RED HAT TECHNICAL SYMPOSIUM NSA R&E Symposium Center Monday November 8th, 2010 1300-1600
Slide 1

Slide 2

AGENDA 1:00-1:20 Software Central Opening Notes 1:20-2:20 Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 Update 2:20-2:30 Break 2:30-3:30 Red Hat in the Virtualized Environment & Security 3:30-4:00 Q&A Panel w/ Red Hat Technologists 2
Slide 3

RED HAT ENTERPRISE LINUX 6 UPDATE Shawn D. Wells Technical Director, Intelligence Programs sdw@redhat.com / 443-534-0130
Slide 4
RED HAT ENTERPRISE LINUX 6 UPDATE RHEL6 FOUNDATION FEATURES & THEMES ● Trusted data center platform Ideally positioned to provide non-disruptive path forward. ● Application and infrastructure performance, scalability and security Support for varied workloads and advanced hardware capabilities. ● Making IT agile across physical, virtual and Cloud The right operating system across any environment. 4
Slide 5
RED HAT ENTERPRISE LINUX 6 UPDATE RHEL6 FOUNDATION FEATURES & THEMES ● Improved manageability For large scale virtualization deployments, server & desktop. Samba enhancements for Windows active directory and file sharing ● Power management Efficiency for lower deployment costs, reduced carbon footprint for virt, bare metal, desktop. Hardware level as well as dynamic system service startup and suspend. ● RAS (Reliability, Availability, Serviceability) Hotplug, memory error reporting, filesystem and data integrity. Support tools such as automated crash detection and bug reporting. 5
Slide 6
RED HAT ENTERPRISE LINUX 6 UPDATE RHEL6 FOUNDATION FEATURES & THEMES ● Hardware enablement and scalability Maximum efficiency, large configurations (cpu, memory, busses, I/O), NUMA awareness, new BIOS boot loader interface Supported architectures: x86, x86_64, PPC64, s390x 6
Slide 7
RED HAT ENTERPRISE LINUX 6 UPDATE SYSTEMS MANAGEMENT INTEGRATION ● Red Hat Network Satellite ● ● ● ● ● 7 Install & provision new systems Update existing Manage configuration files & maintain over time Monitoring system metrics Multiple managed Satellites on ELA
Slide 8
RED HAT ENTERPRISE LINUX 6 UPDATE SYSTEMS MANAGEMENT INTEGRATION ● Red Hat Network Satellite 5.4 ● ● ● ● 8 ● RPMs will be now be encrypted with 256-bit keys, up from 128-bit. Find & remove stale instances that are no longer being used Flex Guest / Floating Entitlements Centrally manage SELinux Context on remote files Expanded APIs for 3rd party integration
Slide 9
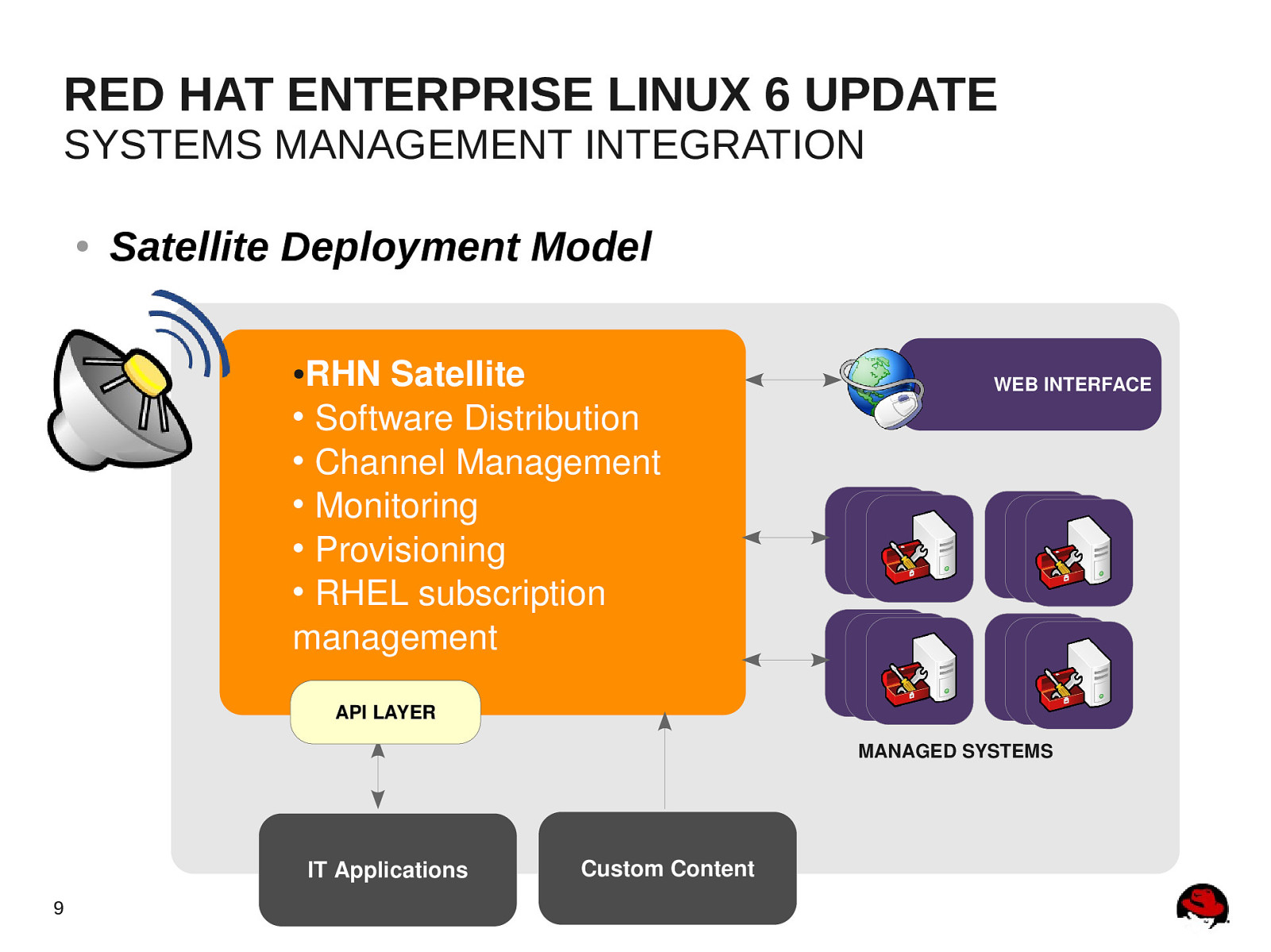
RED HAT ENTERPRISE LINUX 6 UPDATE SYSTEMS MANAGEMENT INTEGRATION ● Satellite Deployment Model RHN Satellite • Software Distribution • Channel Management • Monitoring • Provisioning • RHEL subscription management ● WEB INTERFACE API LAYER MANAGED SYSTEMS IT Applications 9 Custom Content
Slide 10
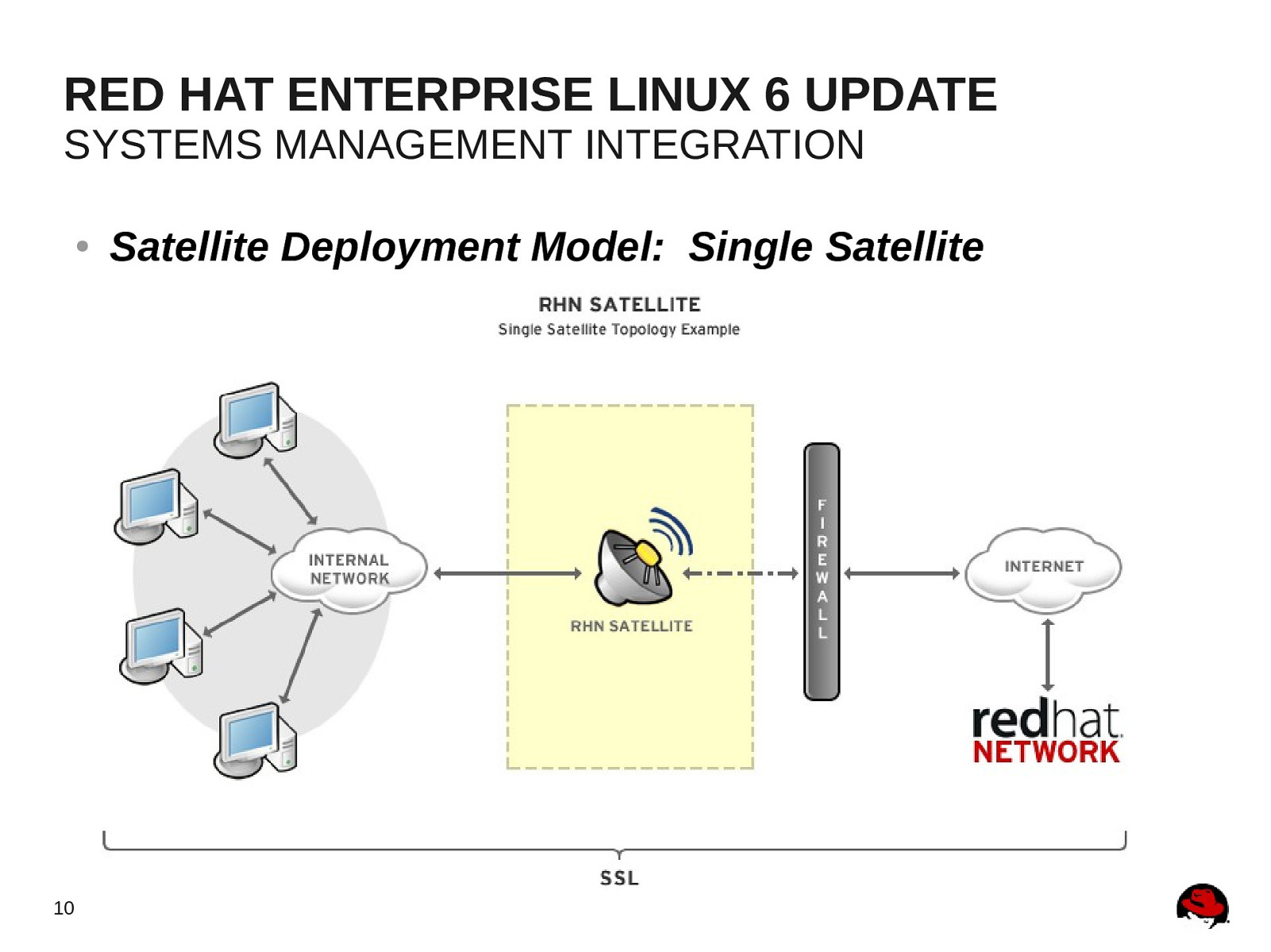
RED HAT ENTERPRISE LINUX 6 UPDATE SYSTEMS MANAGEMENT INTEGRATION ● 10 Satellite Deployment Model: Single Satellite
Slide 11
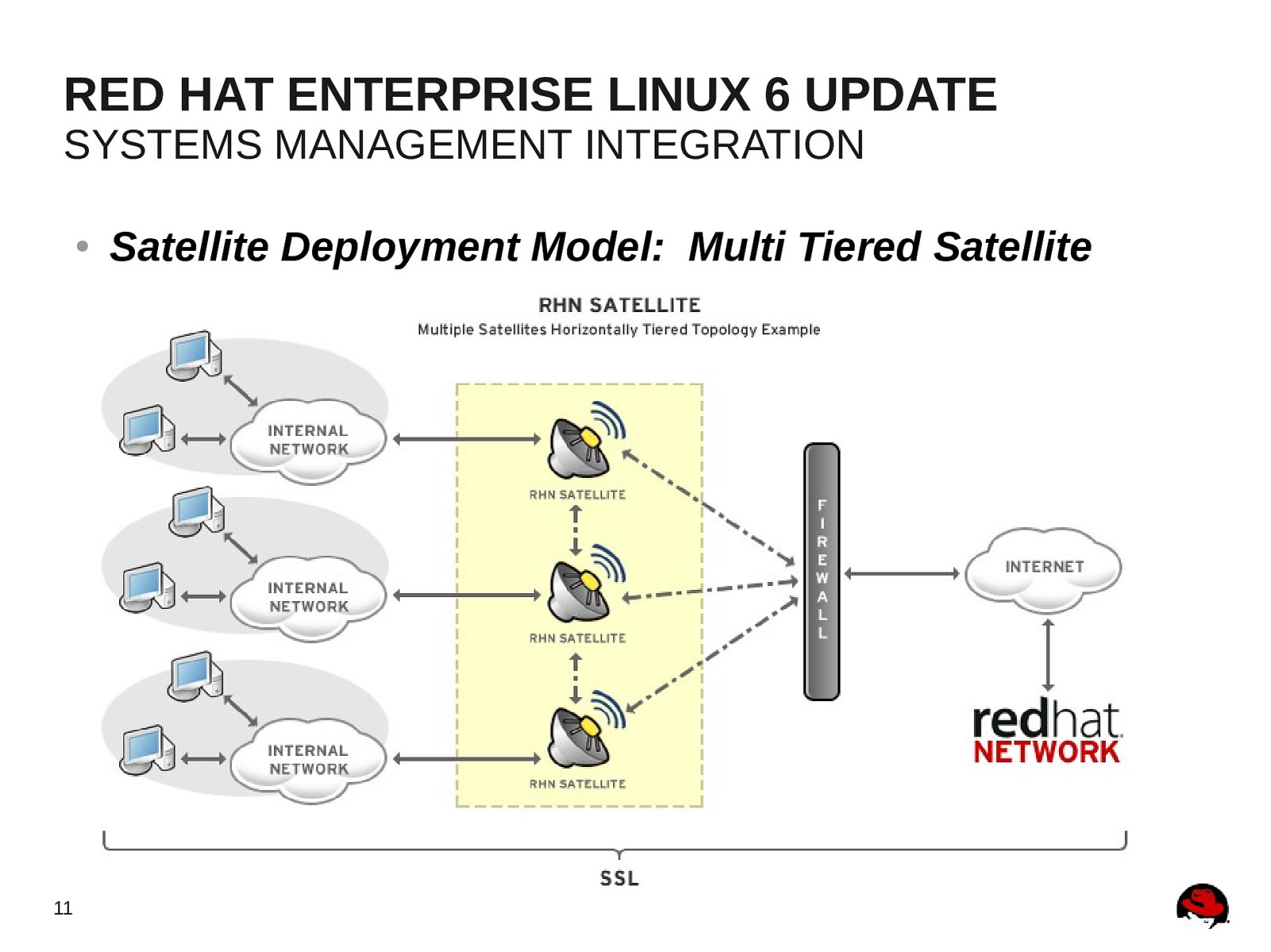
RED HAT ENTERPRISE LINUX 6 UPDATE SYSTEMS MANAGEMENT INTEGRATION ● 11 Satellite Deployment Model: Multi Tiered Satellite
Slide 12

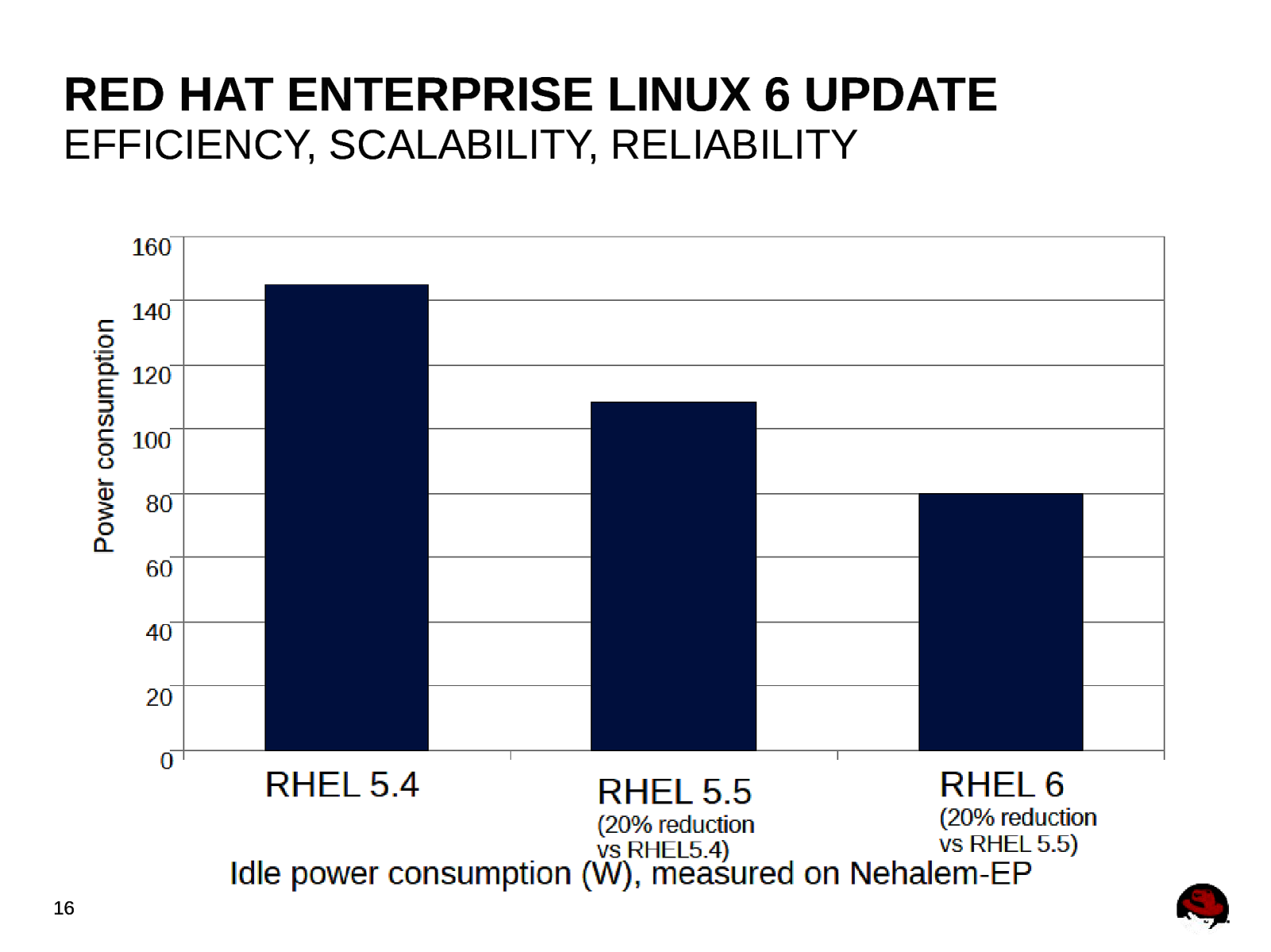
RED HAT ENTERPRISE LINUX 6 UPDATE EFFICIENCY, SCALABILITY, RELIABILITY Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 evolves in concert with hardware advances, reducing system power consumption, taking advantage of hardware with greater numbers of processing and memory resources, and withstanding hardware failures better. 12
Slide 13
RED HAT ENTERPRISE LINUX 6 UPDATE EFFICIENCY, SCALABILITY, RELIABILITY ● New scheduler (Completely Fair Scheduler) ● Dynamic addition of processor and memory ● ● 13 More robust error reporting for PCIe devices (PCIe AER) Isolation of memory hardware failures with minimal downtime
Slide 14
RED HAT ENTERPRISE LINUX 6 UPDATE EFFICIENCY, SCALABILITY, RELIABILITY ● ● 14 Mature file systems to cater to varied usage and performance characteristics. ● Ext4: Now default, scales to 16TB ● GFS2: Scales to 25TB ● XFS: Scales up to 100TB, tuned for storage arrays ● NFSv4 Configured to reduce chances of data corruption for low-end locally attached storage.
Slide 15
RED HAT ENTERPRISE LINUX 6 UPDATE EFFICIENCY, SCALABILITY, RELIABILITY ● 15 Power management ● Tickless kernel ● User-space tools – powertop ● Dynamic throttling of power to devices ● Relatime drive optimization
Slide 16
RED HAT ENTERPRISE LINUX 6 UPDATE EFFICIENCY, SCALABILITY, RELIABILITY 16
Slide 17
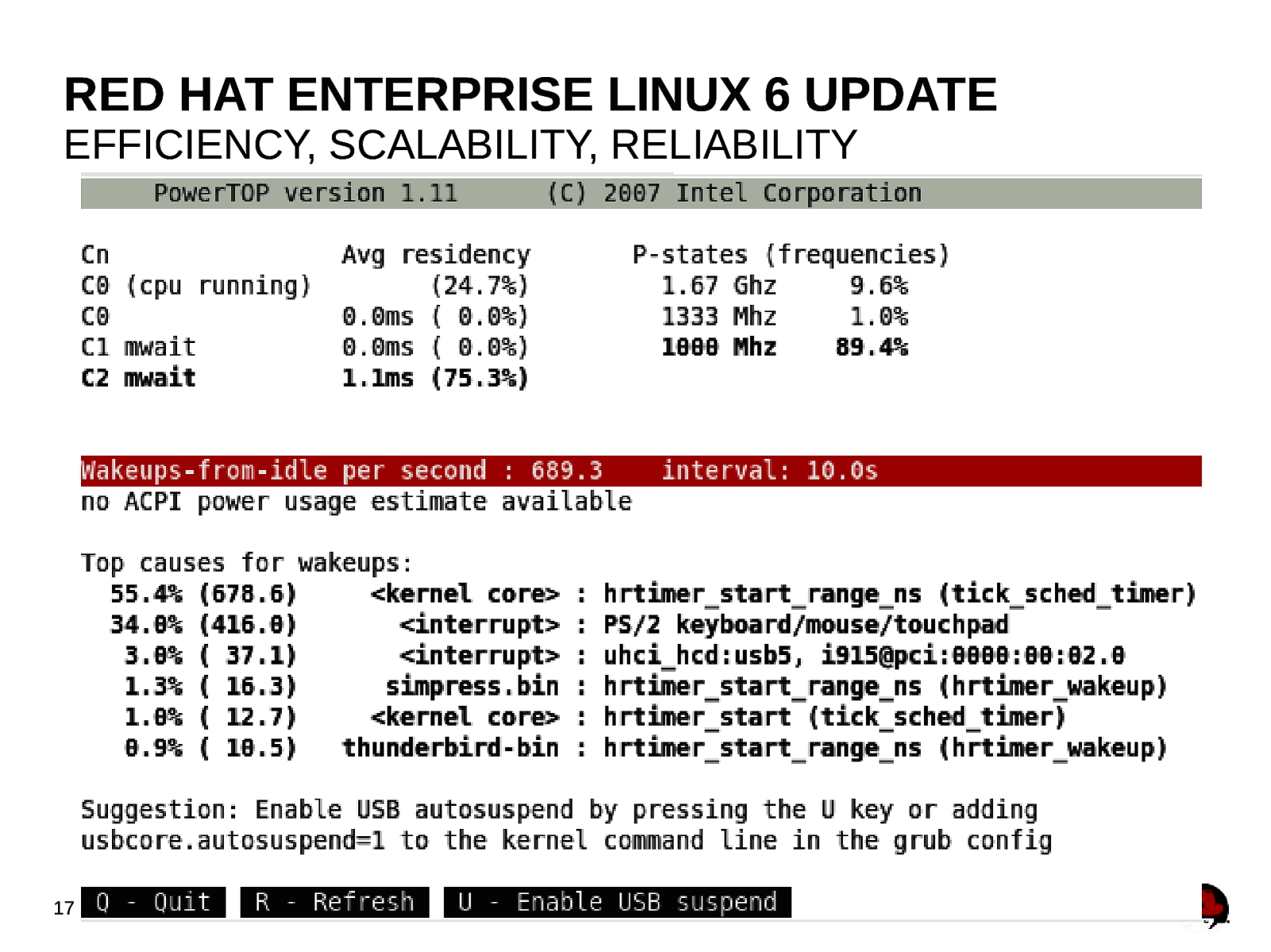
RED HAT ENTERPRISE LINUX 6 UPDATE EFFICIENCY, SCALABILITY, RELIABILITY 17
Slide 18

RED HAT ENTERPRISE LINUX 6 UPDATE EFFICIENCY, SCALABILITY, RELIABILITY Objective: Providing scaling headroom anticipating many years of upcoming hardware generations. Tested and supported limits will likely grow over the course of product lifespan. 18
Slide 19
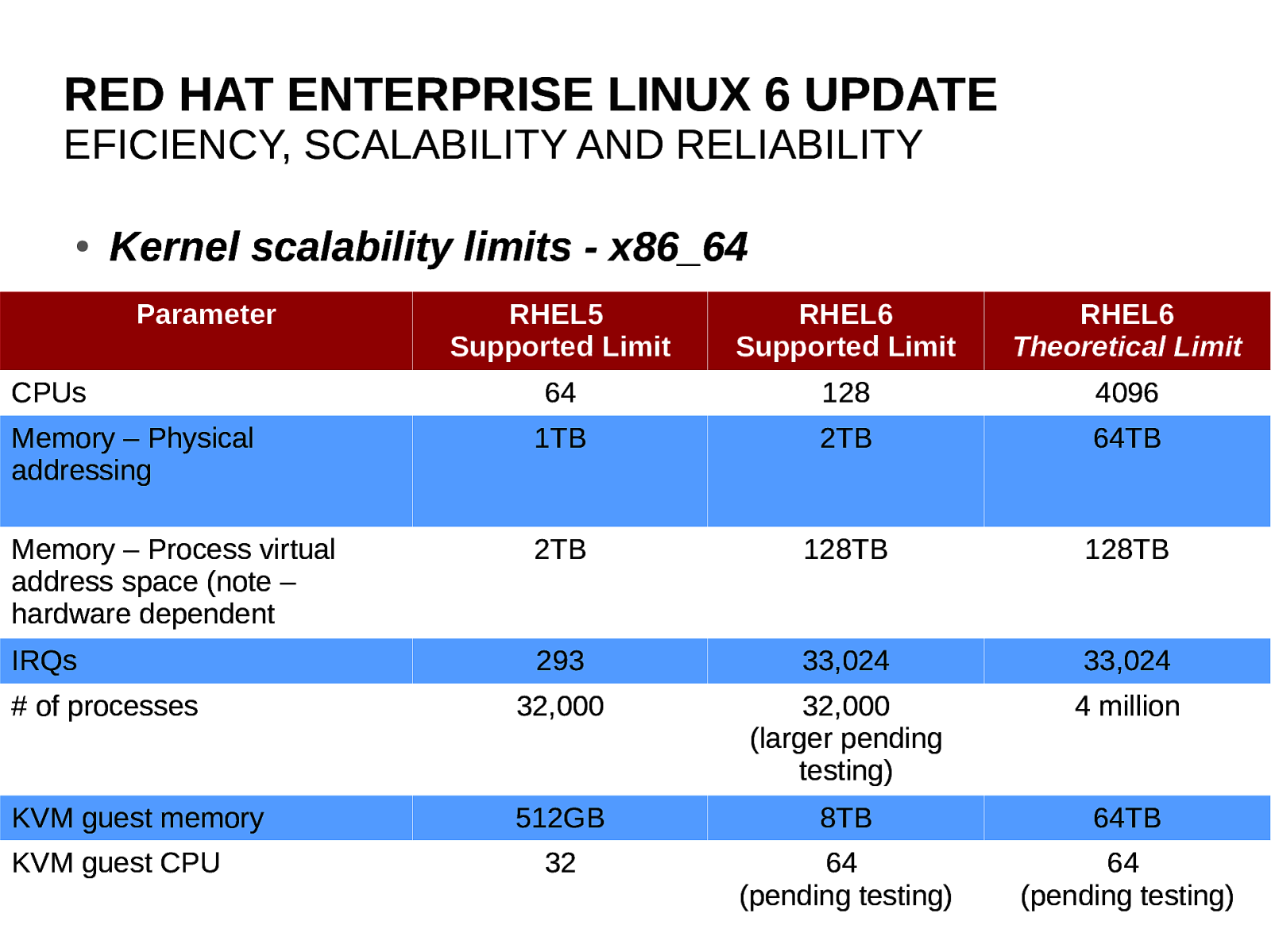
RED HAT ENTERPRISE LINUX 6 UPDATE EFICIENCY, SCALABILITY AND RELIABILITY ● Kernel scalability limits - x86_64 Parameter RHEL5 Supported Limit RHEL6 Supported Limit RHEL6 Theoretical Limit 64 128 4096 Memory – Physical addressing 1TB 2TB 64TB Memory – Process virtual address space (note – hardware dependent 2TB 128TB 128TB IRQs 293 33,024 33,024
of processes
32,000 32,000 (larger pending testing) 4 million KVM guest memory 512GB 8TB 64TB 32 64 (pending testing) 64 (pending testing) CPUs KVM guest CPU 19
Slide 20
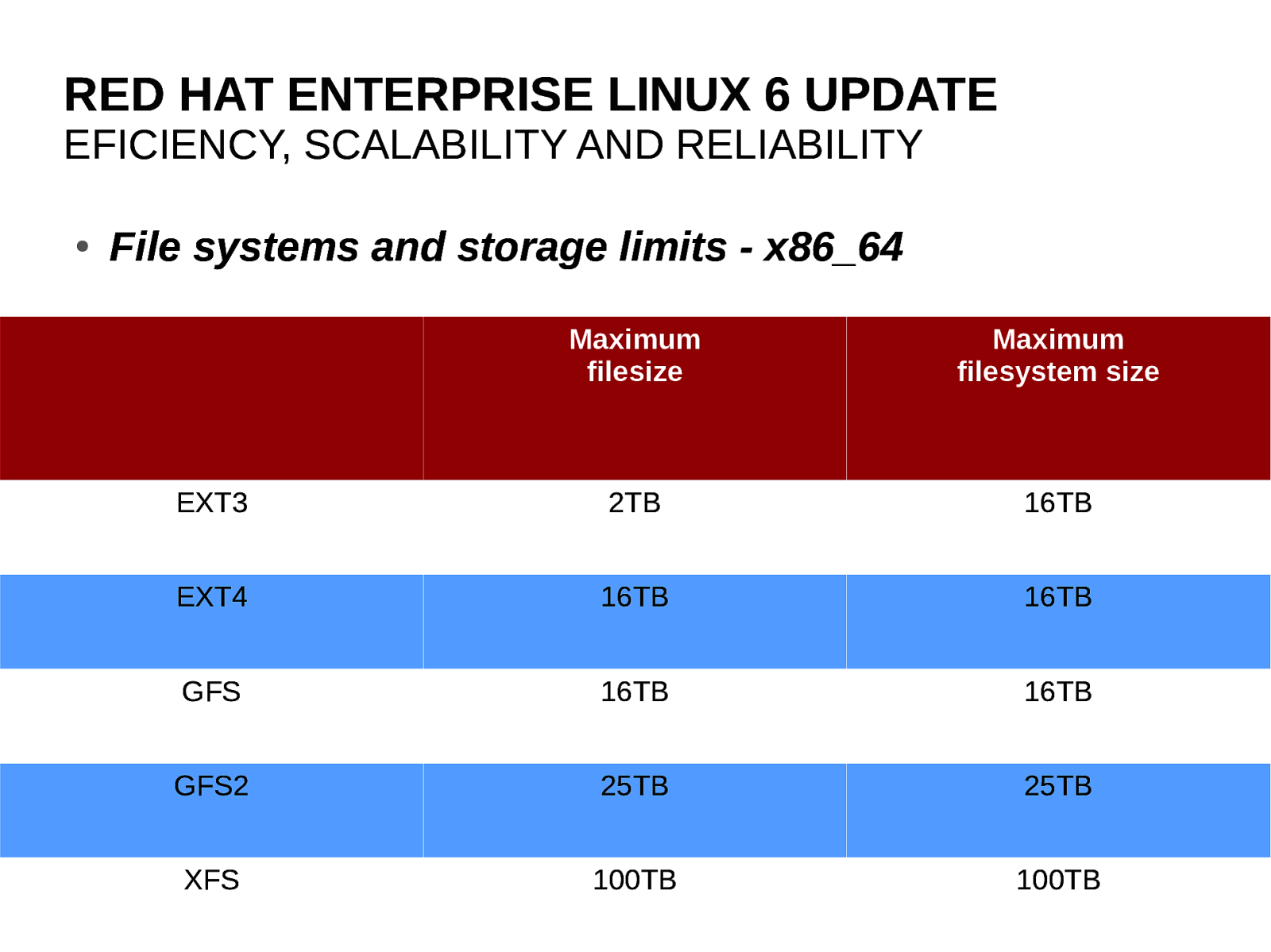
RED HAT ENTERPRISE LINUX 6 UPDATE EFICIENCY, SCALABILITY AND RELIABILITY ● 20 File systems and storage limits - x86_64 Maximum filesize Maximum filesystem size EXT3 2TB 16TB EXT4 16TB 16TB GFS 16TB 16TB GFS2 25TB 25TB XFS 100TB 100TB
Slide 21
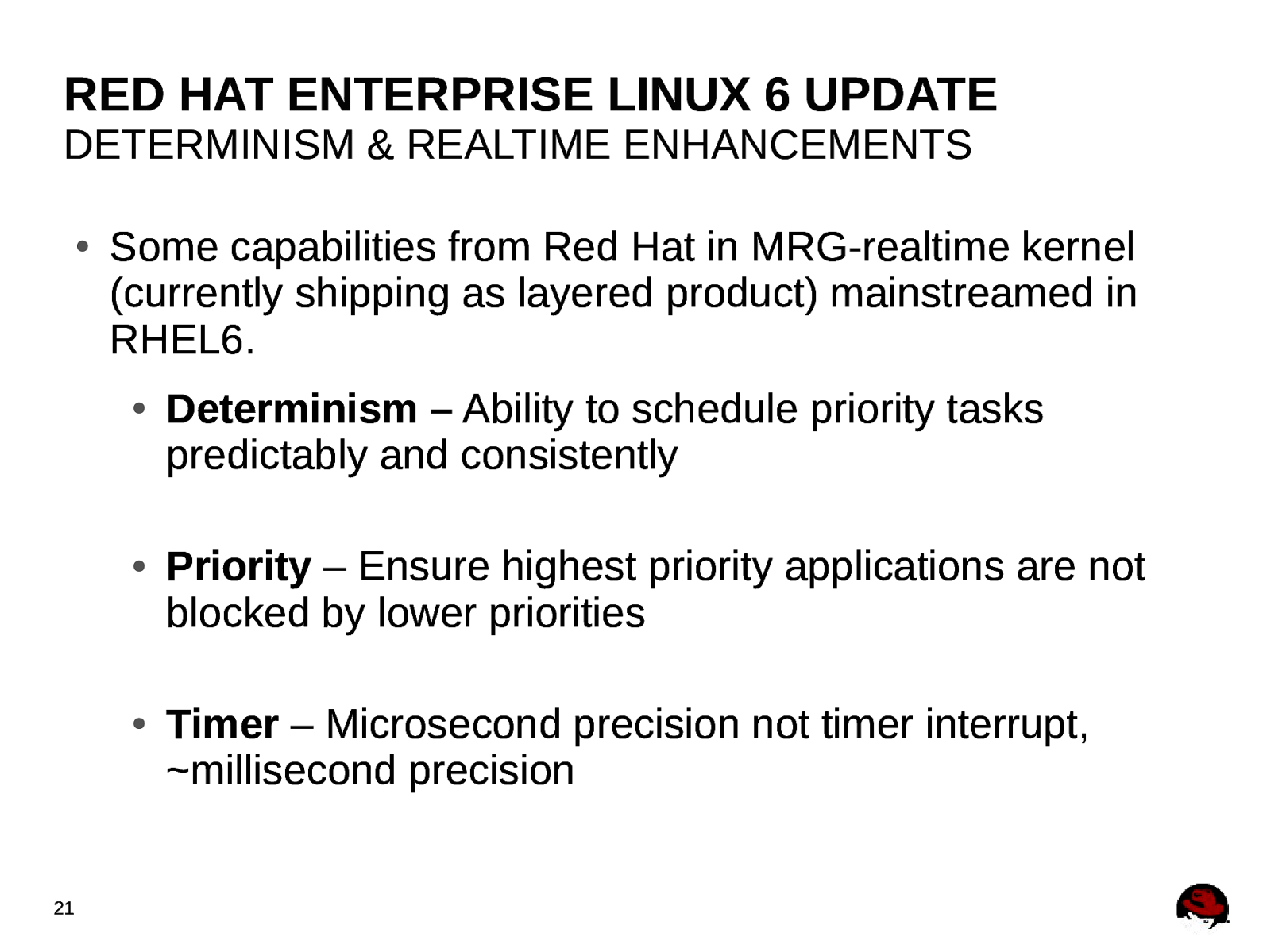
RED HAT ENTERPRISE LINUX 6 UPDATE DETERMINISM & REALTIME ENHANCEMENTS ● Some capabilities from Red Hat in MRG-realtime kernel (currently shipping as layered product) mainstreamed in RHEL6. ● ● ● 21 Determinism – Ability to schedule priority tasks predictably and consistently Priority – Ensure highest priority applications are not blocked by lower priorities Timer – Microsecond precision not timer interrupt, ~millisecond precision
Slide 22

RED HAT ENTERPRISE LINUX 6 UPDATE STORAGE MANAGEMENT ● ● 22 Topology awareness – I/O (alignment and chunk size) based on info from the storage device. This is in dm, LVM, md, and utilities such as parted and mkfs. Interfaces standardized to obtain alignment and optimal I/O stripe width. FcoE (fibre channel over ethernet) on specialized adapters (Emulex, Qlogic, Cisco), and on standard NICs. FcoE install & boot support with DCB. ● ISCSI root/boot, including target ● NPIV – n_Port ID Virtualization
Slide 23
RED HAT ENTERPRISE LINUX 6 UPDATE STORAGE MANAGEMENT: LVM/MD ● LVM hot spare; a disk or group of disks used to replace one failing ● Online resize or mirrored & multipath volumes ● Snapshot scalability enhancements for virtualization ● Multipath enhancements ● ● Mirroring enhancements ● ● 23 Dynamic multipath load balancing. Path selection based on queue depth, or I/O service time Mirrored mirror log, avoids need for re-sync after failure Selectable hash algorithm for LUKS header, new cryptsetup commands, new libcryptsetup
Slide 24

SOFTWARE RELEASE VERSIONING & SUBSCRIPTIONS ● Red Hat Enterprise Linux Advanced Platform (RHEL AP) ● ● ●
2 CPUs Includes Global File System (GFS), Red Hat Cluster Suite (RHCS) Red Hat Enterprise Linux Enterprise Server (RHEL ES) ● Less than 2 CPUs ● Does not include GFS & RHCS All servers, bare metal or virtual, must have an active Red Hat subscription. 24
Slide 25

SOFTWARE RELEASE VERSIONING & SUBSCRIPTIONS ● ● ● 25 Production 1: Ongoing, active development of features and hardware enablement for inclusion into RHEL. Production 2: New software functionality is not available during this phase. The focus for minor releases during this life cycle phase lies on resolving defects with a minimum priority of high. Production 3: No new functionality, new hardware enablement or updated installation images are planned. Commonly known as “Maintenance Mode.”
Slide 26
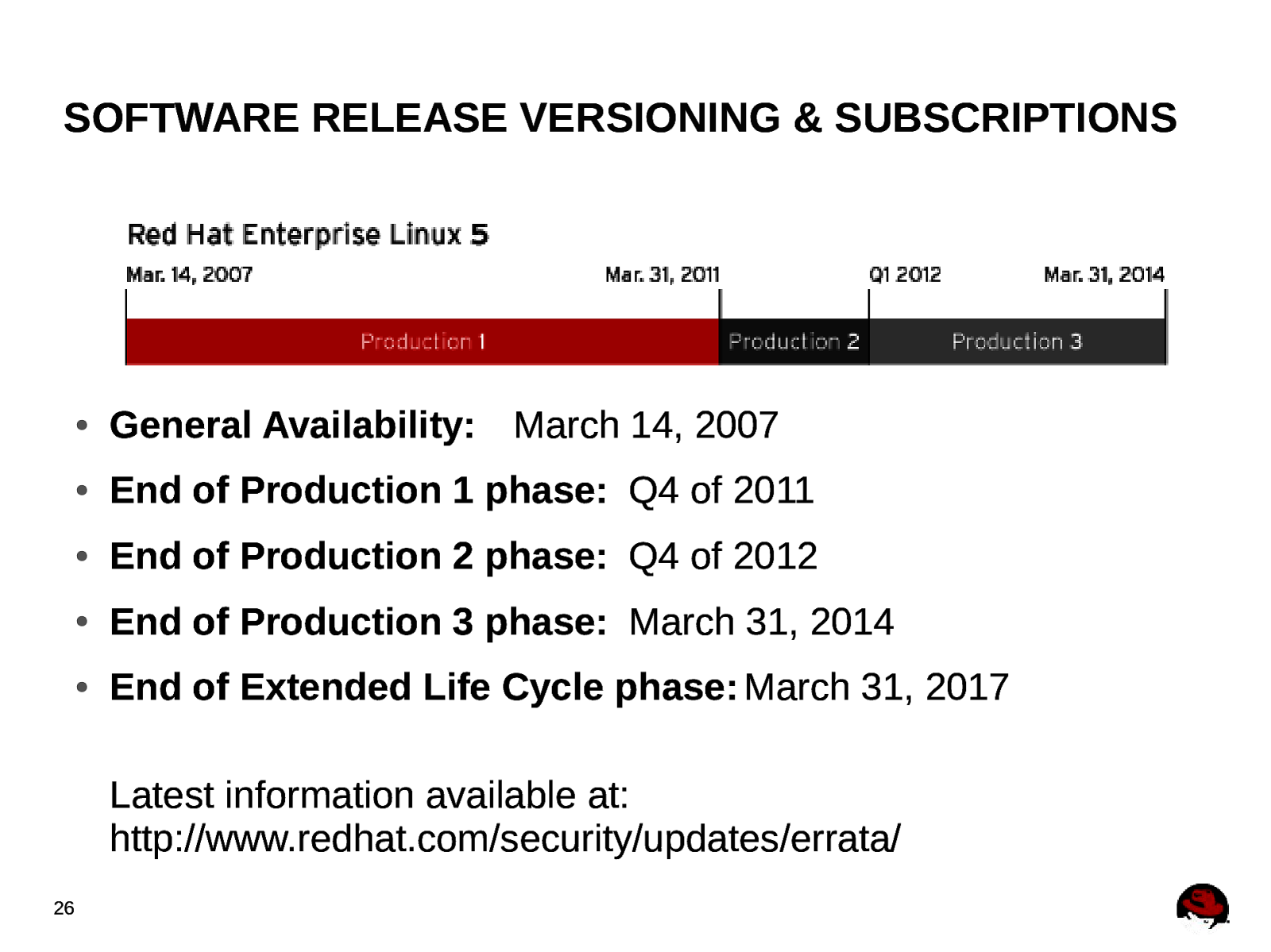
SOFTWARE RELEASE VERSIONING & SUBSCRIPTIONS ● General Availability: March 14, 2007 ● End of Production 1 phase: Q4 of 2011 ● End of Production 2 phase: Q4 of 2012 ● End of Production 3 phase: March 31, 2014 ● End of Extended Life Cycle phase: March 31, 2017 Latest information available at: http://www.redhat.com/security/updates/errata/ 26
Slide 27

CONSUMING NSA ENTERPRISE SUBSCRIPTIONS HOW & WHERE TO GET THE SOFTWARE ● Two on-site badged technical consultants at NBP1 ● Jeff Weatherford: jweatherford@redhat.com (u) 240-373-0842 ● Joe Glenn jglenn@redhat.com (u) 410-854-3104 Highside contact information on SearchLight or “go redhat” 27
Slide 28

RED HAT IN THE VIRTUALIZED ENVIRONMENT Chris Runge Technical Director, U.S crunge@redhat.com / 703-748-2202
Slide 29
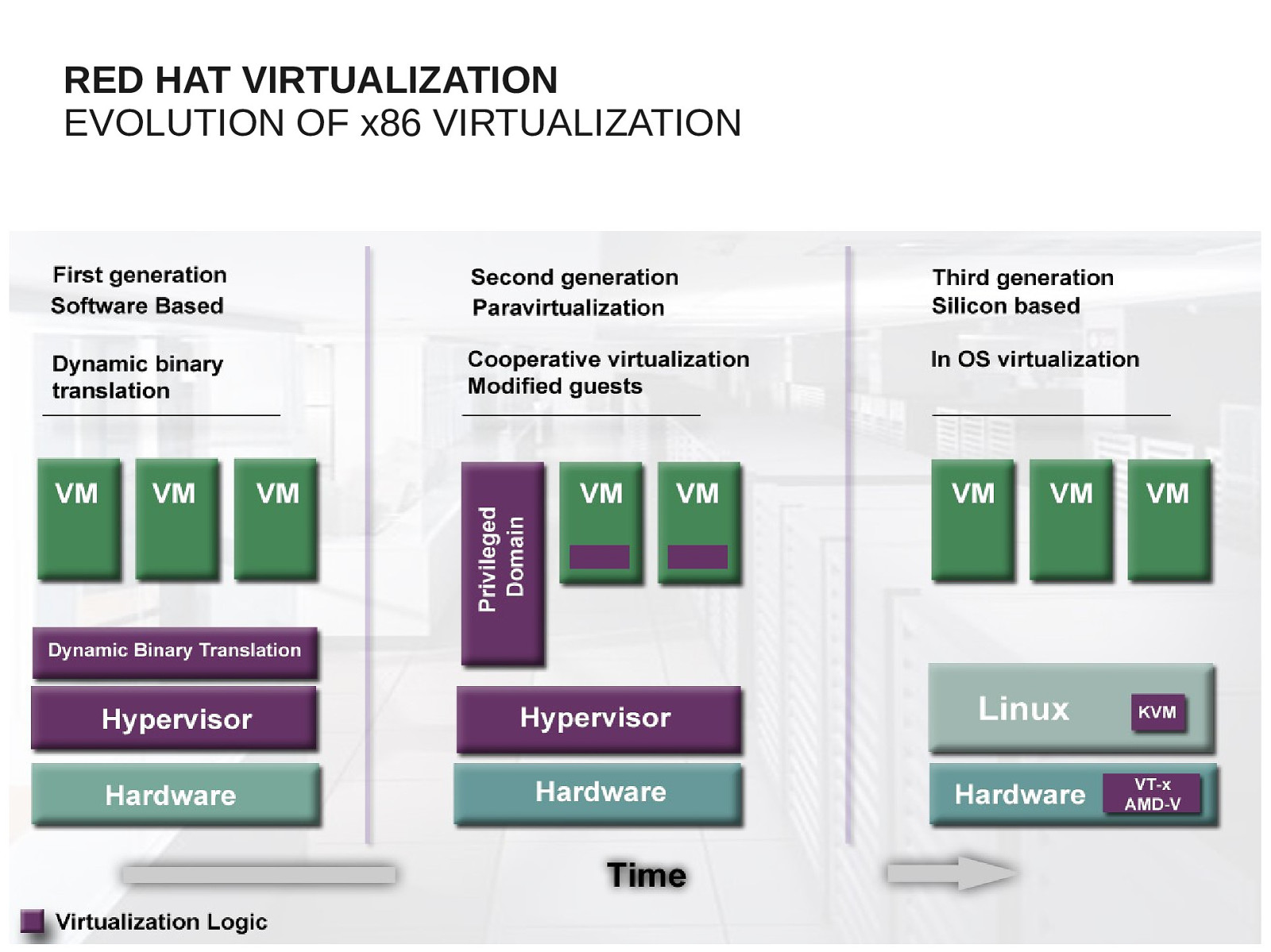
RED HAT VIRTUALIZATION EVOLUTION OF x86 VIRTUALIZATION 29
Slide 30
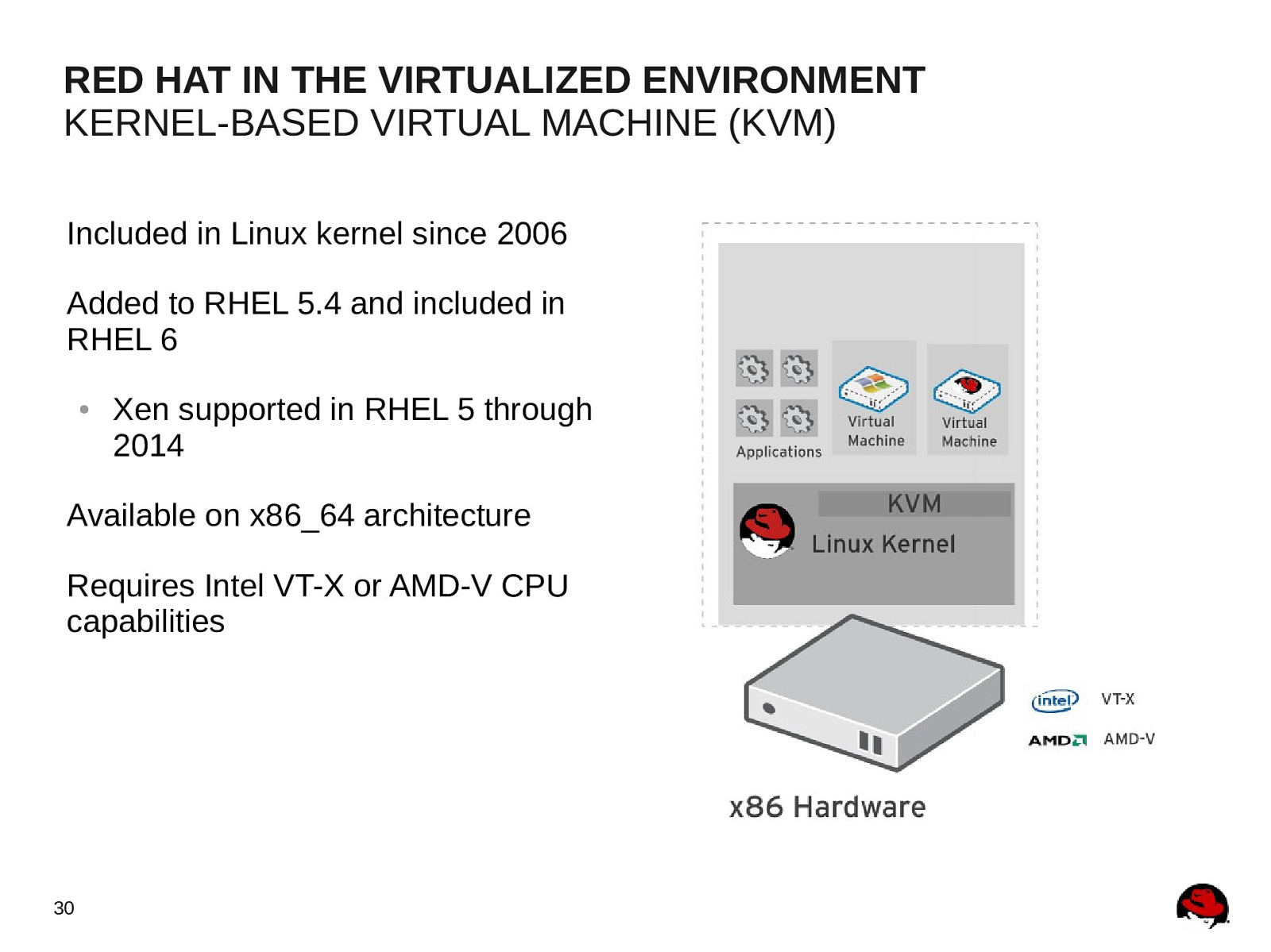
RED HAT IN THE VIRTUALIZED ENVIRONMENT KERNEL-BASED VIRTUAL MACHINE (KVM) Included in Linux kernel since 2006 Added to RHEL 5.4 and included in RHEL 6 ● Xen supported in RHEL 5 through 2014 Available on x86_64 architecture Requires Intel VT-X or AMD-V CPU capabilities 30
Slide 31
RED HAT IN THE VIRTUALIZED ENVIRONMENT KVM GUEST SUPPORT Runs Linux, Windows and other operating system guests RHEL guests supported on third-party hypervisors: ● Microsoft Hyper-V ● VMWare Microsoft certified drivers ensure compliance and support (WHQL and SVVP) 31
Slide 32
RED HAT IN THE VIRTUALIZED ENVIRONMENT KVM ADVANTAGES The OS is the hypervisor Same platform for bare-metal, virtualization, and cloud KVM is a Linux kernel module VM’s run as Linux processes Simplifies certification KVM architecture provides high “feature-velocity” 32
Slide 33
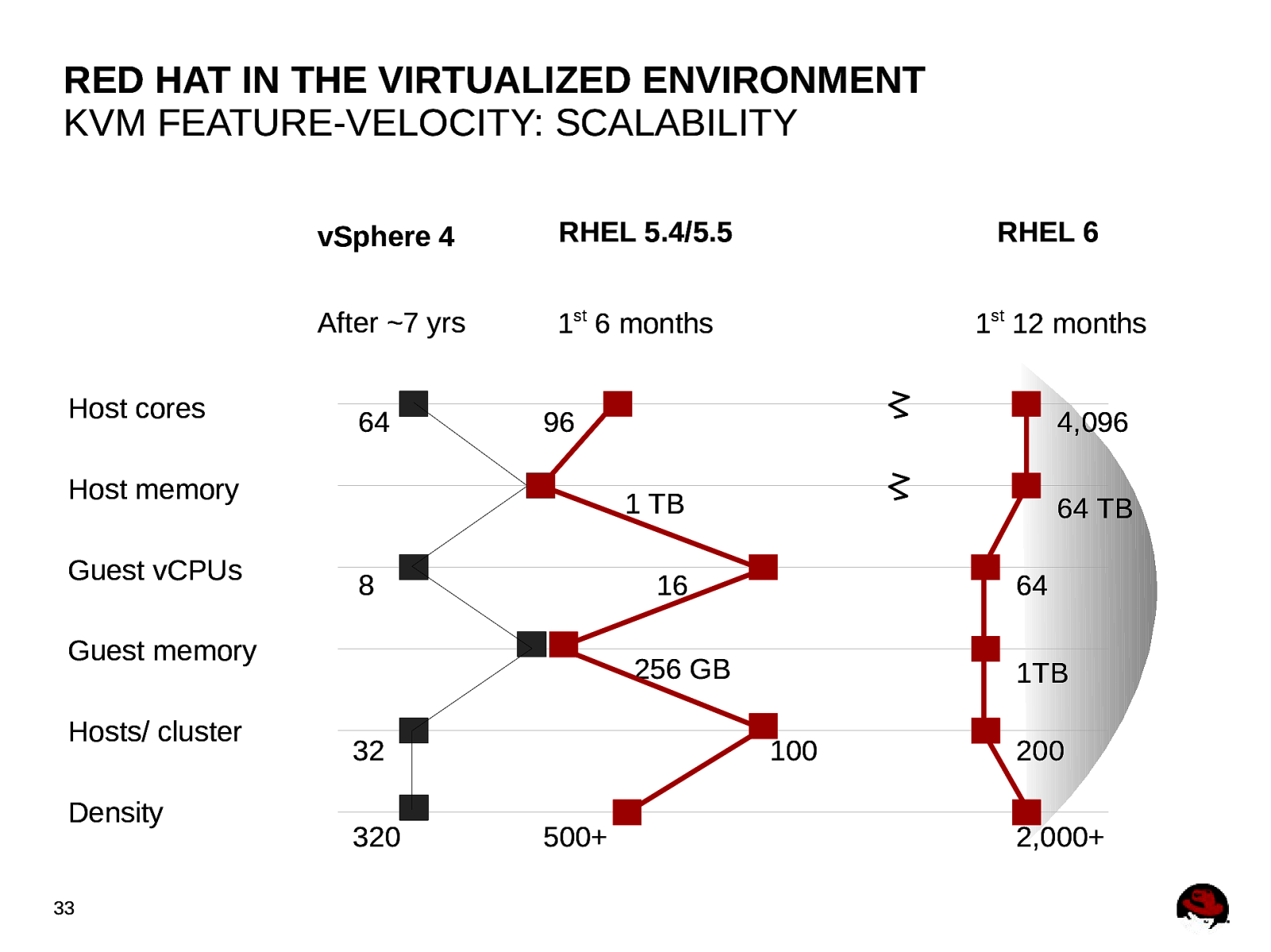
RED HAT IN THE VIRTUALIZED ENVIRONMENT KVM FEATURE-VELOCITY: SCALABILITY Host cores vSphere 4 RHEL 5.4/5.5 After ~7 yrs 1st 6 months 64 Density 33 4,096 1 TB 8 64 TB 16 Guest memory Hosts/ cluster 1st 12 months 96 Host memory Guest vCPUs RHEL 6 64 256 GB 32 320 1TB 100 500+ 200 2,000+
Slide 34
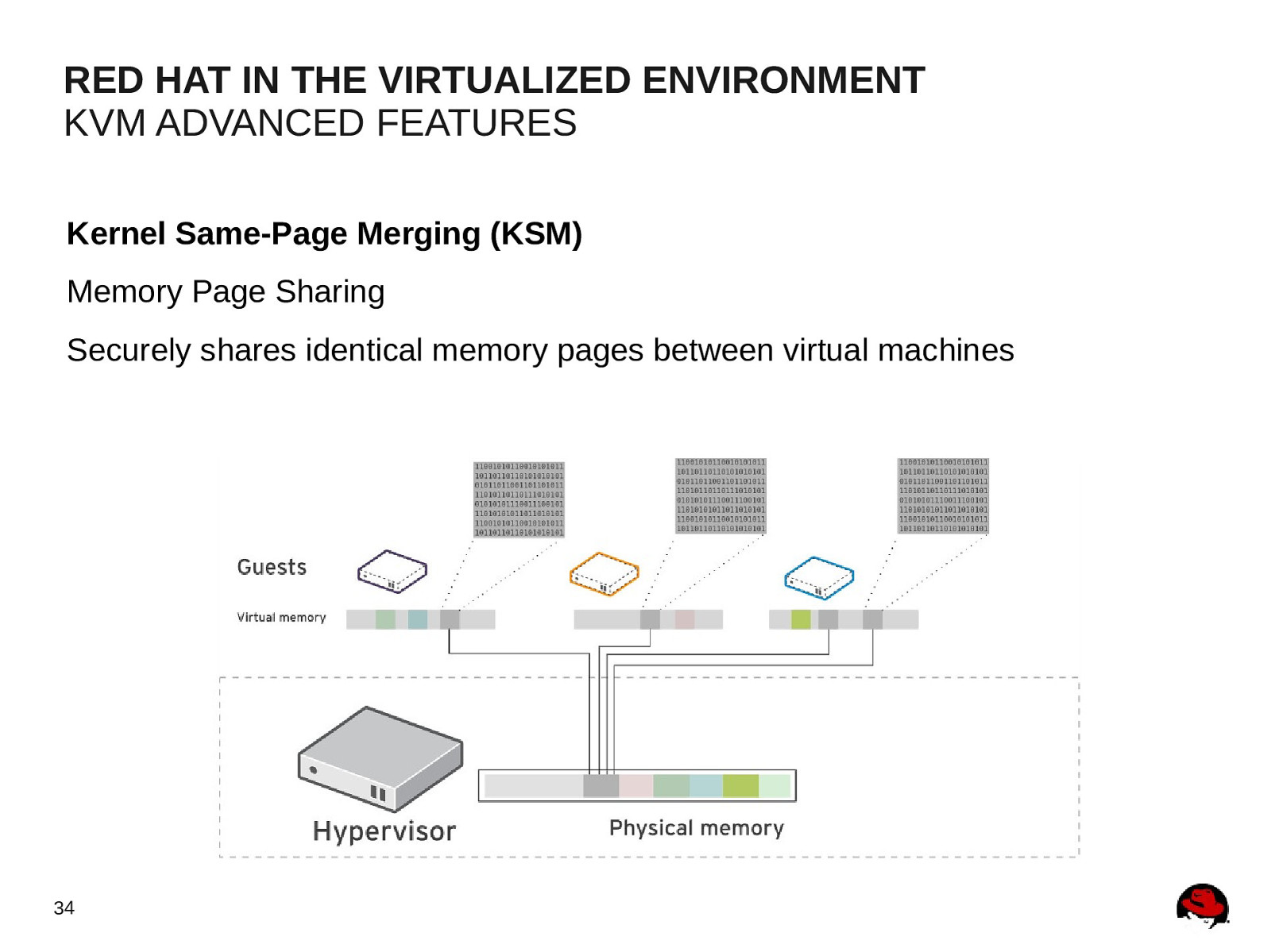
RED HAT IN THE VIRTUALIZED ENVIRONMENT KVM ADVANCED FEATURES Kernel Same-Page Merging (KSM) Memory Page Sharing Securely shares identical memory pages between virtual machines 34
Slide 35
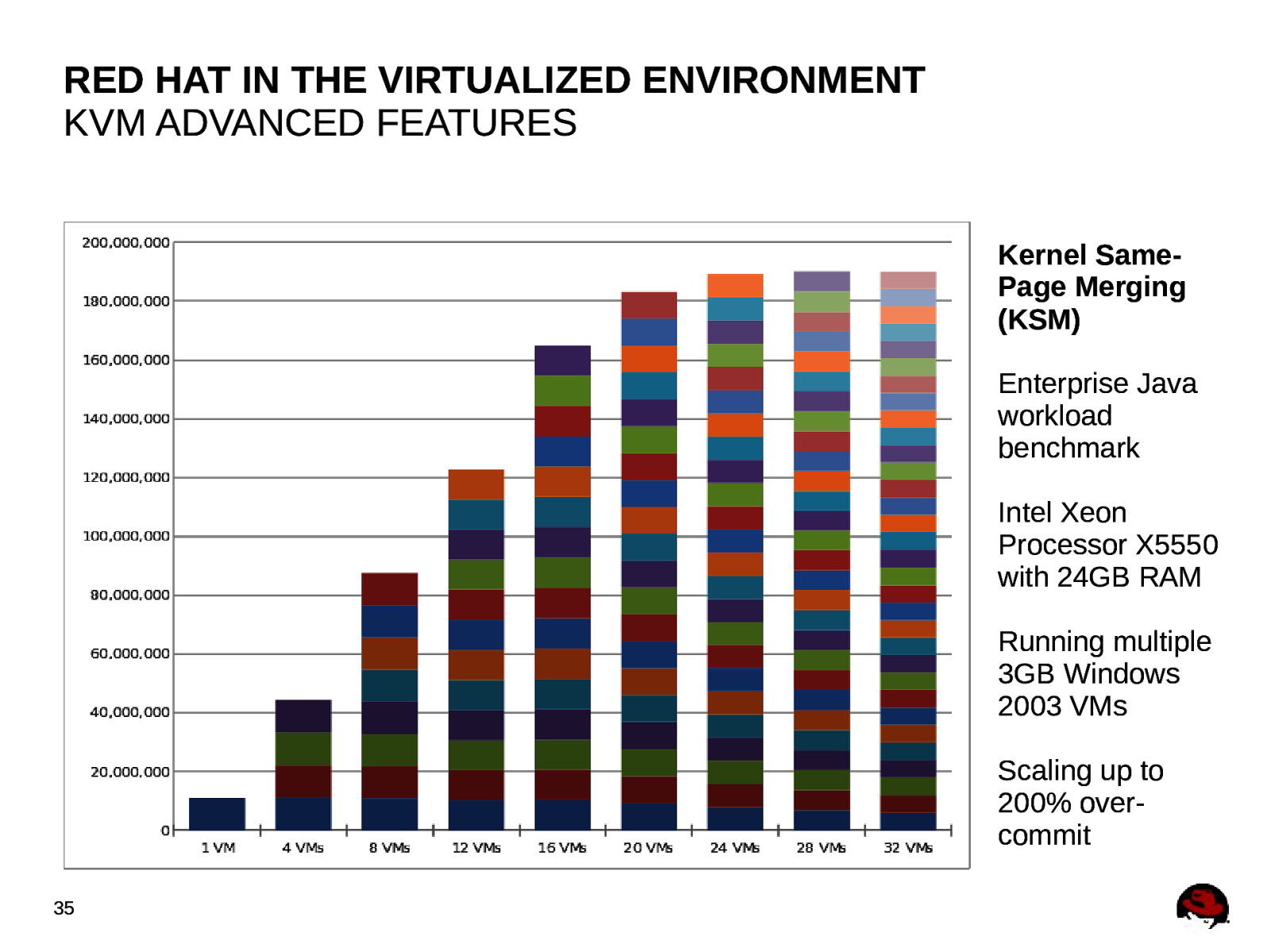
RED HAT IN THE VIRTUALIZED ENVIRONMENT KVM ADVANCED FEATURES Kernel SamePage Merging (KSM) Enterprise Java workload benchmark Intel Xeon Processor X5550 with 24GB RAM Running multiple 3GB Windows 2003 VMs Scaling up to 200% overcommit 35
Slide 36
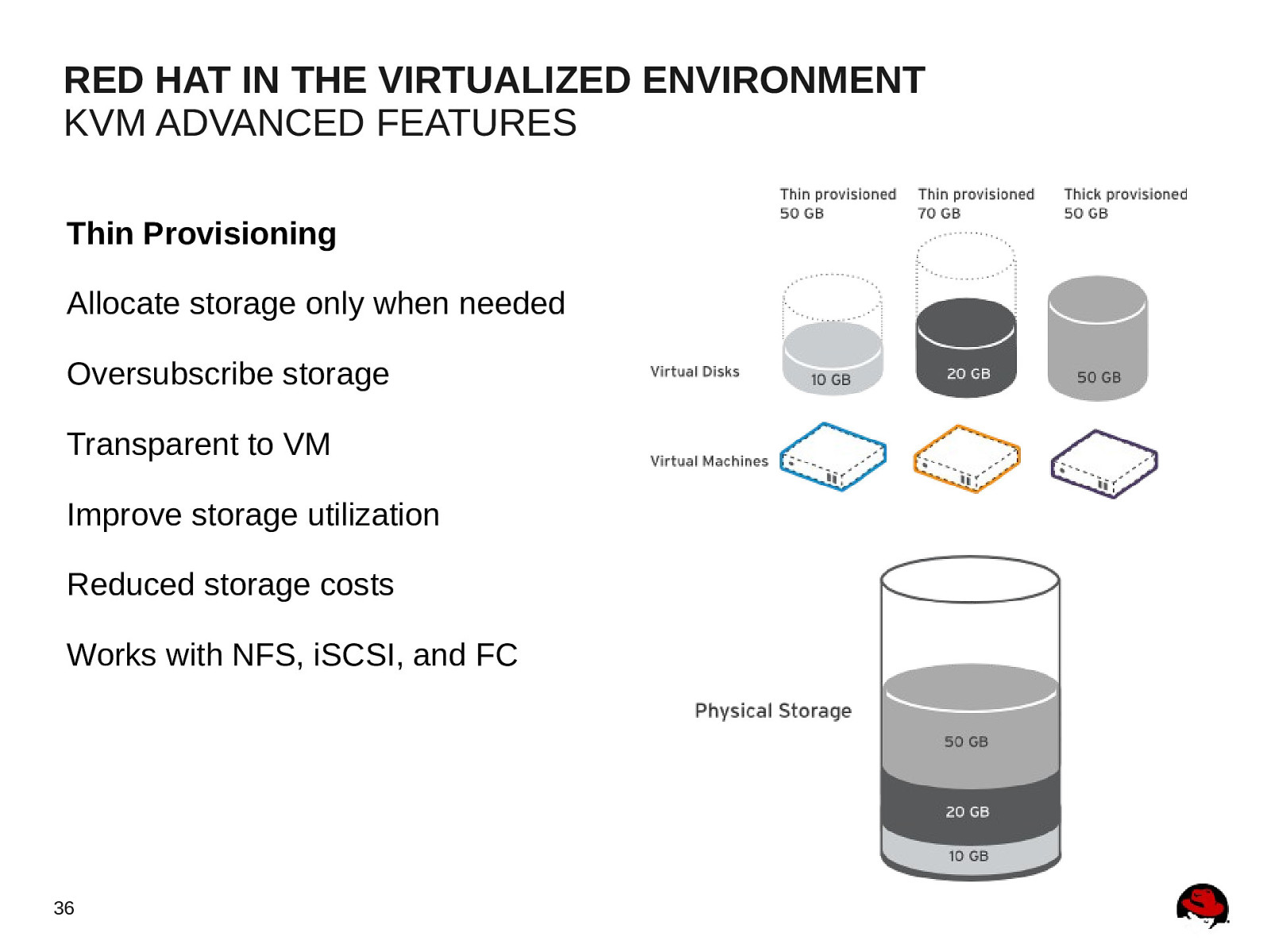
RED HAT IN THE VIRTUALIZED ENVIRONMENT KVM ADVANCED FEATURES Thin Provisioning Allocate storage only when needed Oversubscribe storage Transparent to VM Improve storage utilization Reduced storage costs Works with NFS, iSCSI, and FC 36
Slide 37
RED HAT IN THE VIRTUALIZED ENVIRONMENT VIRTUALIZATION IN RHEL 6 Increased scalability ● Guest/host CPU and memory ● Host: 4096 cores, 64 TB ● Guest: 64 vCPUs, 1 TB Increased Security ● Migration Tools Available ● Increased performance ● 37 Improved guest/host memory management ● Networking improvements ● Storage improvements sVirt v2v – convert Xen VM’s to KVM
Slide 38
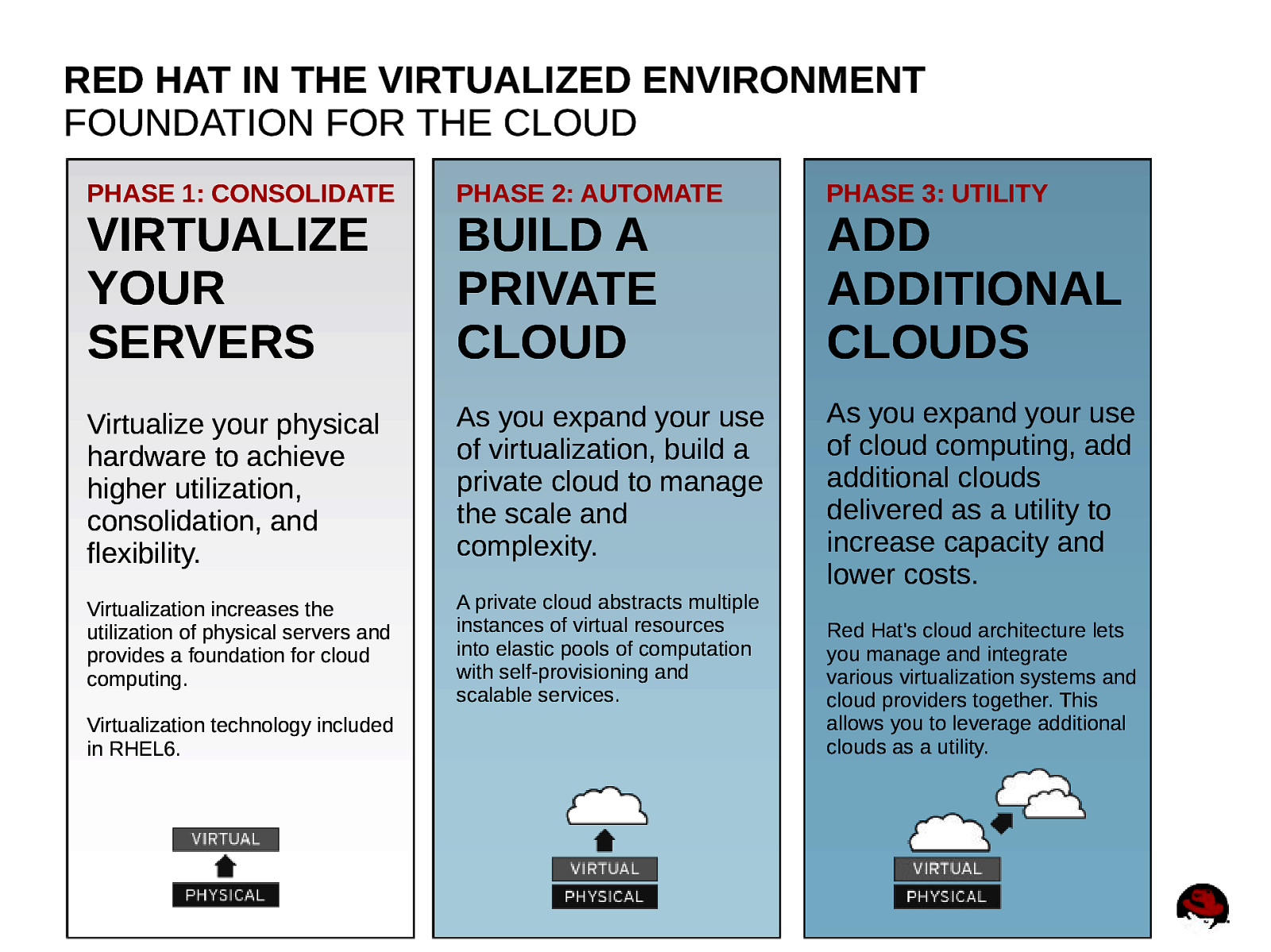
RED HAT IN THE VIRTUALIZED ENVIRONMENT FOUNDATION FOR THE CLOUD PHASE 1: CONSOLIDATE PHASE 2: AUTOMATE PHASE 3: UTILITY Virtualize your physical hardware to achieve higher utilization, consolidation, and flexibility. As you expand your use of virtualization, build a private cloud to manage the scale and complexity. As you expand your use of cloud computing, add additional clouds delivered as a utility to increase capacity and lower costs. Virtualization increases the utilization of physical servers and provides a foundation for cloud computing. A private cloud abstracts multiple instances of virtual resources into elastic pools of computation with self-provisioning and scalable services. VIRTUALIZE YOUR SERVERS Virtualization technology included in RHEL6. 38 BUILD A PRIVATE CLOUD ADD ADDITIONAL CLOUDS Red Hat’s cloud architecture lets you manage and integrate various virtualization systems and cloud providers together. This allows you to leverage additional clouds as a utility.
Slide 39
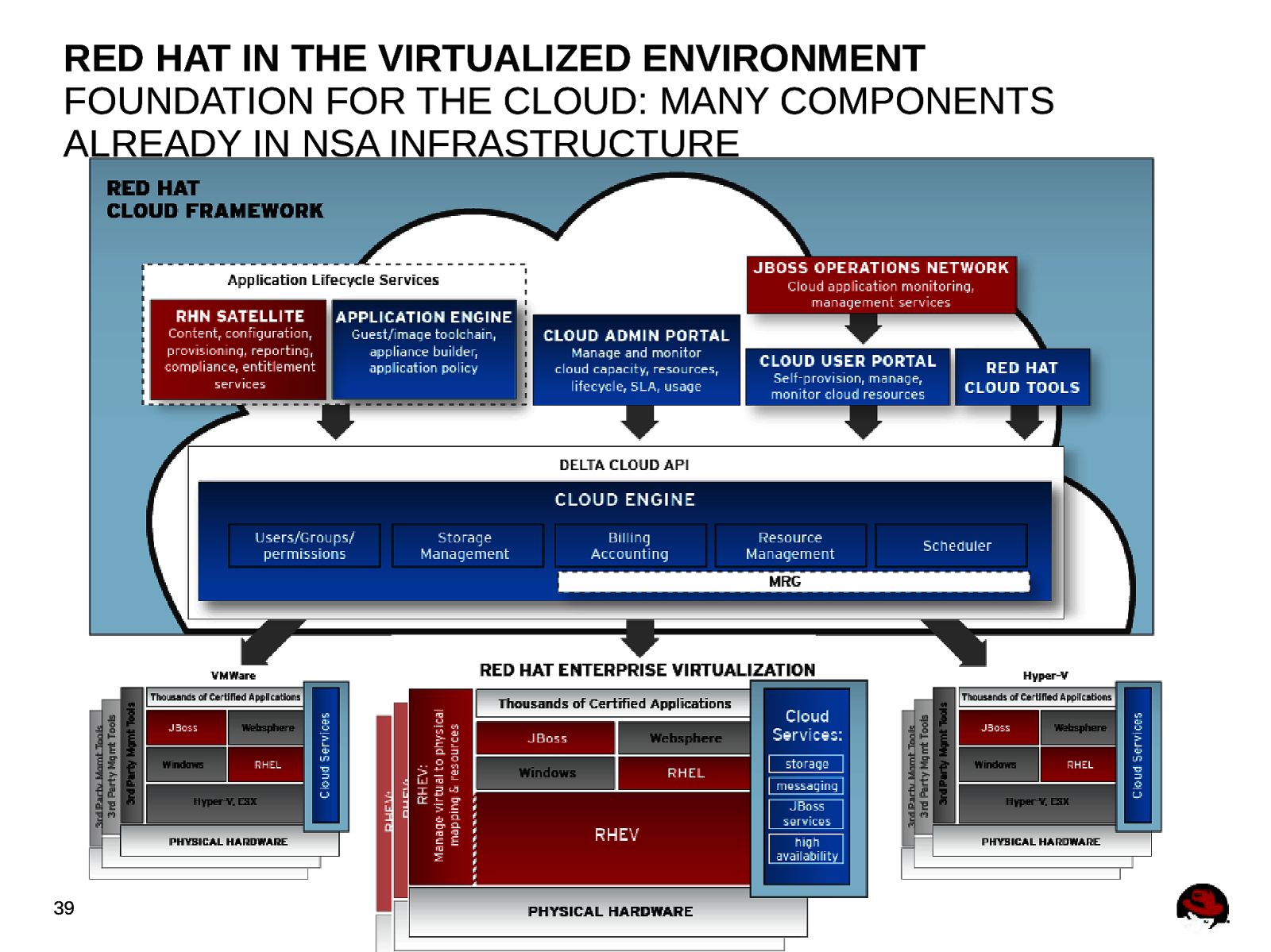
RED HAT IN THE VIRTUALIZED ENVIRONMENT FOUNDATION FOR THE CLOUD: MANY COMPONENTS ALREADY IN NSA INFRASTRUCTURE 39
Slide 40

RED HAT SECURITY UPDATE Gunnar Hellekson CTO, Red Hat Public Sector gunnar.hellekson@redhat.com / 202-507-9027
Slide 41

SECURITY SELINUX ● Confined users ● ● Sandbox ● Untrusted applications can be run confined to prevent compromising the entire system ● X Access Control Extension (XACE). ● SELinux Kiosk Mode ● 41 Role-based controls to limit system access for users. Creation of a user session environment that is valid for a limited time.
Slide 42
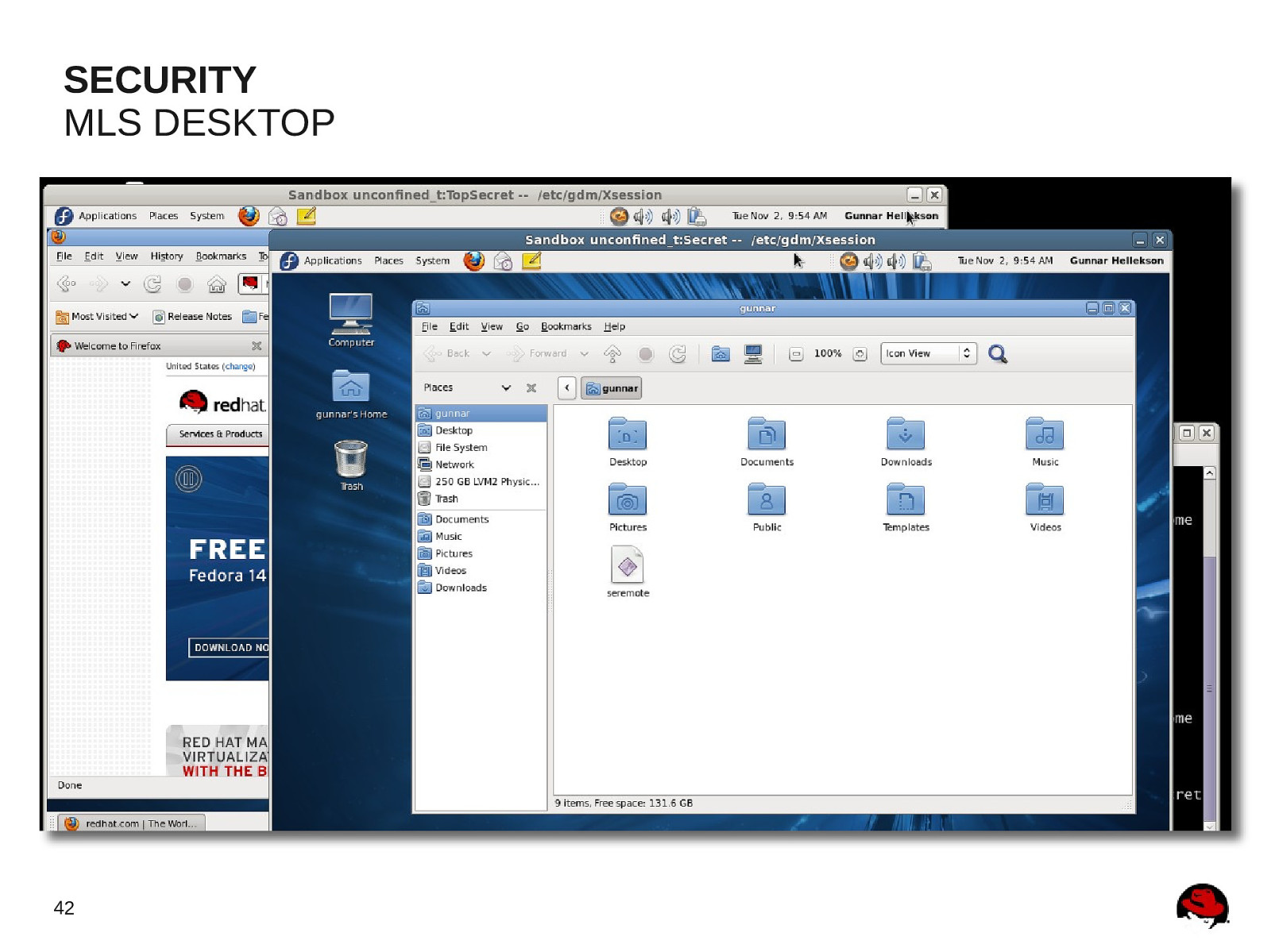
SECURITY MLS DESKTOP 42
Slide 43
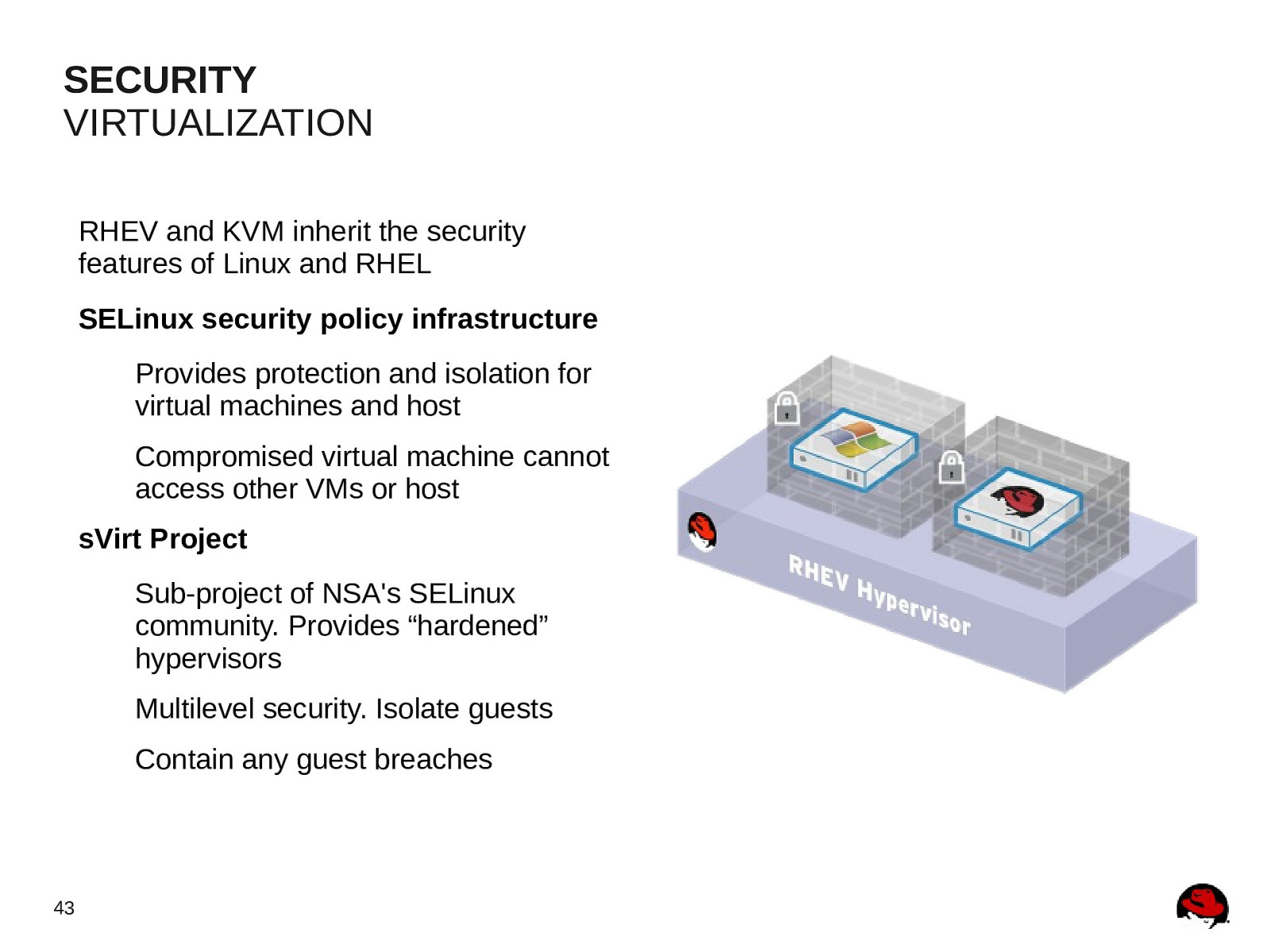
SECURITY VIRTUALIZATION RHEV and KVM inherit the security features of Linux and RHEL SELinux security policy infrastructure Provides protection and isolation for virtual machines and host Compromised virtual machine cannot access other VMs or host sVirt Project Sub-project of NSA’s SELinux community. Provides “hardened” hypervisors Multilevel security. Isolate guests Contain any guest breaches 43
Slide 44
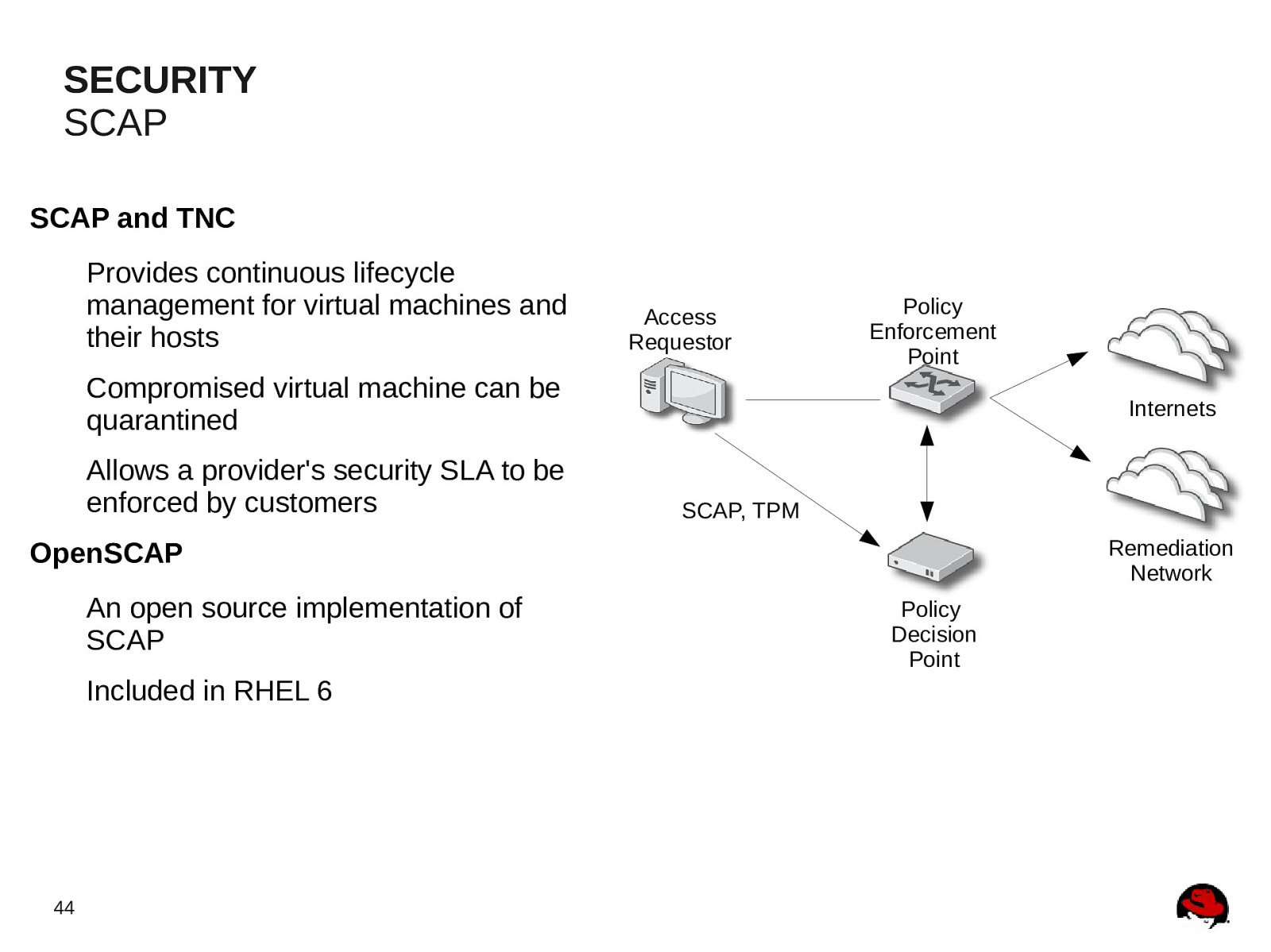
SECURITY SCAP SCAP and TNC Provides continuous lifecycle management for virtual machines and their hosts Access Requestor Policy Enforcement Point Compromised virtual machine can be quarantined Allows a provider’s security SLA to be enforced by customers Internets SCAP, TPM Remediation Network OpenSCAP An open source implementation of SCAP Included in RHEL 6 44 Policy Decision Point
Slide 45

SECURITY COMMON CRITERIA UPDATE RHEL 5.6 ● Refreshed to include KVM ● Custom protection profile RHEL 6 45 ● Will include sVirt, IPSec ● Targeting EAL 4 ● Again, custom protection profile
Slide 46

www.redhat.com Q&A PANEL SESSION 46