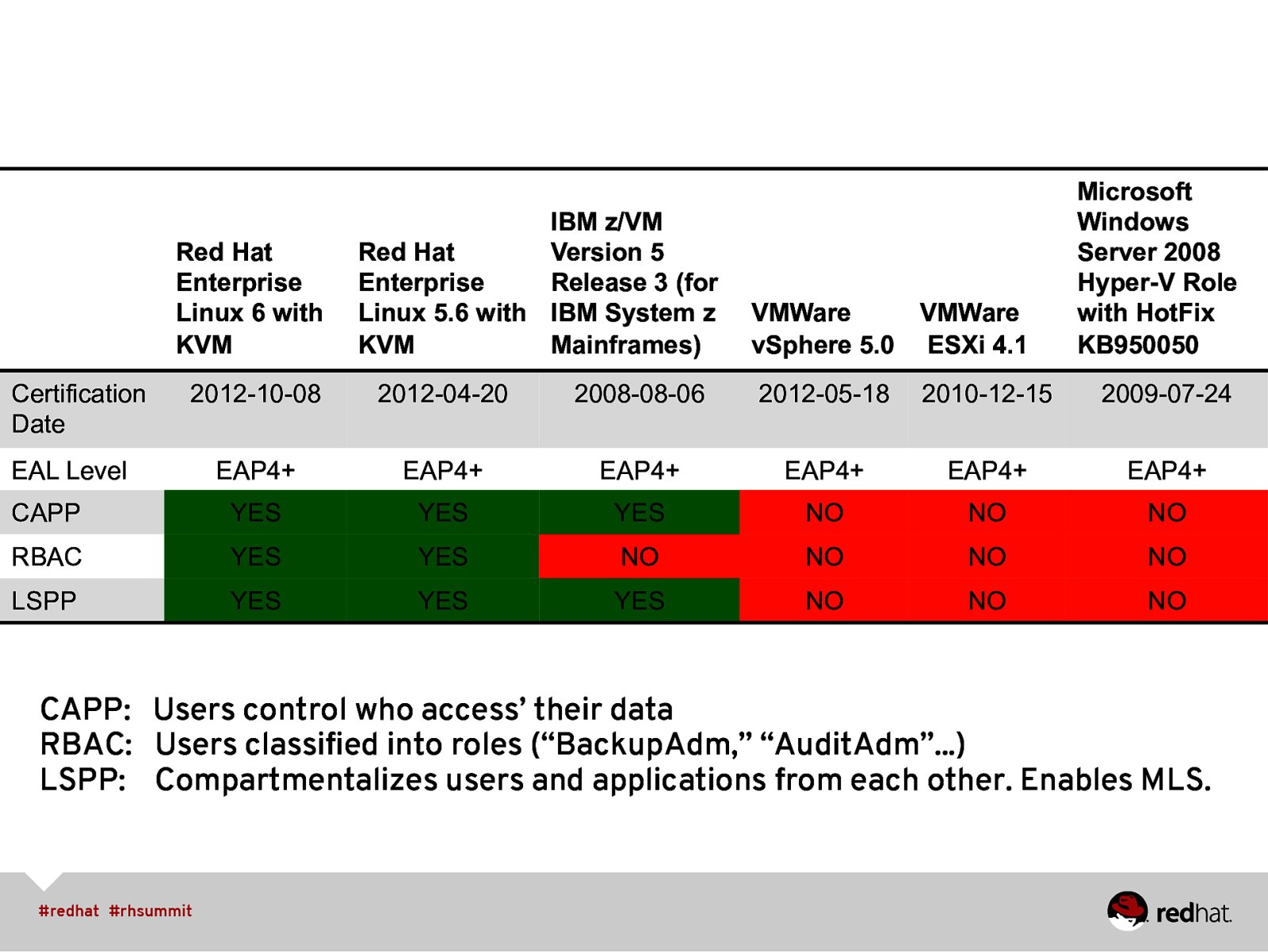
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 with KVM Certification Date IBM z/VM Red Hat Version 5 Enterprise Release 3 (for Linux 5.6 with IBM System z KVM Mainframes) VMWare VMWare vSphere 5.0 ESXi 4.1 Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Hyper-V Role with HotFix KB950050 2012-10-08 2012-04-20 2008-08-06 2012-05-18 2010-12-15 2009-07-24 EAP4+ EAP4+ EAP4+ EAP4+ EAP4+ EAP4+ CAPP YES YES YES NO NO NO RBAC YES YES NO NO NO NO LSPP YES YES YES NO NO NO EAL Level CAPP: Users control who access’ their data RBAC: Users classified into roles (“BackupAdm,” “AuditAdm”…) LSPP: Compartmentalizes users and applications from each other. Enables MLS.
Slide 10

Common Criteria tells the government software can be “trusted” ê ê ê
Slide 11

Common Criteria tells the government software can be “trusted” ê NIST publishes catalog of best practices (“You must use secure passwords”) ê ê
Slide 12

Common Criteria tells the government software can be “trusted” ê NIST publishes catalog of best practices (“You must use secure passwords”) ê Agencies select and refine practices they agree with (“NSA passwords must be 14 characters”) ê
Slide 13

Common Criteria tells the government software can be “trusted” ê NIST publishes catalog of best practices (“You must use secure passwords”) ê Agencies select and refine practices they agree with (“NSA passwords must be 14 characters”) ê Agencies aggregate refined values into Agency baselines (e.g. STIG for DoD, USGCB for Civilian)
Slide 14

RHEL5 STIG Delay: 1,988 days
Slide 15

RHEL5 STIG Delay: 1,988 days RHEL6 STIG Delay: 932 days
Slide 16

SCAP Security Guide
Slide 17

SCAP HTML
Slide 18

SCAP OpenSCAP HTML Firefox
Slide 19
Slide 20
GUIDANCE
Slide 21
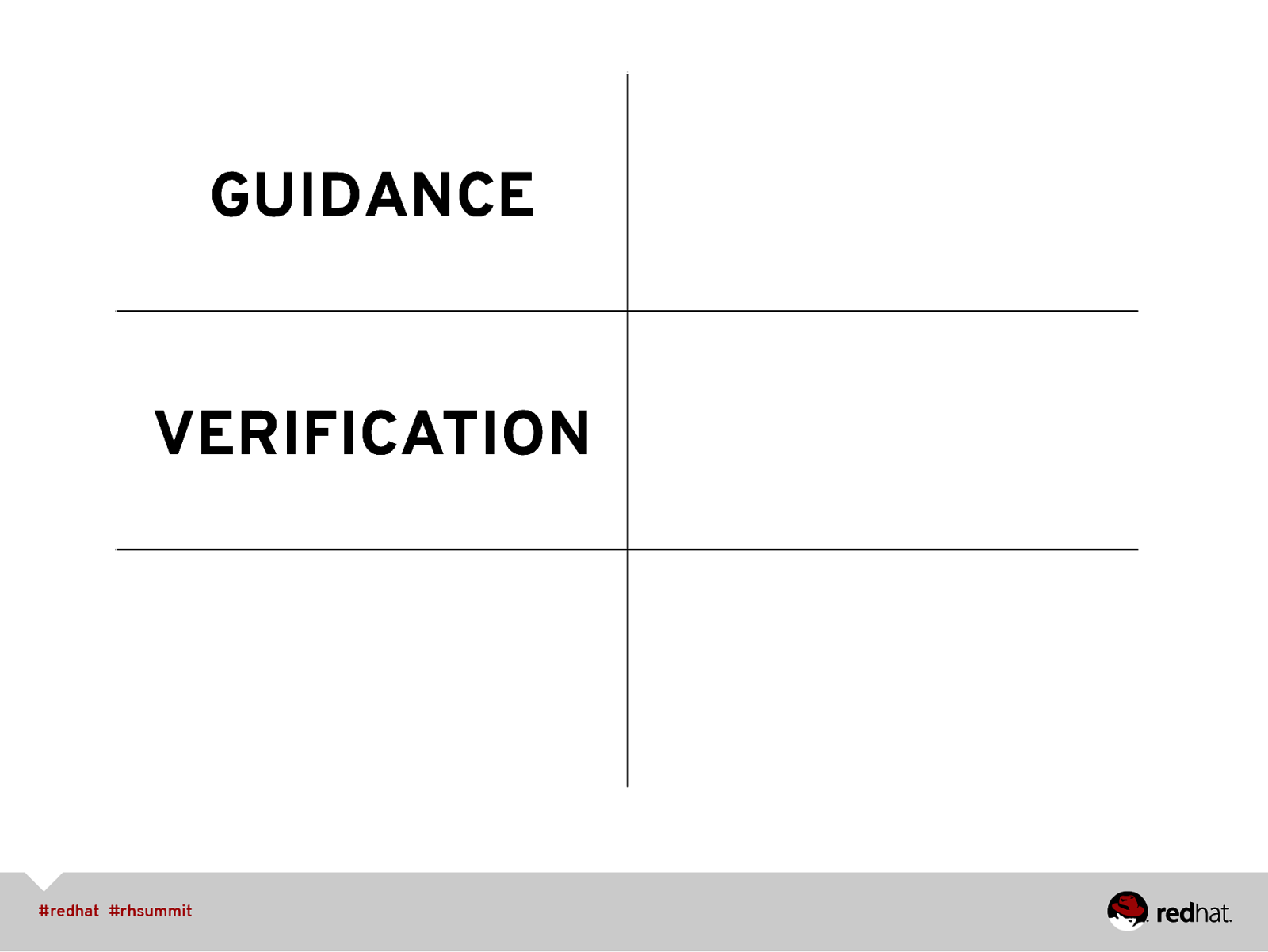
GUIDANCE VERIFICATION
Slide 22
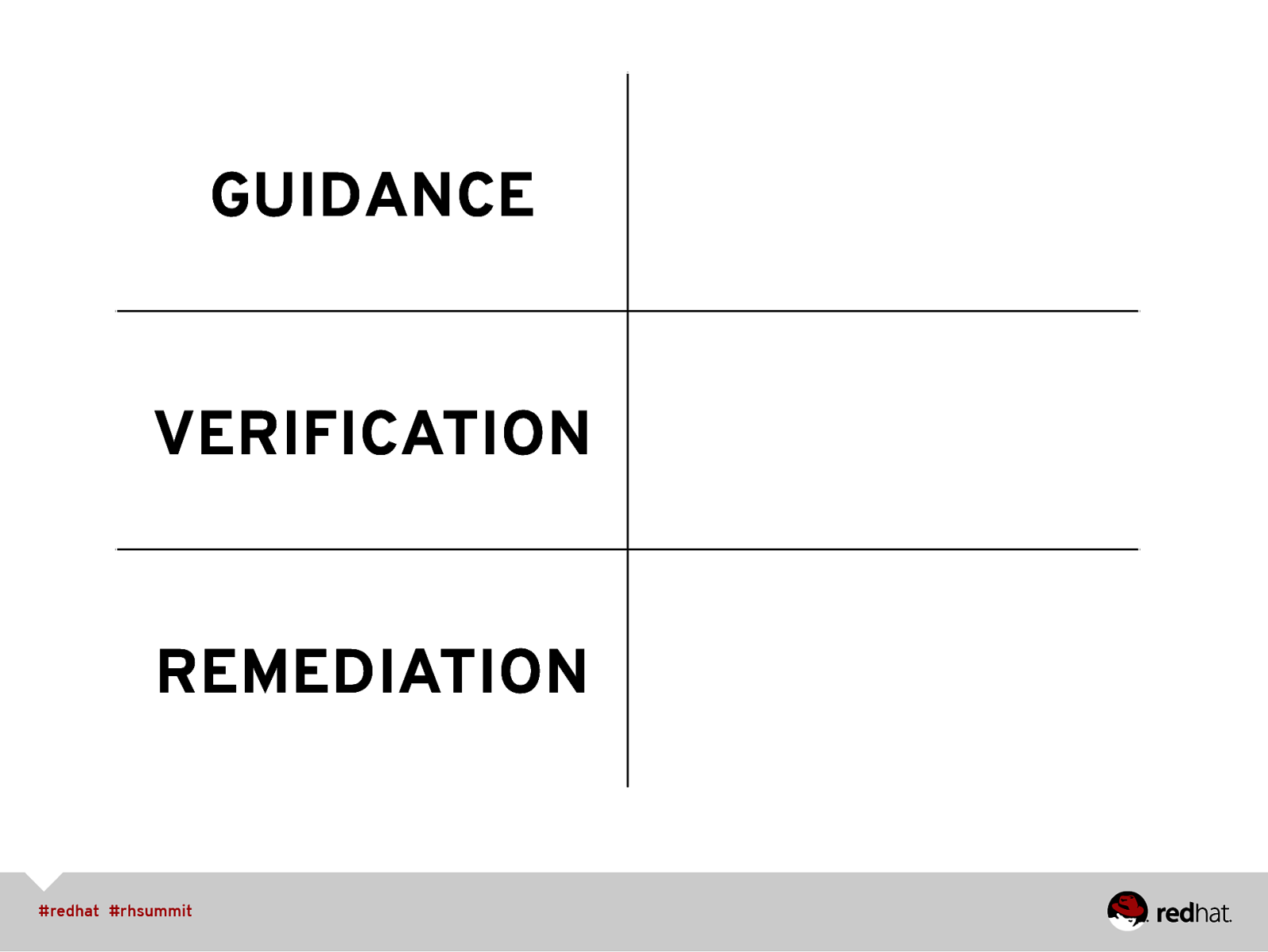
GUIDANCE VERIFICATION REMEDIATION
Slide 23
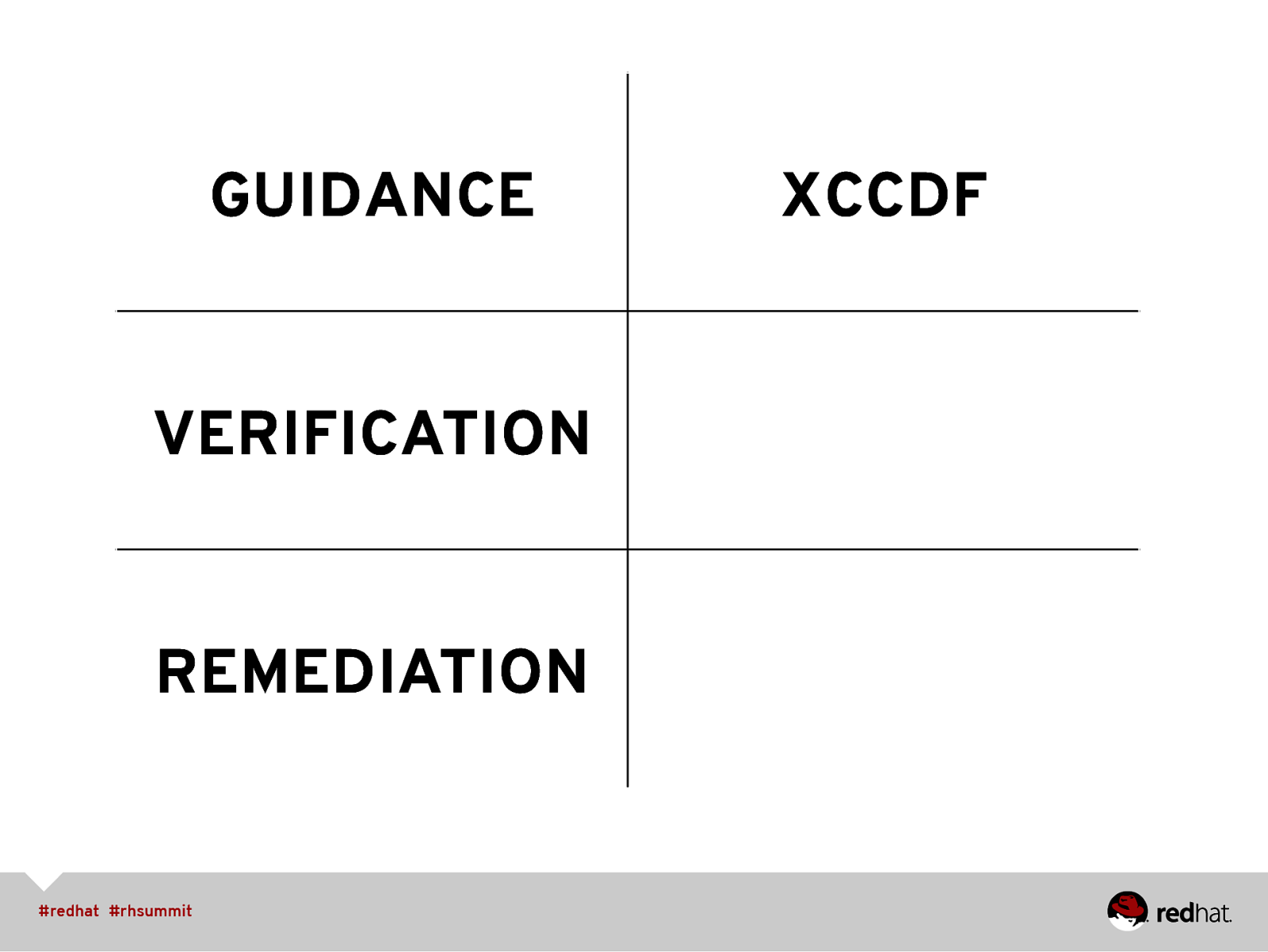
GUIDANCE VERIFICATION REMEDIATION XCCDF
Slide 24
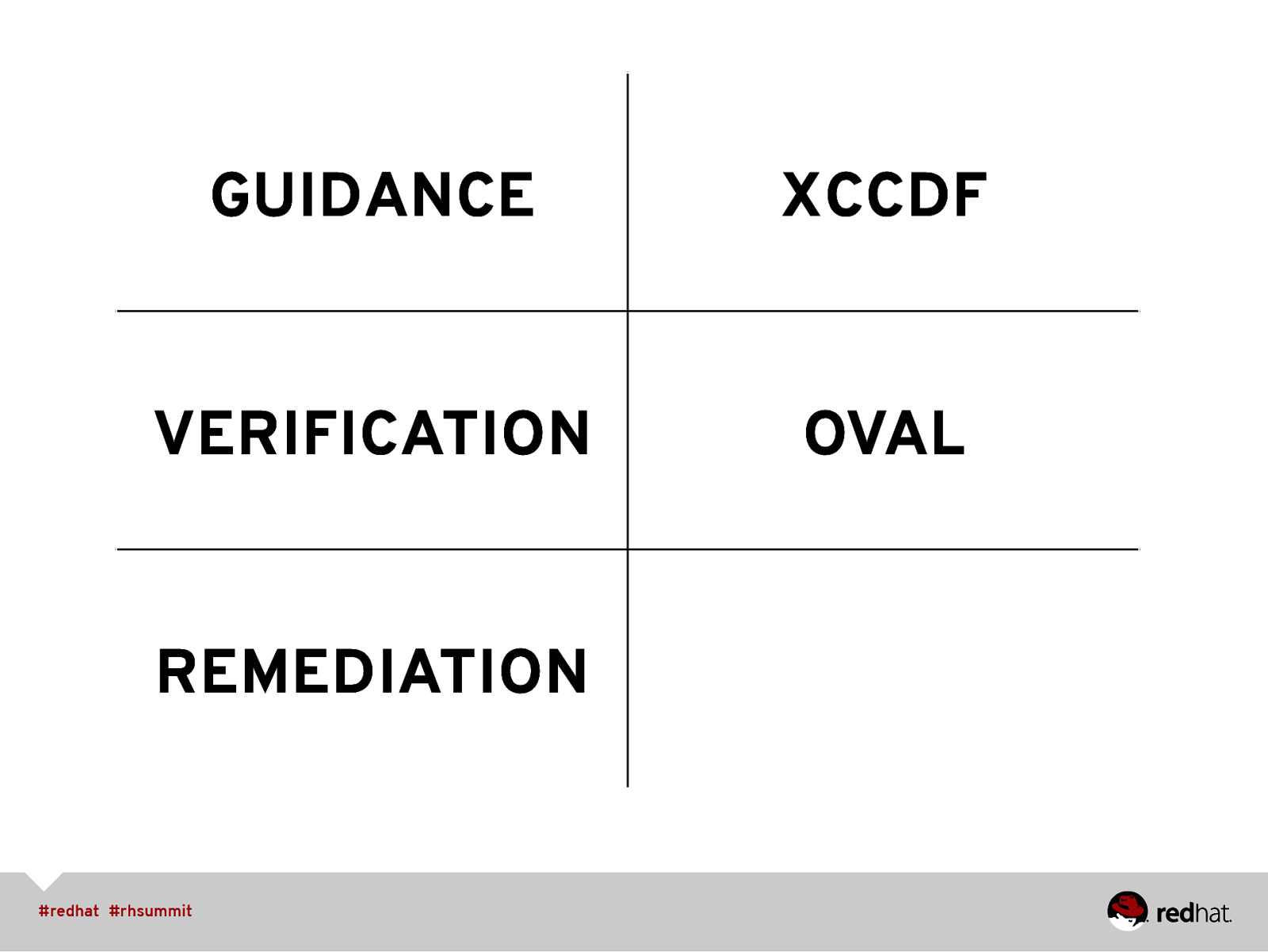
GUIDANCE XCCDF VERIFICATION OVAL REMEDIATION
Slide 25
GUIDANCE XCCDF VERIFICATION OVAL REMEDIATION bash
Slide 26

Slide 27
ROADMAP • OpenStack Security Guide begins 24-JUNE-2013 • Content will be incorporated into SCAP Security Guide • Formation of Red Hat OpenStack STIG (eta Q4 2013) • Want to participate? • https://fedorahosted.org/scap-security-guide/ We need your feedback to prioritize other tech! • OpenShift vs JBoss vs Red Hat Storage vs ……..
Slide 28

MORE INFO Web http://fedorahosted.org/scap-security-guide Mail https://fedorahosted.org/mailman/listinfo/scap-security-guide DISA STIG http://iase.disa.mil/stigs/os/unix/red_hat.html
Slide 29

APPENDIX I: Additional SSG Project Info 29
Slide 30

• Delivers practical security guidance, baselines, and associated validation mechanisms using the Security Content Automation Protocol (SCAP) • Current content for RHEL6, JBoss EAP5 • Upstream source for government implementation guidance • Specifically, DISA STIG and NSA SNAC Guide • First example of US Government policy, not just technology, derived from community open source project!
Slide 31

• Open Source project • https://fedorahosted.org/scap-security-guide (and yes, government can contribute!) (and yes, we checked with the lawyers) • Why? • • Enables agile government—vendor—consumer interaction Ensures consensus among stakeholders • Enables development in SCAP formats
Slide 32

• Recommendations map to compliance standards wherever possible • Because of this mapping, creation of custom “profiles” possible • RHEL6 STIG • RHEL6 Security Guide (via NSA) • Baseline content for FedRAMP • Your own?
Slide 33
• SCAP Formats • XML schemas, managed by NIST • Configuration checklist / guide format is XCCDF • Automated checking via OVAL
Slide 34

• COSTS • Complex XML schema • OVAL just a bit verbose </understatement> • BENEFITS • Ingestible by SCAP-compatible tools • OpenSCAP ships within RHEL! • XCCDF Profiles • Standardized outputs/reporting
Slide 35

APPENDIX: USAGE DEMO 35
Slide 36

USE THE WORKBOOK! • Available on wiki: https://fedorahosted.org/scap-security-guide/
Slide 37

STEP 1: DOWNLOAD • RPM yum repository (EPEL) $ sudo sh -c “wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel-6-scap-security-guide.repo \ http://repos.fedorapeople.org/repos/scap-security-guide/epel-6-scap-securityguide.repo” $ sudo sh –c “yum install scap-security-guide” ” • Source Code $ git clone ssh://git.fedorahosted.org/git/scap-security-guide.git ” • Note: RPMs place files into /usr/share/xml/scap/ssg
Slide 38

STEP 2: REVIEW GUIDANCE • HTML guides located in /usr/share/xml/scap/ssg/guides/ • As of SSG v0.1-11, shipping EAP5 and RHEL6 guides $ firefox \ /usr/share/xml/scap/ssg/guides/rhel6-guide.html”
Slide 39

STEP 3: REVIEW POLICY MAPPINGS • Policy mappings located in /usr/share/xml/scap/ssg/policytables/ • Frequently used as Security Requirements Traceability Matrix (STRM) foundations $ firefox \ /usr/share/xml/scap/ssg/policytables/table-rhel6nistrefs.html”
Slide 40

STEP 4: RUN A SCAN $ sudo sh -c “oscap xccdf eval −−profile stig-rhel6-server \ −−results /root/ssg-results.xml \ −−report /root/ssg-results.html \ −−cpe /usr/share/xml/scap/ssg/content/ssg-rhel6-cpedictionary.xml \ /usr/share/xml/scap/ssg/content/ssg-rhel6-xccdf.xml”
”
—results:
XML formatted results
—report:
HTML formatted results
Need help? man scap-security-guide
Slide 41
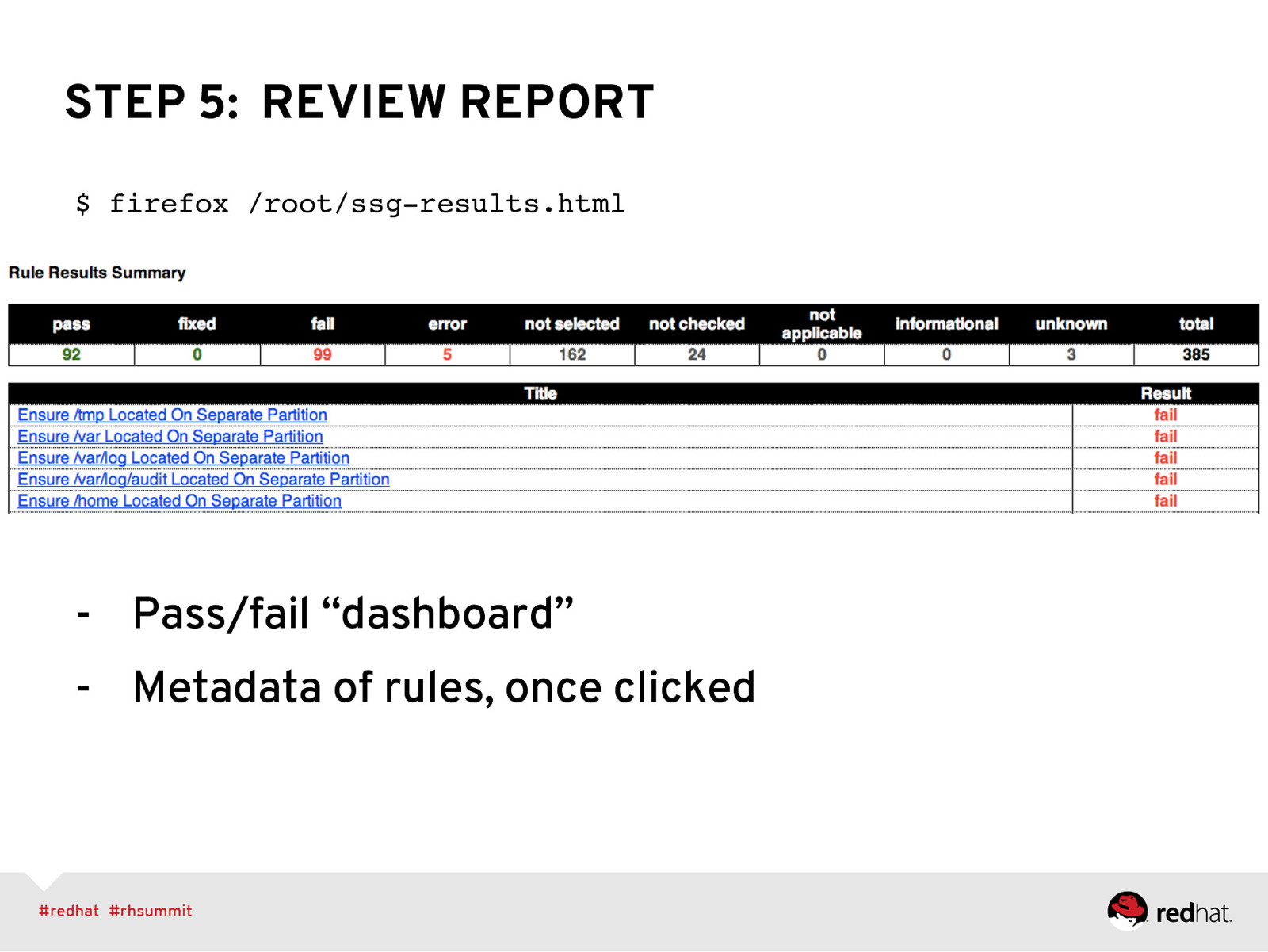
STEP 5: REVIEW REPORT $ firefox /root/ssg-results.html” ” ” ” ” “
- Pass/fail “dashboard” - Metadata of rules, once clicked
Slide 42

STEP 6: GENERATE REMEDIATION SCRIPTS As of SSG v0.1-11 (e.g. June 2013) this feature is undergoing rapid development. Not complete, not fully tested, not ready for production! $ oscap xccdf generate fix \ —result-id xccdf_org.open-scap_testresult_stig-rhel6-server \ /var/www/html/results/results.xml “
Slide 43

STEP 6: GENERATE REMEDIATION SCRIPTS $ oscap xccdf generate fix \ —result-id xccdf_org.open-scap_testresult_stig-rhel6-server \ /var/www/html/results/results.xml #!/bin/bash” # OpenSCAP fix generator output for benchmark: Guide to the # Secure Configuration of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6” # Generating fixes for all failed rules in test result # ‘xccdf_org.open-scap_testresult_stig-rhel6-server’.” # XCCDF rule: set_sysctl_net_ipv4_conf_all_accept_redirects # CCE-27027-2 # Set runtime for net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_redirects” sysctl -q -n -w net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_redirects=0 if grep —silent ^net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_redirects /etc/sysctl.conf ; then “sed –i \ ‘s/^net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_redirects.*/net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_redirects = 0/g’ \ /etc/sysctl.conf else “echo “” >> /etc/sysctl.conf “echo “# Set net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_redirects to 0 per security requirements” \ >> /etc/sysctl.conf “echo “net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_redirects = 0” >> /etc/sysctl.conf fi”
Slide 44

STEP 7: XCCDF Review
Slide 45

STEP 8: OVAL REVIEW <ind:textfilecontent54_object id=”obj_20134” version=”1”>” ind:path/etc</ind:path>” ind:filenamesysctl.conf</ind:filename>” <ind:pattern operation=”pattern match”>^\snet.ipv6.conf.all .disable_ipv6\s=\s*1$</ind:pattern>” <ind:instance datatype=”int”>1</ind:instance>” </ind:textfilecontent54_object>”