IAM CAPABILITY BLUEPRINT Shawn Wells Managing Director shawn.wells@accenturefederal.com 443-534-0130 1
Slide 1

Slide 2
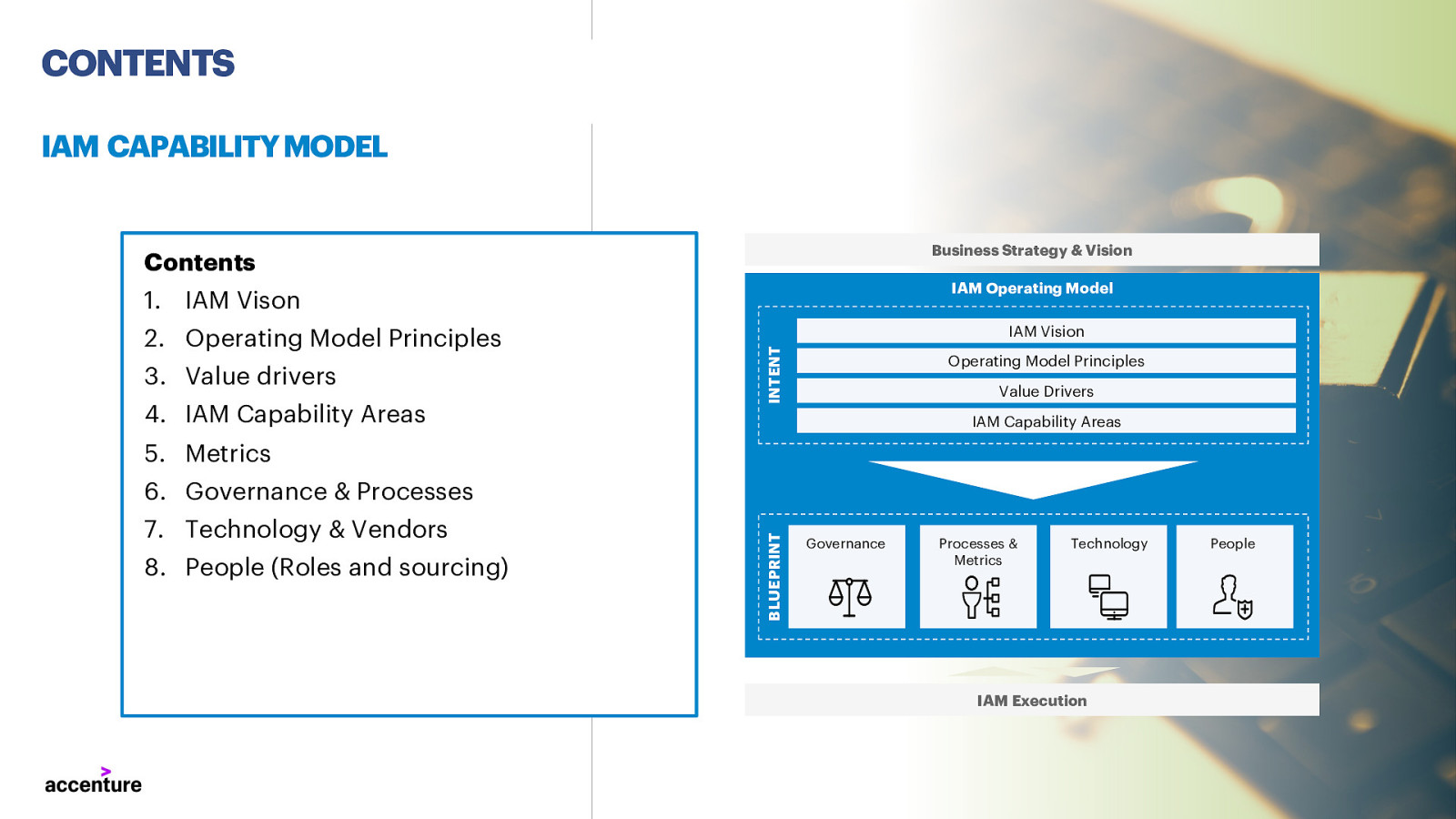
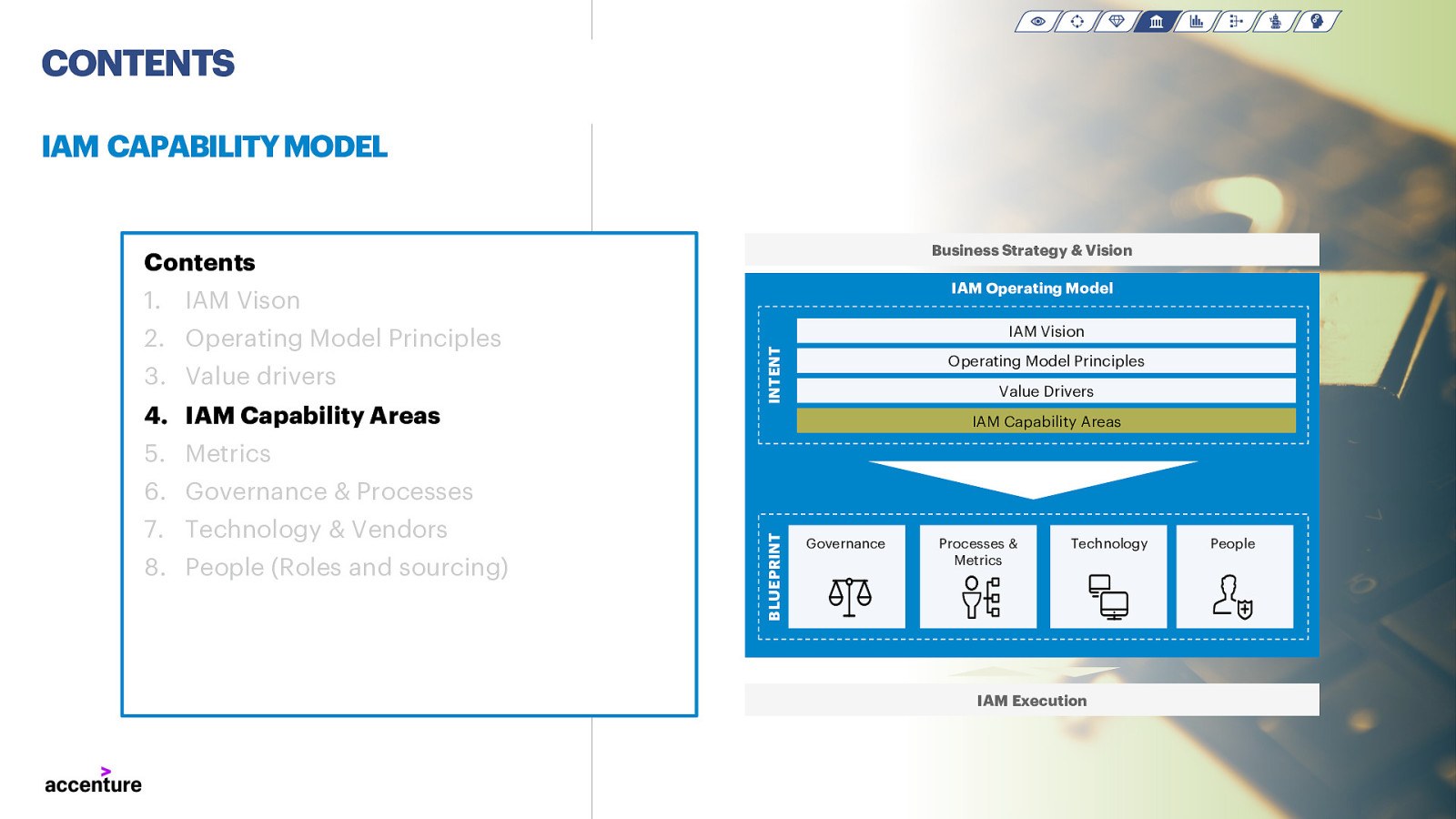
CONTENTS IAM CAPABILITY MODEL Business Strategy & Vision Contents IAM Operating Model
- IAM Vison 3. Value drivers 4. IAM Capability Areas IAM Vision INTENT
- Operating Model Principles Operating Model Principles Value Drivers IAM Capability Areas
- Metrics 7. Technology & Vendors 8. People (Roles and sourcing) BLUEPRINT
- Governance & Processes Governance Processes & Metrics Technology People IAM Execution 2
Slide 3
FOR READABILITY OF THIS DOCUMENT A TRACKER HAS BEEN ADDED READERS’ GUIDE Vision Principles Value drivers IAM capability areas Metrics Governance & Processes Technology People (Roles and sourcing) 3
Slide 4

WHAT WOULD WE LIKE TO ACHIEVE WITH THE IAM OPERATING MODEL? VISION STATEMENT Vision A future-proof and self-sufficient IAM platform that enables (and secures) <CLIENT NAME> business objectives 4
Slide 5
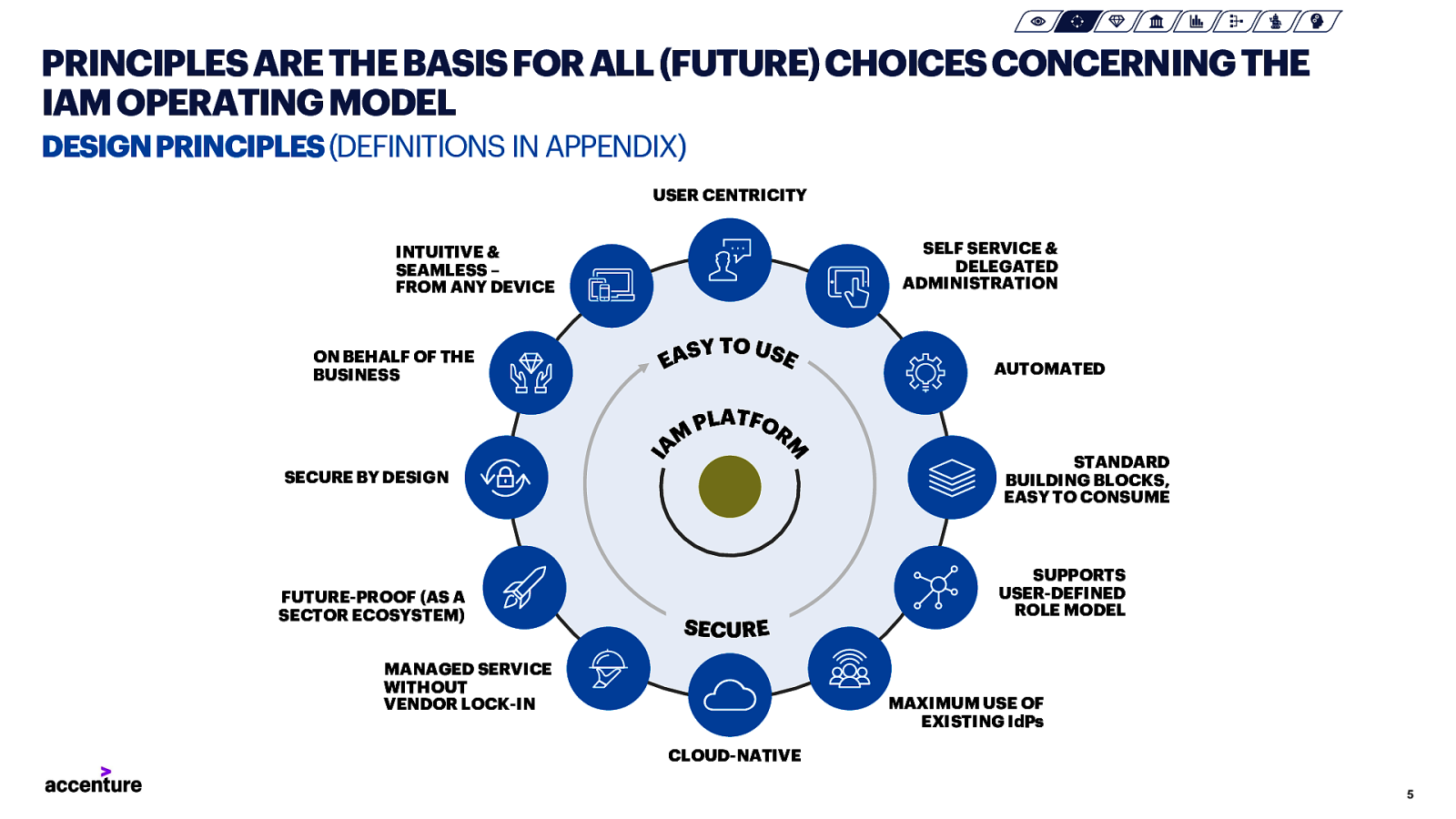
PRINCIPLES ARE THE BASIS FOR ALL (FUTURE) CHOICES CONCERNING THE IAM OPERATING MODEL DESIGN PRINCIPLES (DEFINITIONS IN APPENDIX) USER CENTRICITY SELF SERVICE & DELEGATED ADMINISTRATION INTUITIVE & SEAMLESS – FROM ANY DEVICE ON BEHALF OF THE BUSINESS AUTOMATED STANDARD BUILDING BLOCKS, EASY TO CONSUME SECURE BY DESIGN SUPPORTS USER-DEFINED ROLE MODEL FUTURE-PROOF (AS A SECTOR ECOSYSTEM) MANAGED SERVICE WITHOUT VENDOR LOCK-IN MAXIMUM USE OF EXISTING IdPs CLOUD-NATIVE 5
Slide 6
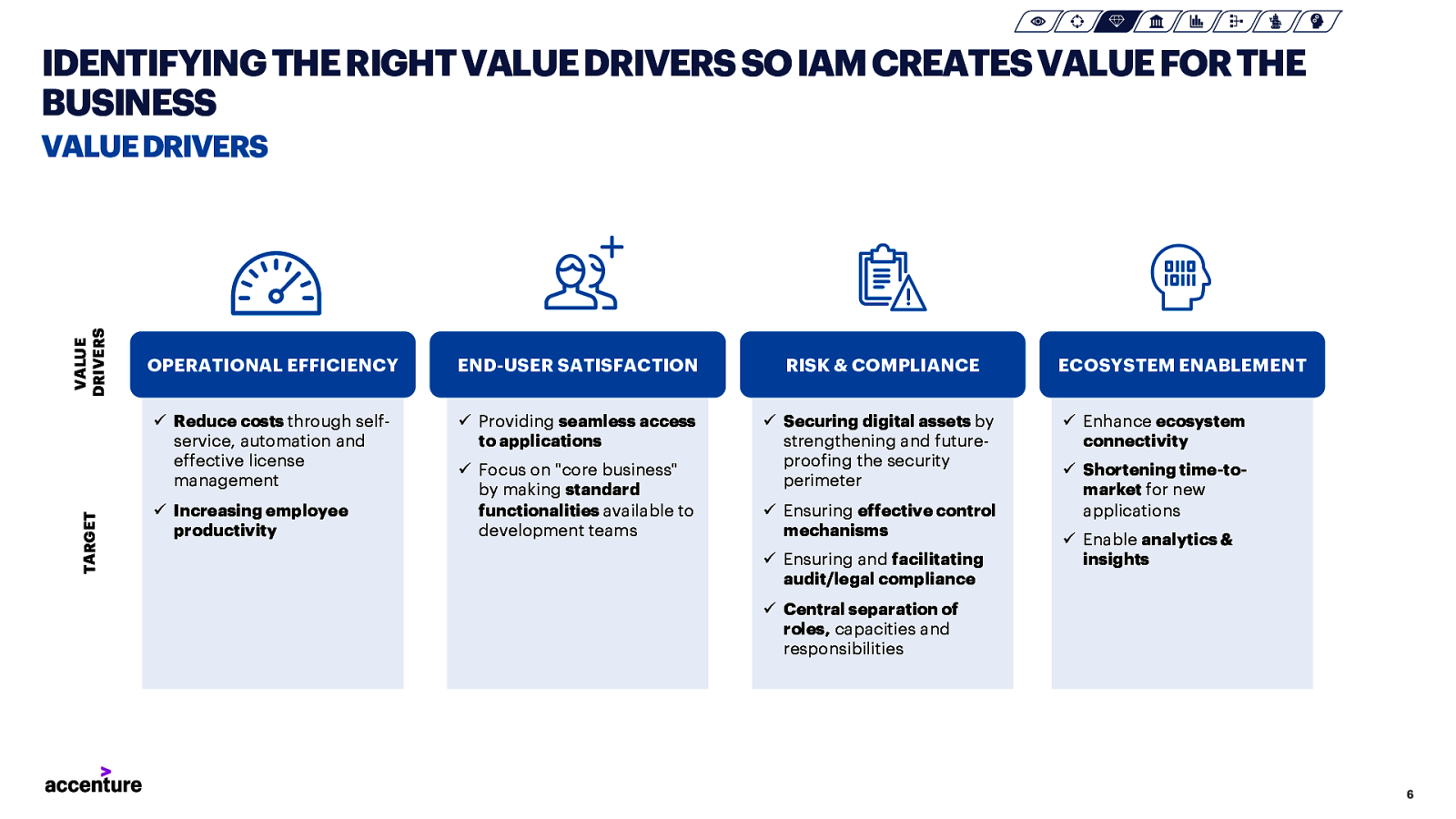
IDENTIFYING THE RIGHT VALUE DRIVERS SO IAM CREATES VALUE FOR THE BUSINESS TARGET VALUE DRIVERS VALUE DRIVERS OPERATIONAL EFFICIENCY END-USER SATISFACTION RISK & COMPLIANCE ü Reduce costs through selfservice, automation and effective license management ü Providing seamless access to applications ü Securing digital assets by strengthening and futureproofing the security perimeter ü Increasing employee productivity ü Focus on “core business” by making standard functionalities available to development teams ü Ensuring effective control mechanisms ü Ensuring and facilitating audit/legal compliance ECOSYSTEM ENABLEMENT ü Enhance ecosystem connectivity ü Shortening time-tomarket for new applications ü Enable analytics & insights ü Central separation of roles, capacities and responsibilities 6
Slide 7
CONTENTS IAM CAPABILITY MODEL Business Strategy & Vision Contents IAM Operating Model
- IAM Vison 3. Value drivers IAM Vision INTENT
- Operating Model Principles Operating Model Principles Value Drivers
- IAM Capability Areas IAM Capability Areas
- Metrics 7. Technology & Vendors 8. People (Roles and sourcing) BLUEPRINT
- Governance & Processes Governance Processes & Metrics Technology People IAM Execution 7
Slide 8
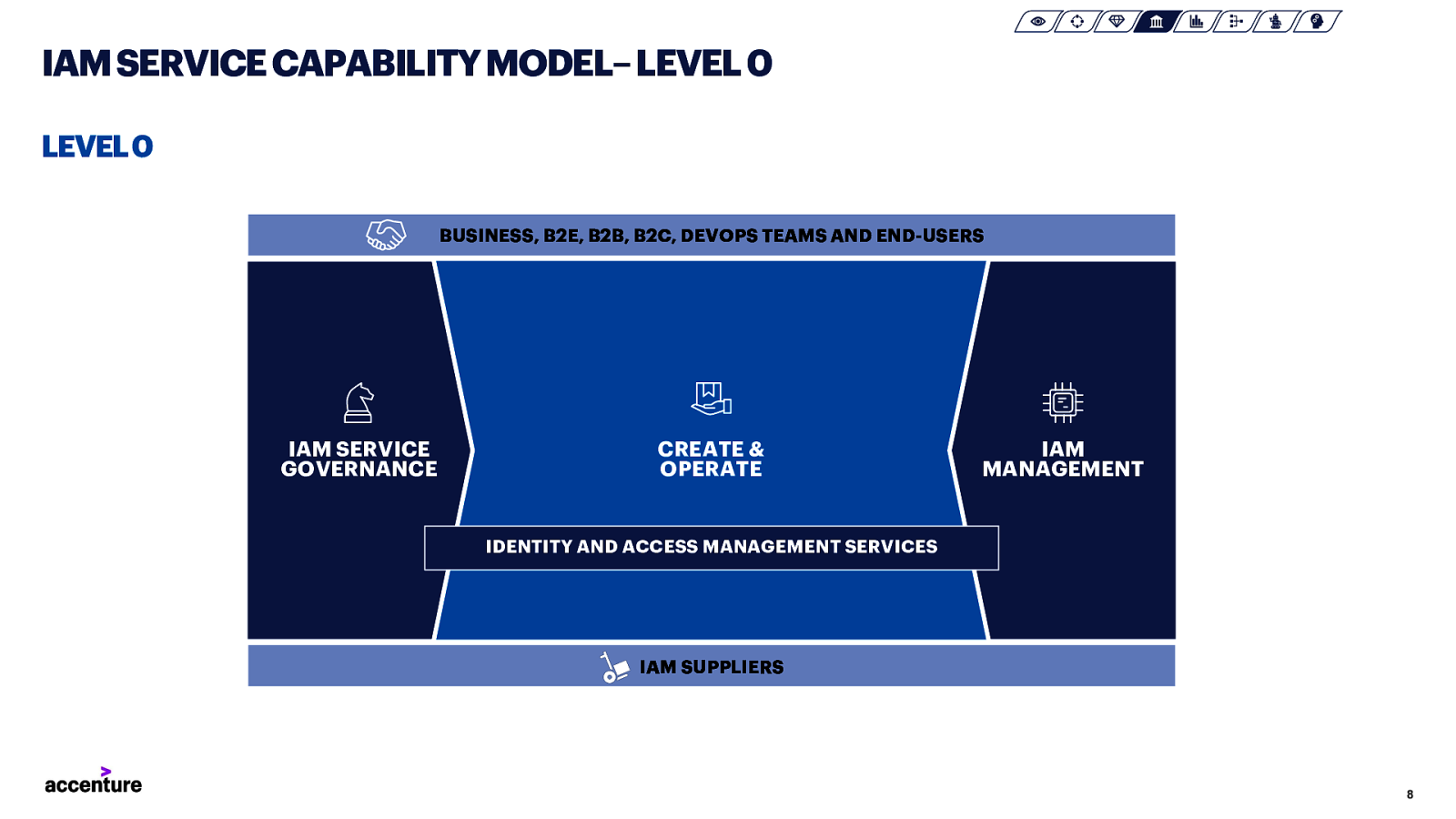
IAM SERVICE CAPABILITY MODEL–LEVEL 0 LEVEL 0 BUSINESS, B2E, B2B, B2C, DEVOPS TEAMS AND END-USERS IAM SERVICE GOVERNANCE CREATE & OPERATE IAM MANAGEMENT IDENTITY AND ACCESS MANAGEMENT SERVICES IAM SUPPLIERS 8
Slide 9
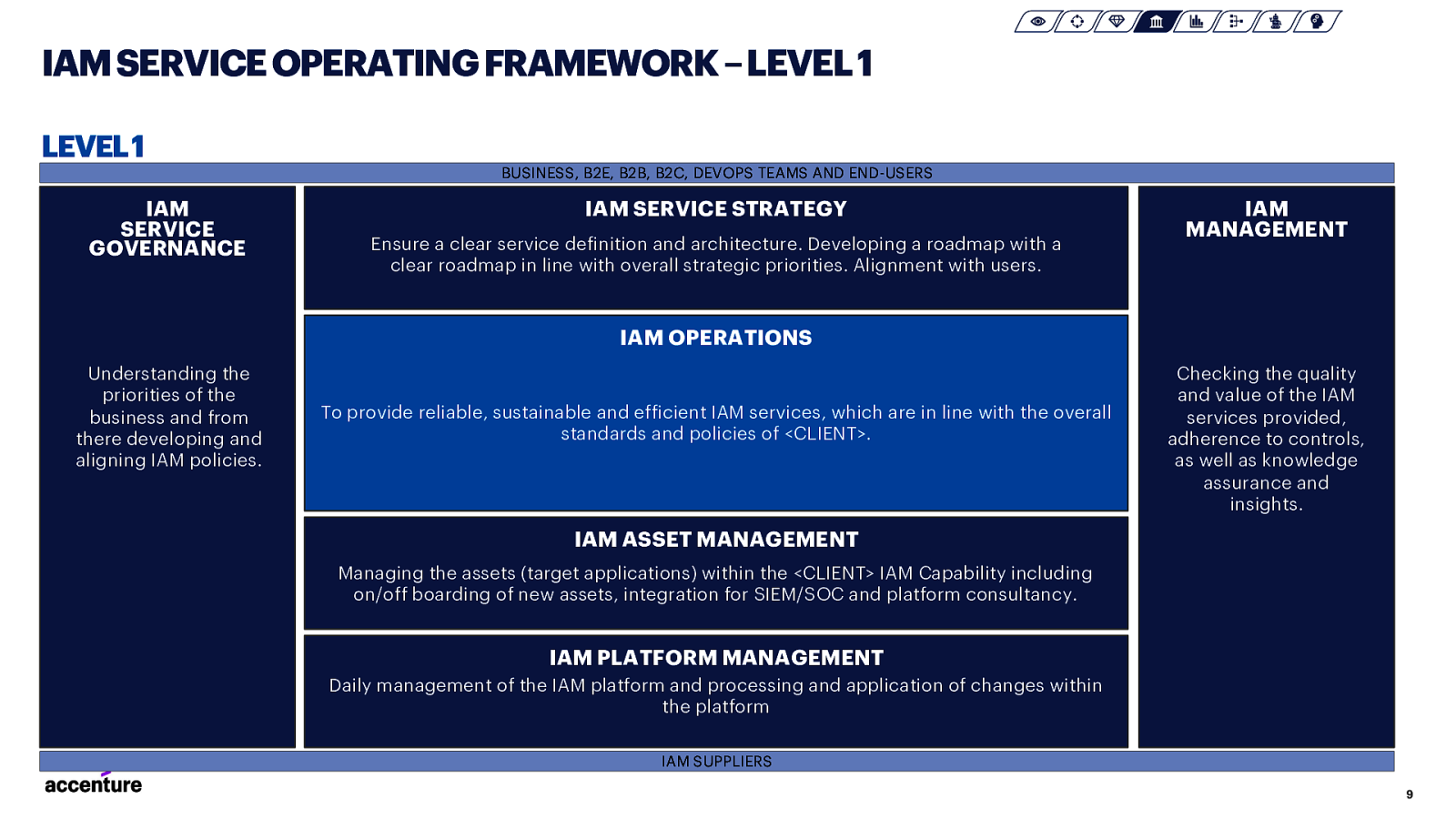
IAM SERVICE OPERATING FRAMEWORK –LEVEL 1 LEVEL 1 BUSINESS, B2E, B2B, B2C, DEVOPS TEAMS AND END-USERS IAM SERVICE GOVERNANCE IAM SERVICE STRATEGY Ensure a clear service definition and architecture. Developing a roadmap with a clear roadmap in line with overall strategic priorities. Alignment with users. IAM MANAGEMENT IAM OPERATIONS Understanding the priorities of the business and from there developing and aligning IAM policies. To provide reliable, sustainable and efficient IAM services, which are in line with the overall standards and policies of <CLIENT>. Checking the quality and value of the IAM services provided, adherence to controls, as well as knowledge assurance and insights. IAM ASSET MANAGEMENT Managing the assets (target applications) within the <CLIENT> IAM Capability including on/off boarding of new assets, integration for SIEM/SOC and platform consultancy. IAM PLATFORM MANAGEMENT Daily management of the IAM platform and processing and application of changes within the platform IAM SUPPLIERS 9
Slide 10
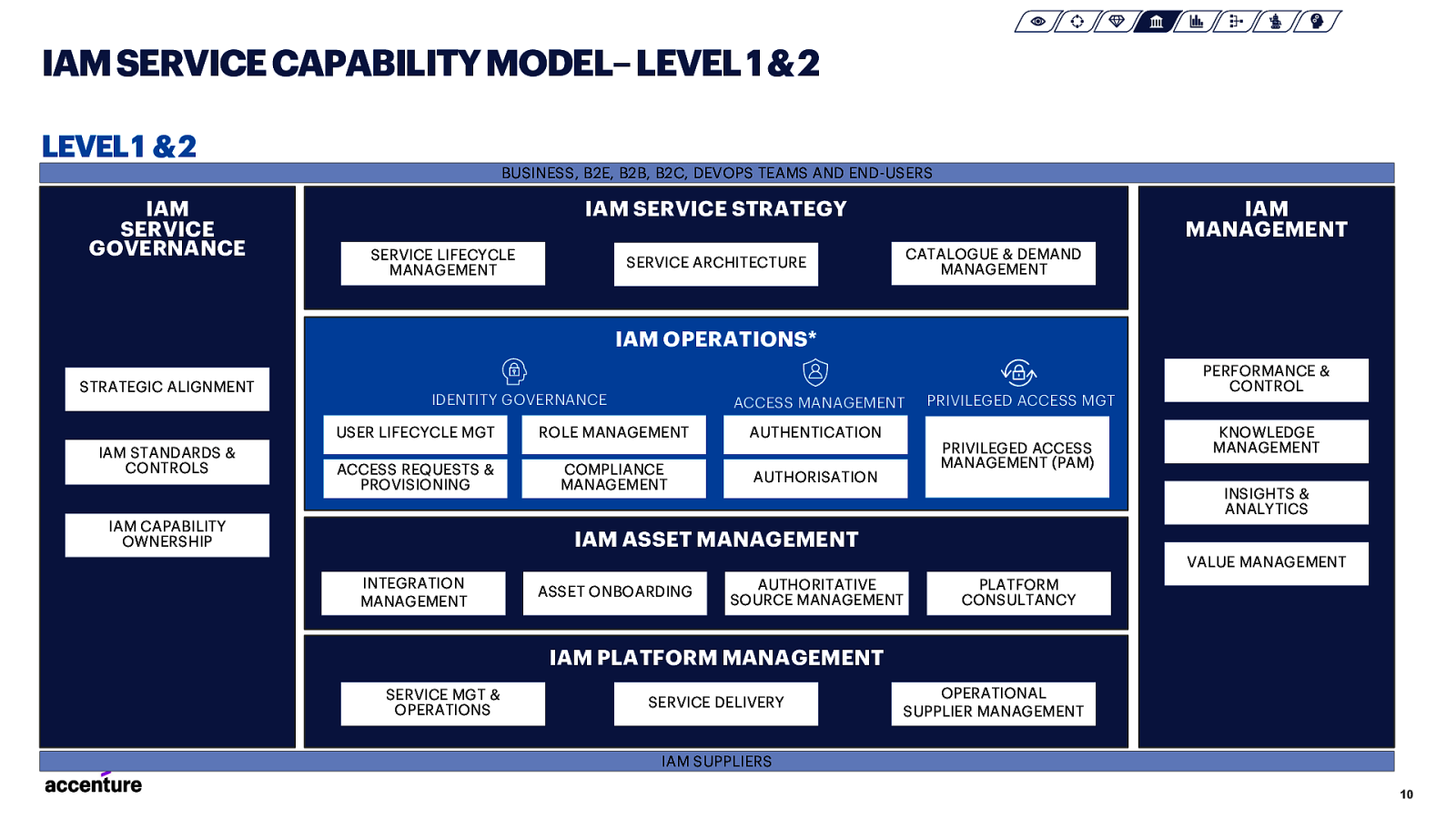
IAM SERVICE CAPABILITY MODEL–LEVEL 1 & 2 LEVEL 1 & 2 BUSINESS, B2E, B2B, B2C, DEVOPS TEAMS AND END-USERS IAM SERVICE GOVERNANCE IAM SERVICE STRATEGY SERVICE LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT IAM MANAGEMENT CATALOGUE & DEMAND MANAGEMENT SERVICE ARCHITECTURE IAM OPERATIONS* STRATEGIC ALIGNMENT IDENTITY GOVERNANCE USER LIFECYCLE MGT IAM STANDARDS & CONTROLS ACCESS REQUESTS & PROVISIONING IAM CAPABILITY OWNERSHIP ACCESS MANAGEMENT ROLE MANAGEMENT COMPLIANCE MANAGEMENT PRIVILEGED ACCESS MGT AUTHENTICATION PRIVILEGED ACCESS MANAGEMENT (PAM) AUTHORISATION PERFORMANCE & CONTROL KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT INSIGHTS & ANALYTICS IAM ASSET MANAGEMENT VALUE MANAGEMENT INTEGRATION MANAGEMENT ASSET ONBOARDING AUTHORITATIVE SOURCE MANAGEMENT PLATFORM CONSULTANCY IAM PLATFORM MANAGEMENT SERVICE MGT & OPERATIONS SERVICE DELIVERY OPERATIONAL SUPPLIER MANAGEMENT IAM SUPPLIERS 10
Slide 11

IAM SERVICE GOVERNANCE, IAM SERVICE STRATEGY AND IAM ASSET MANAGEMENT LEVEL 2 CAPABILITY DEFINITIONS (1/3) L1 Capability L2 Capability STRATEGIC ALIGNMENT IAM SERVICE STRATEGY IAM MANAGEMENT Aligning frameworks and prioritization around IAM in line with the broader <CLIENT> business strategy and objectives. IAM STANDARDS & CONTROLS Prescribing IAM policies, control frameworks and standards to which the IAM service must adhere to. IAM CAPABILITY OWNERSHIP Managing this capability model and related definitions. PERFORMANCE & CONTROL Continuously improving the IAM service by monitoring the established KPIs and validating whether IAM operates within the set frameworks. KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT Ensure that relevant information for users and developers, such as policies and training materials, is documented and available in a central location within <CLIENT>. INSIGHTS & ANALYTICS Develop and maintain dashboards and reports around the IAM service for, for example, compliance. VALUE MANAGEMENT Continuously monitoring and validating how the IAM services contribute to the defined value drivers. SERVICE LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT IAM SERVICE STRATEGY Definition Managing and safeguarding the lifecycle and roadmap of all IAM services. SERVICE ARCHITECTURE Setting the standards around the IAM service architecture in line with the overall enterprise architecture of <CLIENT>. Architecture means a detailed (technical) overview of IAM, as well as the relationships between the components and the environment in which they reside. Additional standards and guidelines that guide the design and development of IAM are also included in the architecture. CATALOGUE & DEMAND MANAGEMENT Providing and managing a service catalogue at a central location (e.g. a separate IAM portal or integrated in ITSM) that indicates which IAM services are delivered (whether or not in standard building blocks) to the business and IT teams. The available services should be coordinated with the customers, who are also offered the opportunity to give feedback on the IAM service. 11
Slide 12
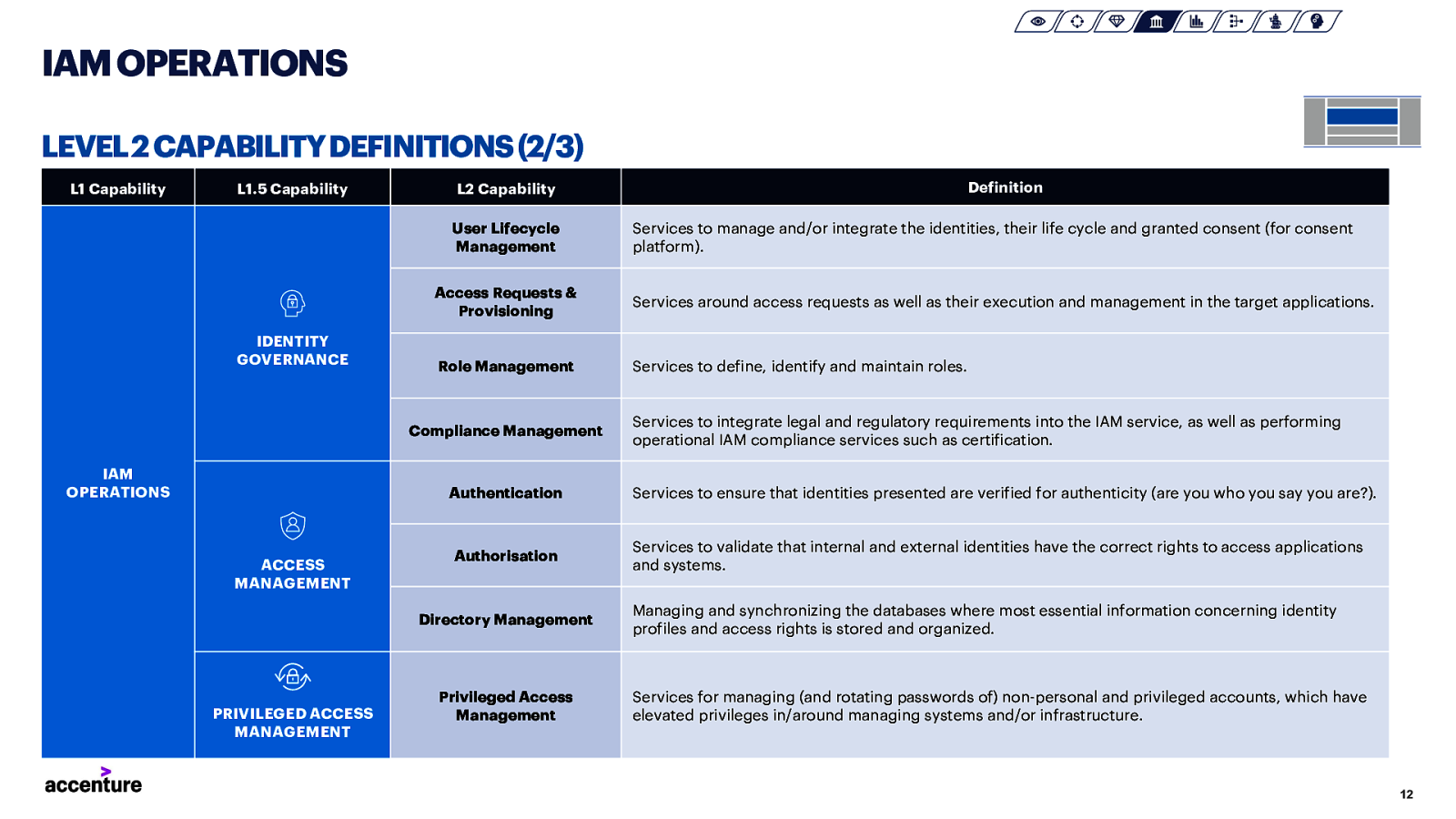
IAM OPERATIONS LEVEL 2 CAPABILITY DEFINITIONS (2/3) L1 Capability L1.5 Capability User Lifecycle Management IDENTITY GOVERNANCE Services around access requests as well as their execution and management in the target applications. Role Management Services to define, identify and maintain roles. Authentication ACCESS MANAGEMENT Authorisation Directory Management PRIVILEGED ACCESS MANAGEMENT Services to manage and/or integrate the identities, their life cycle and granted consent (for consent platform). Access Requests & Provisioning Compliance Management IAM OPERATIONS Definition L2 Capability Privileged Access Management Services to integrate legal and regulatory requirements into the IAM service, as well as performing operational IAM compliance services such as certification. Services to ensure that identities presented are verified for authenticity (are you who you say you are?). Services to validate that internal and external identities have the correct rights to access applications and systems. Managing and synchronizing the databases where most essential information concerning identity profiles and access rights is stored and organized. Services for managing (and rotating passwords of) non-personal and privileged accounts, which have elevated privileges in/around managing systems and/or infrastructure. 12
Slide 13
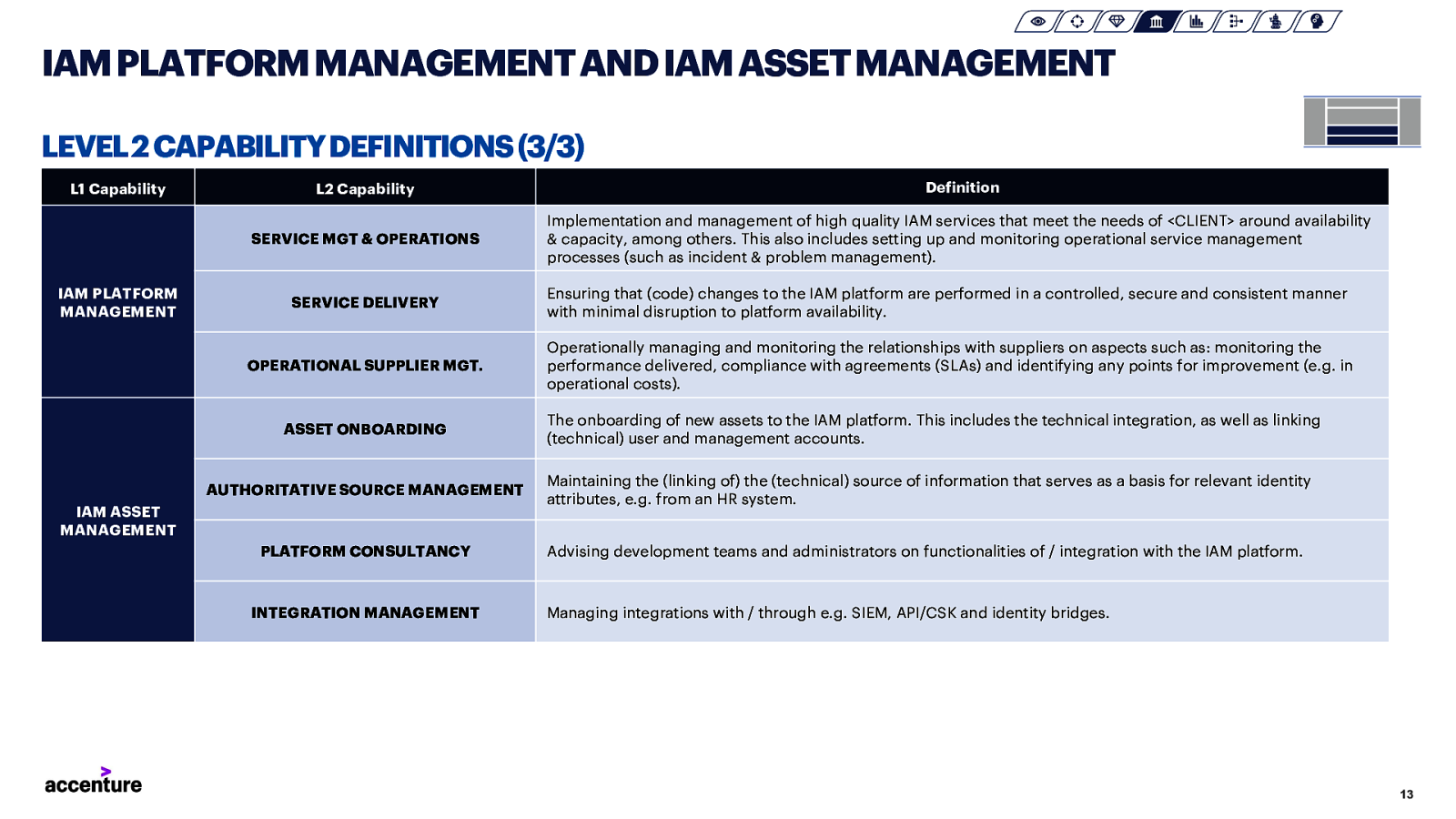
IAM PLATFORM MANAGEMENT AND IAM ASSET MANAGEMENT LEVEL 2 CAPABILITY DEFINITIONS (3/3) L1 Capability IAM PLATFORM MANAGEMENT L2 Capability Definition SERVICE MGT & OPERATIONS Implementation and management of high quality IAM services that meet the needs of <CLIENT> around availability & capacity, among others. This also includes setting up and monitoring operational service management processes (such as incident & problem management). SERVICE DELIVERY Ensuring that (code) changes to the IAM platform are performed in a controlled, secure and consistent manner with minimal disruption to platform availability. OPERATIONAL SUPPLIER MGT. Operationally managing and monitoring the relationships with suppliers on aspects such as: monitoring the performance delivered, compliance with agreements (SLAs) and identifying any points for improvement (e.g. in operational costs). ASSET ONBOARDING The onboarding of new assets to the IAM platform. This includes the technical integration, as well as linking (technical) user and management accounts. AUTHORITATIVE SOURCE MANAGEMENT Maintaining the (linking of) the (technical) source of information that serves as a basis for relevant identity attributes, e.g. from an HR system. PLATFORM CONSULTANCY Advising development teams and administrators on functionalities of / integration with the IAM platform. IAM ASSET MANAGEMENT INTEGRATION MANAGEMENT Managing integrations with / through e.g. SIEM, API/CSK and identity bridges. 13
Slide 14
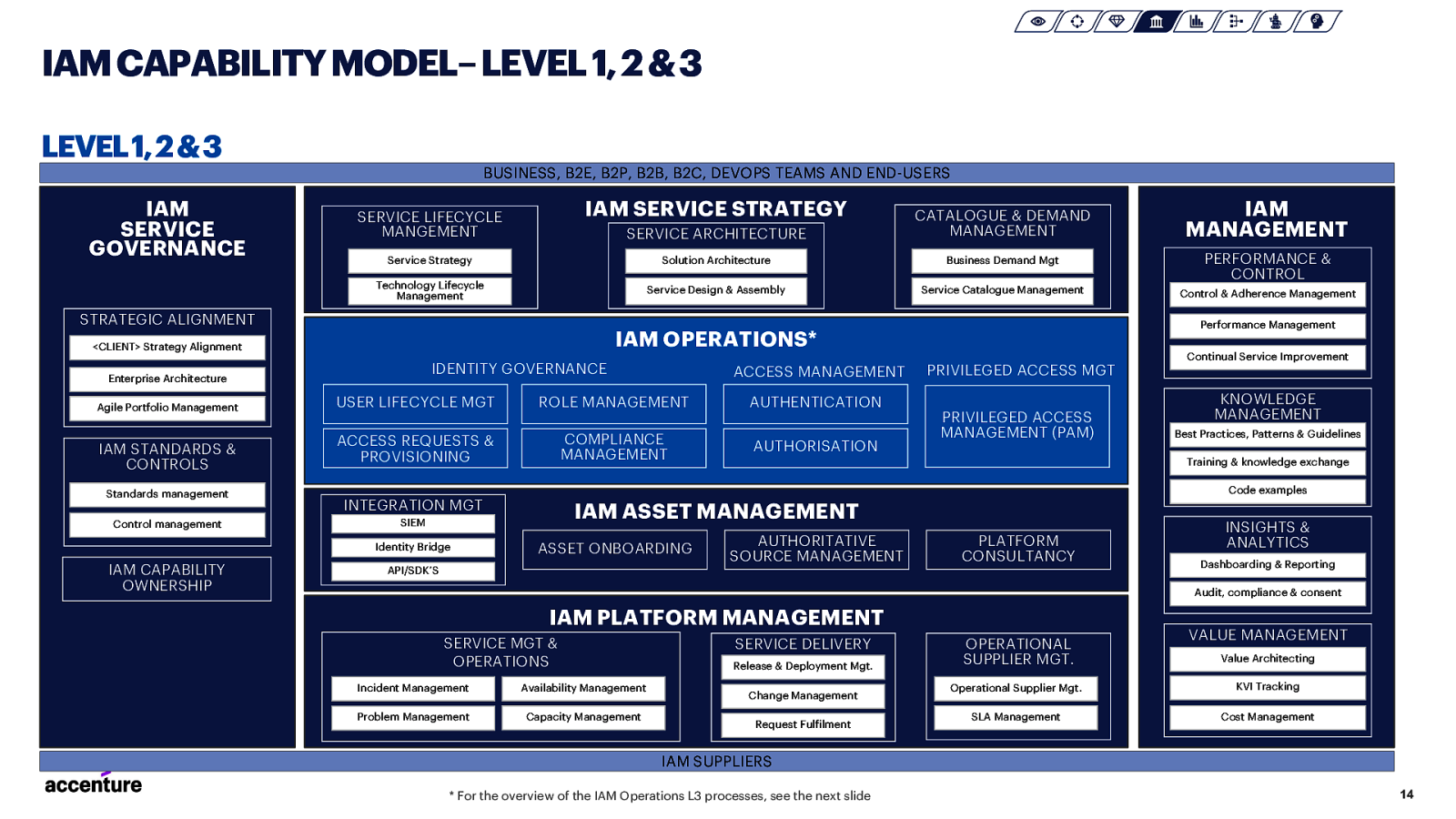
IAM CAPABILITY MODEL–LEVEL 1, 2 & 3 LEVEL 1, 2 & 3 BUSINESS, B2E, B2P, B2B, B2C, DEVOPS TEAMS AND END-USERS IAM SERVICE GOVERNANCE IAM SERVICE STRATEGY SERVICE ARCHITECTURE Service Strategy Solution Architecture Business Demand Mgt Technology Lifecycle Management PERFORMANCE & CONTROL Service Design & Assembly Service Catalogue Management Control & Adherence Management STRATEGIC ALIGNMENT Standards management Control management USER LIFECYCLE MGT ACCESS MANAGEMENT ROLE MANAGEMENT COMPLIANCE MANAGEMENT ACCESS REQUESTS & PROVISIONING PRIVILEGED ACCESS MGT AUTHENTICATION AUTHORISATION PRIVILEGED ACCESS MANAGEMENT (PAM) KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT Best Practices, Patterns & Guidelines Training & knowledge exchange Code examples INTEGRATION MGT IAM ASSET MANAGEMENT SIEM Identity Bridge IAM CAPABILITY OWNERSHIP Continual Service Improvement IDENTITY GOVERNANCE Enterprise Architecture IAM STANDARDS & CONTROLS Performance Management IAM OPERATIONS* <CLIENT> Strategy Alignment Agile Portfolio Management IAM MANAGEMENT CATALOGUE & DEMAND MANAGEMENT SERVICE LIFECYCLE MANGEMENT ASSET ONBOARDING AUTHORITATIVE SOURCE MANAGEMENT PLATFORM CONSULTANCY API/SDK’S INSIGHTS & ANALYTICS Dashboarding & Reporting Audit, compliance & consent IAM PLATFORM MANAGEMENT SERVICE MGT & OPERATIONS Incident Management Availability Management Problem Management Capacity Management SERVICE DELIVERY Release & Deployment Mgt. Change Management Request Fulfilment OPERATIONAL SUPPLIER MGT. VALUE MANAGEMENT Value Architecting Operational Supplier Mgt. KVI Tracking SLA Management Cost Management IAM SUPPLIERS * For the overview of the IAM Operations L3 processes, see the next slide 14
Slide 15

IAM OPERATIONS LEVEL 1, 2 & 3 –OVERVIEW IAM CAPABILITIES IAM OPERATIONS IDENTITY GOVERNANCE ACCESS MANAGEMENT USER LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT AUTHENTICATION PRIVILEGED ACCESS MGT PRIVILEGED ACCESS MANAGEMENT (PAM) Identity Journey Management Delegated Administration Basic Authentication Strong Authentication Privileged Account LCM Hard-Coded Password Mgt. Privacy & User Consent Self-Service Session Management Single Sign-On (SSO) Privileged Session Management Remote Maintenance Access Identity Integration Progressive Profiling Federation Adaptive Authentication Firefighter Access DevOps Pipeline Management API Gateway Token Management Credential Rotation ACCESS REQUESTS & PROVISIONING Provisioning / Deprovisioning Workflow Management Reconciliation Account Management Entitlement Management Just-In-Time Provisioning AUTHORISATION Role-Based Access control Policy-Based Access control DIRECTORY MANAGEMENT Directory Management Directory Synchronization ROLE MANAGEMENT Role Management Role Mining Policy Management COMPLIANCE MANAGEMENT Subject Rights Management Certification Segregation of Duties 15
Slide 16
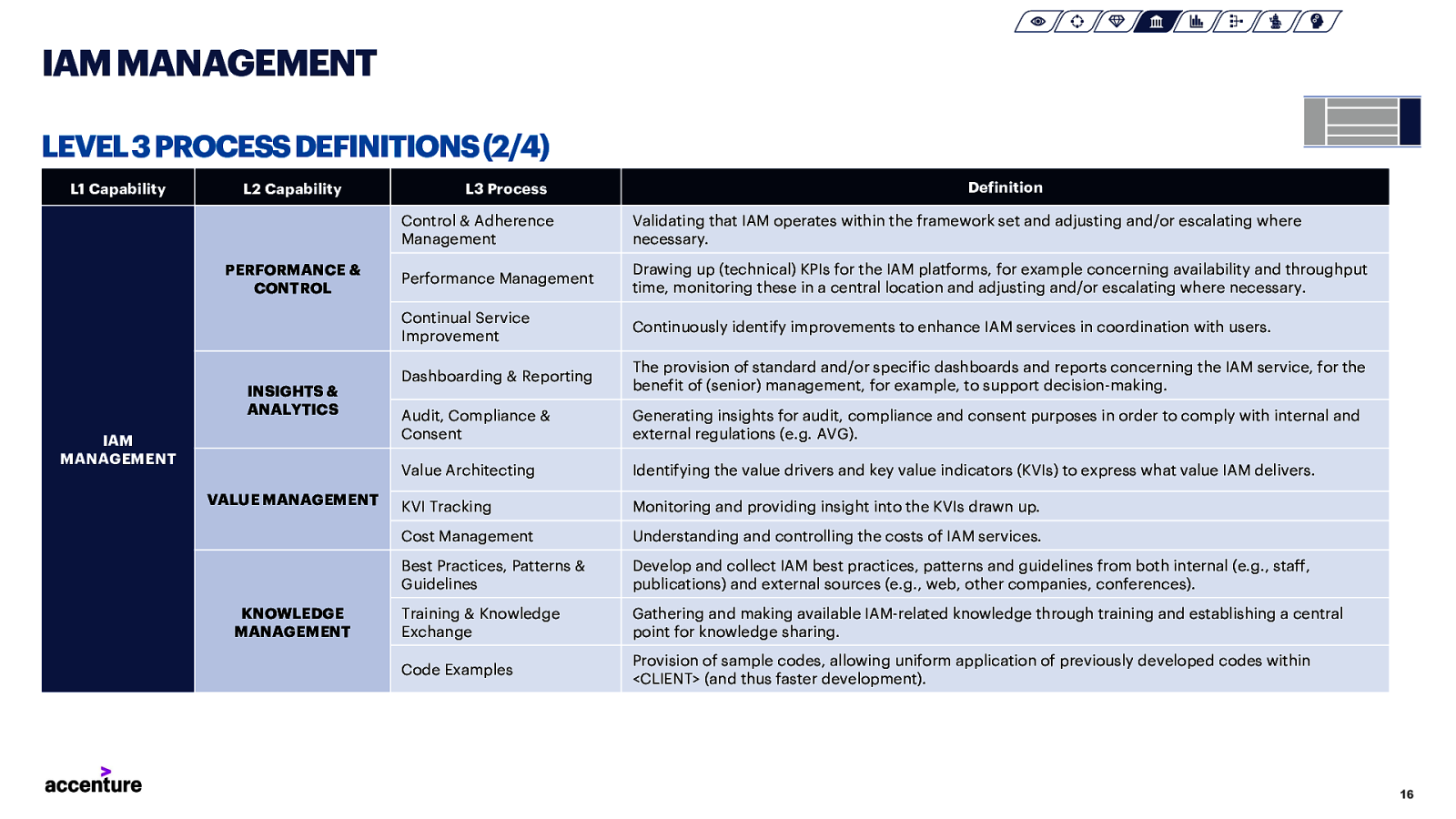
IAM MANAGEMENT LEVEL 3 PROCESS DEFINITIONS (2/4) L1 Capability L2 Capability PERFORMANCE & CONTROL INSIGHTS & ANALYTICS IAM MANAGEMENT VALUE MANAGEMENT KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT L3 Process Definition Control & Adherence Management Validating that IAM operates within the framework set and adjusting and/or escalating where necessary. Performance Management Drawing up (technical) KPIs for the IAM platforms, for example concerning availability and throughput time, monitoring these in a central location and adjusting and/or escalating where necessary. Continual Service Improvement Continuously identify improvements to enhance IAM services in coordination with users. Dashboarding & Reporting The provision of standard and/or specific dashboards and reports concerning the IAM service, for the benefit of (senior) management, for example, to support decision-making. Audit, Compliance & Consent Generating insights for audit, compliance and consent purposes in order to comply with internal and external regulations (e.g. AVG). Value Architecting Identifying the value drivers and key value indicators (KVIs) to express what value IAM delivers. KVI Tracking Monitoring and providing insight into the KVIs drawn up. Cost Management Understanding and controlling the costs of IAM services. Best Practices, Patterns & Guidelines Develop and collect IAM best practices, patterns and guidelines from both internal (e.g., staff, publications) and external sources (e.g., web, other companies, conferences). Training & Knowledge Exchange Gathering and making available IAM-related knowledge through training and establishing a central point for knowledge sharing. Code Examples Provision of sample codes, allowing uniform application of previously developed codes within <CLIENT> (and thus faster development). 16
Slide 17
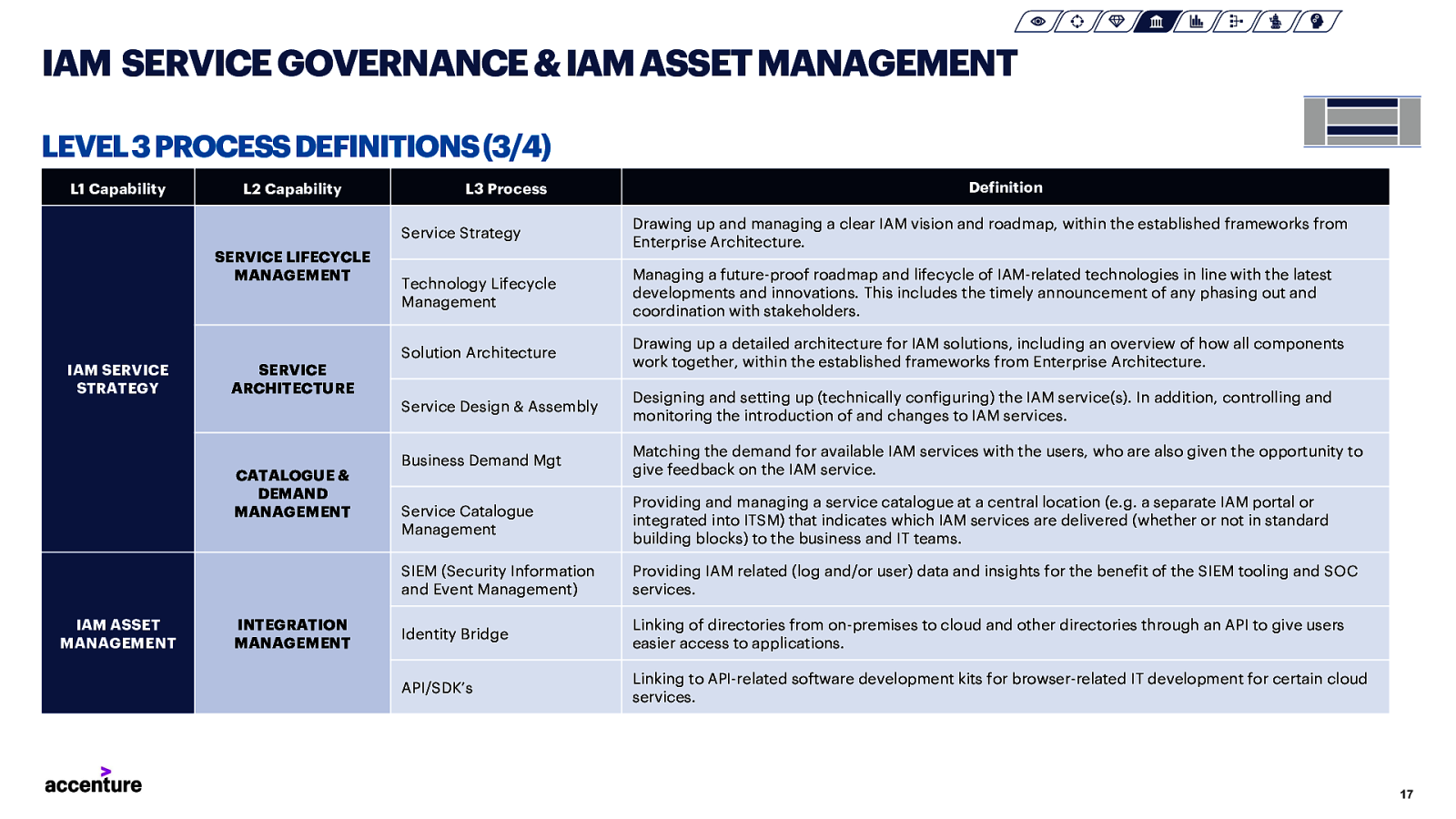
IAM SERVICE GOVERNANCE & IAM ASSET MANAGEMENT LEVEL 3 PROCESS DEFINITIONS (3/4) L1 Capability L2 Capability SERVICE LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT IAM SERVICE STRATEGY INTEGRATION MANAGEMENT Definition Service Strategy Drawing up and managing a clear IAM vision and roadmap, within the established frameworks from Enterprise Architecture. Technology Lifecycle Management Managing a future-proof roadmap and lifecycle of IAM-related technologies in line with the latest developments and innovations. This includes the timely announcement of any phasing out and coordination with stakeholders. Solution Architecture Drawing up a detailed architecture for IAM solutions, including an overview of how all components work together, within the established frameworks from Enterprise Architecture. Service Design & Assembly Designing and setting up (technically configuring) the IAM service(s). In addition, controlling and monitoring the introduction of and changes to IAM services. Business Demand Mgt Matching the demand for available IAM services with the users, who are also given the opportunity to give feedback on the IAM service. Service Catalogue Management Providing and managing a service catalogue at a central location (e.g. a separate IAM portal or integrated into ITSM) that indicates which IAM services are delivered (whether or not in standard building blocks) to the business and IT teams. SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) Providing IAM related (log and/or user) data and insights for the benefit of the SIEM tooling and SOC services. Identity Bridge Linking of directories from on-premises to cloud and other directories through an API to give users easier access to applications. API/SDK’s Linking to API-related software development kits for browser-related IT development for certain cloud services. SERVICE ARCHITECTURE CATALOGUE & DEMAND MANAGEMENT IAM ASSET MANAGEMENT L3 Process 17
Slide 18
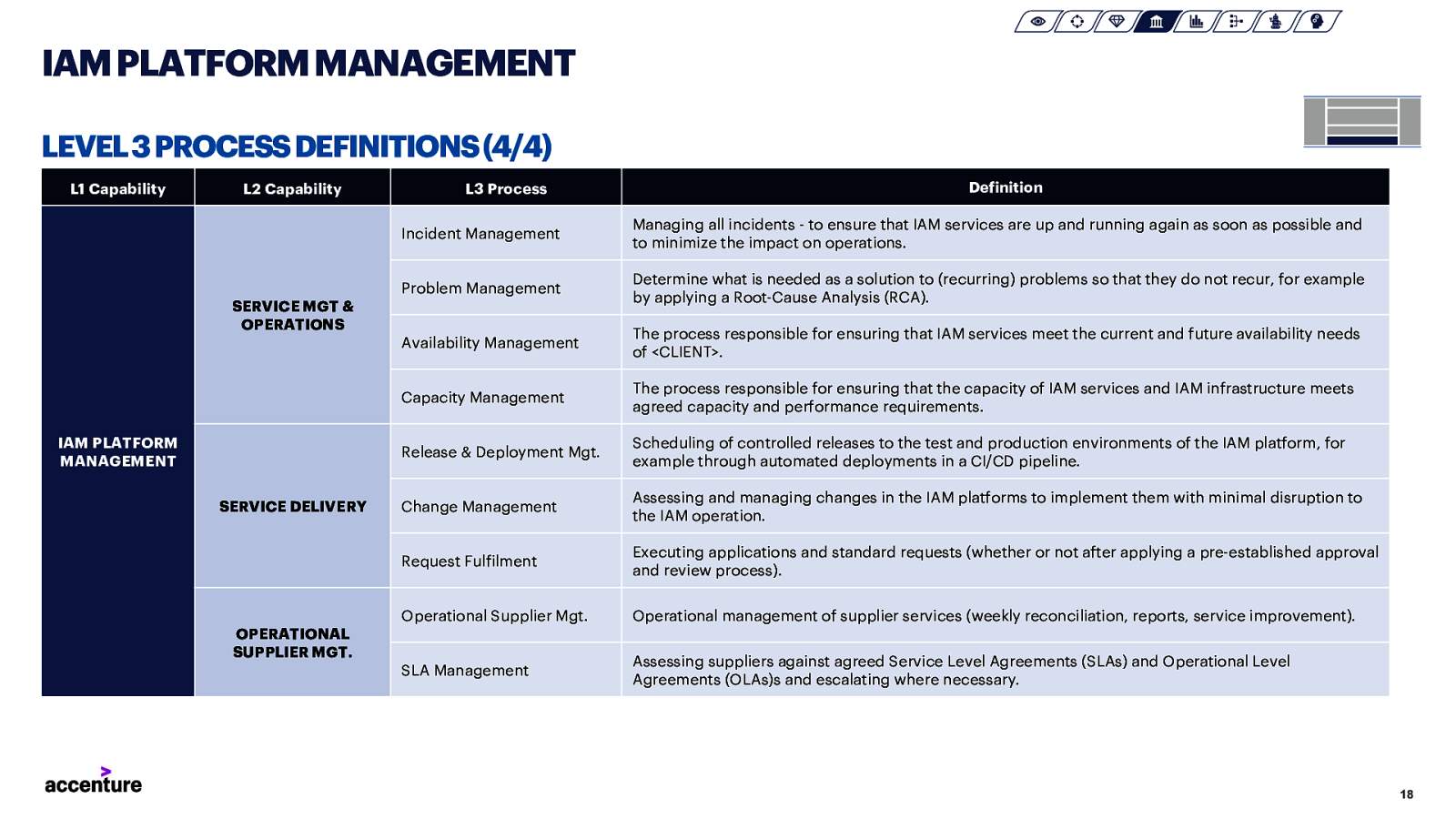
IAM PLATFORM MANAGEMENT LEVEL 3 PROCESS DEFINITIONS (4/4) L1 Capability L2 Capability L3 Process Incident Management Managing all incidents - to ensure that IAM services are up and running again as soon as possible and to minimize the impact on operations. Problem Management Determine what is needed as a solution to (recurring) problems so that they do not recur, for example by applying a Root-Cause Analysis (RCA). Availability Management The process responsible for ensuring that IAM services meet the current and future availability needs of <CLIENT>. Capacity Management The process responsible for ensuring that the capacity of IAM services and IAM infrastructure meets agreed capacity and performance requirements. Release & Deployment Mgt. Scheduling of controlled releases to the test and production environments of the IAM platform, for example through automated deployments in a CI/CD pipeline. Change Management Assessing and managing changes in the IAM platforms to implement them with minimal disruption to the IAM operation. Request Fulfilment Executing applications and standard requests (whether or not after applying a pre-established approval and review process). Operational Supplier Mgt. Operational management of supplier services (weekly reconciliation, reports, service improvement). SLA Management Assessing suppliers against agreed Service Level Agreements (SLAs) and Operational Level Agreements (OLAs)s and escalating where necessary. SERVICE MGT & OPERATIONS IAM PLATFORM MANAGEMENT SERVICE DELIVERY Definition OPERATIONAL SUPPLIER MGT. 18
Slide 19
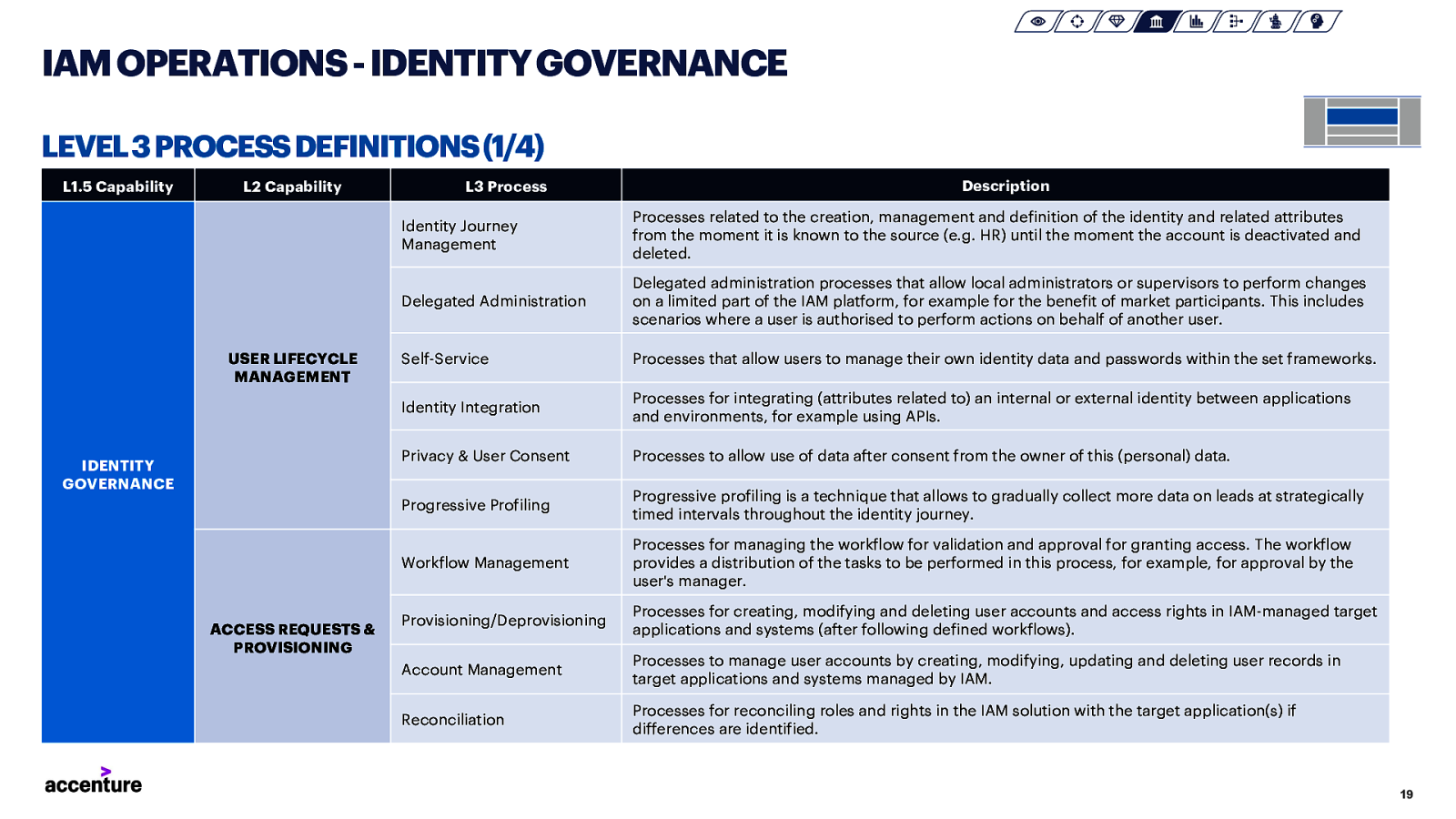
IAM OPERATIONS -IDENTITY GOVERNANCE LEVEL 3 PROCESS DEFINITIONS (1/4) L1.5 Capability L2 Capability USER LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT IDENTITY GOVERNANCE ACCESS REQUESTS & PROVISIONING L3 Process Description Identity Journey Management Processes related to the creation, management and definition of the identity and related attributes from the moment it is known to the source (e.g. HR) until the moment the account is deactivated and deleted. Delegated Administration Delegated administration processes that allow local administrators or supervisors to perform changes on a limited part of the IAM platform, for example for the benefit of market participants. This includes scenarios where a user is authorised to perform actions on behalf of another user. Self-Service Processes that allow users to manage their own identity data and passwords within the set frameworks. Identity Integration Processes for integrating (attributes related to) an internal or external identity between applications and environments, for example using APIs. Privacy & User Consent Processes to allow use of data after consent from the owner of this (personal) data. Progressive Profiling Progressive profiling is a technique that allows to gradually collect more data on leads at strategically timed intervals throughout the identity journey. Workflow Management Processes for managing the workflow for validation and approval for granting access. The workflow provides a distribution of the tasks to be performed in this process, for example, for approval by the user’s manager. Provisioning/Deprovisioning Processes for creating, modifying and deleting user accounts and access rights in IAM-managed target applications and systems (after following defined workflows). Account Management Processes to manage user accounts by creating, modifying, updating and deleting user records in target applications and systems managed by IAM. Reconciliation Processes for reconciling roles and rights in the IAM solution with the target application(s) if differences are identified. 19
Slide 20
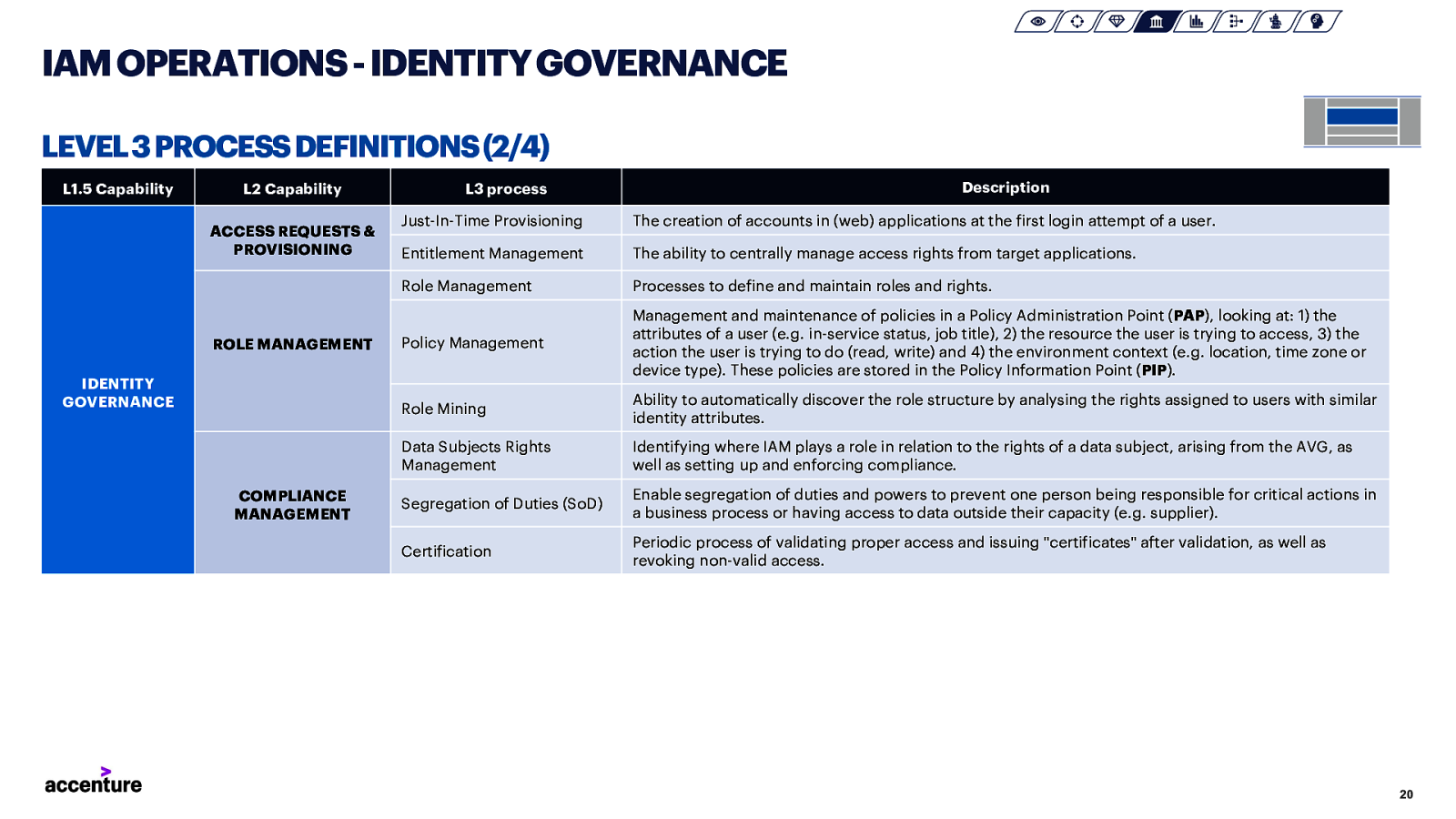
IAM OPERATIONS -IDENTITY GOVERNANCE LEVEL 3 PROCESS DEFINITIONS (2/4) L1.5 Capability L2 Capability ACCESS REQUESTS & PROVISIONING ROLE MANAGEMENT IDENTITY GOVERNANCE COMPLIANCE MANAGEMENT L3 process Description Just-In-Time Provisioning The creation of accounts in (web) applications at the first login attempt of a user. Entitlement Management The ability to centrally manage access rights from target applications. Role Management Processes to define and maintain roles and rights. Policy Management Management and maintenance of policies in a Policy Administration Point (PAP), looking at: 1) the attributes of a user (e.g. in-service status, job title), 2) the resource the user is trying to access, 3) the action the user is trying to do (read, write) and 4) the environment context (e.g. location, time zone or device type). These policies are stored in the Policy Information Point (PIP). Role Mining Ability to automatically discover the role structure by analysing the rights assigned to users with similar identity attributes. Data Subjects Rights Management Identifying where IAM plays a role in relation to the rights of a data subject, arising from the AVG, as well as setting up and enforcing compliance. Segregation of Duties (SoD) Enable segregation of duties and powers to prevent one person being responsible for critical actions in a business process or having access to data outside their capacity (e.g. supplier). Certification Periodic process of validating proper access and issuing “certificates” after validation, as well as revoking non-valid access. 20
Slide 21
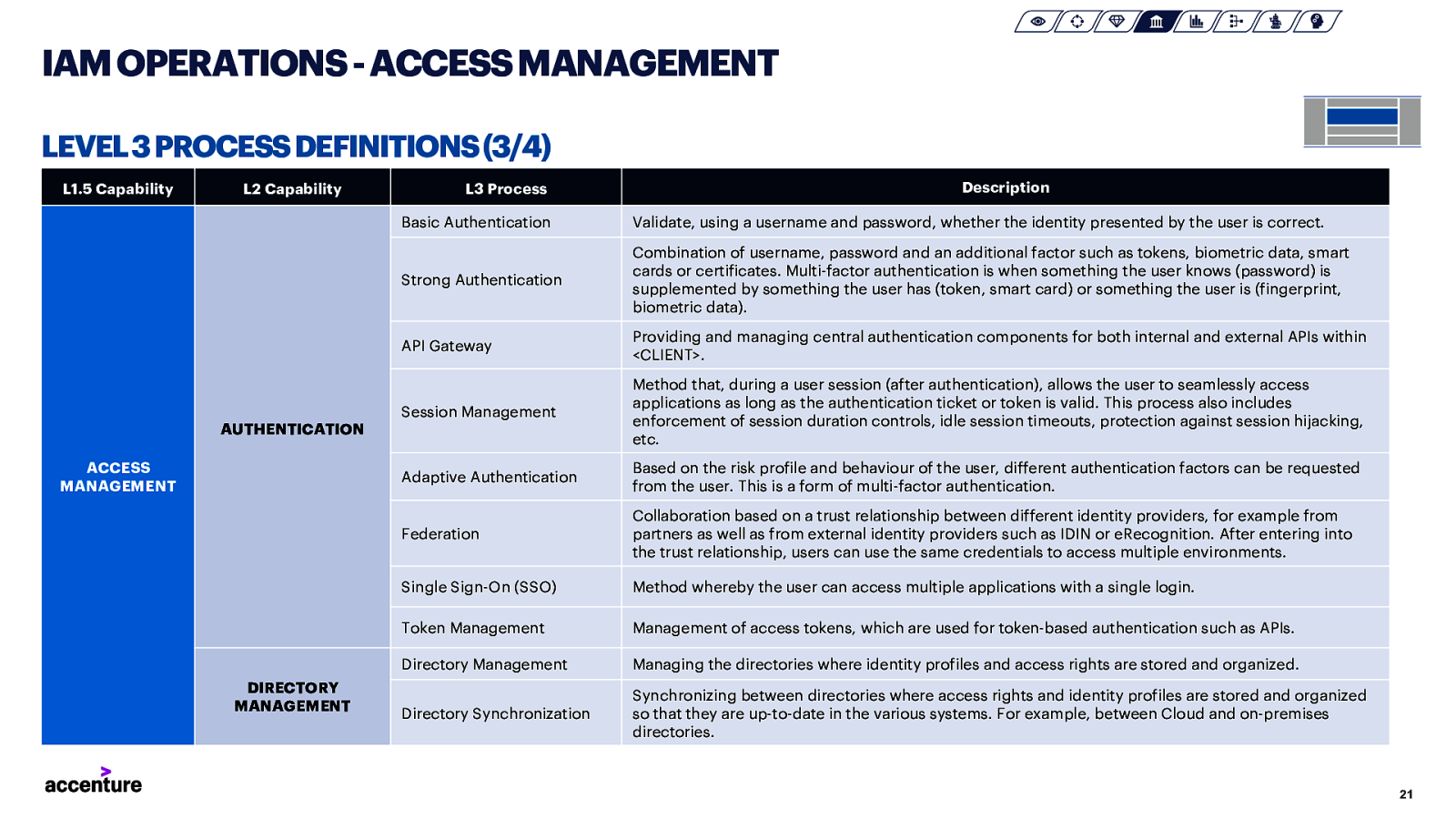
IAM OPERATIONS -ACCESS MANAGEMENT LEVEL 3 PROCESS DEFINITIONS (3/4) L1.5 Capability L2 Capability L3 Process Basic Authentication Validate, using a username and password, whether the identity presented by the user is correct. Strong Authentication Combination of username, password and an additional factor such as tokens, biometric data, smart cards or certificates. Multi-factor authentication is when something the user knows (password) is supplemented by something the user has (token, smart card) or something the user is (fingerprint, biometric data). API Gateway Providing and managing central authentication components for both internal and external APIs within <CLIENT>. Session Management Method that, during a user session (after authentication), allows the user to seamlessly access applications as long as the authentication ticket or token is valid. This process also includes enforcement of session duration controls, idle session timeouts, protection against session hijacking, etc. Adaptive Authentication Based on the risk profile and behaviour of the user, different authentication factors can be requested from the user. This is a form of multi-factor authentication. Federation Collaboration based on a trust relationship between different identity providers, for example from partners as well as from external identity providers such as IDIN or eRecognition. After entering into the trust relationship, users can use the same credentials to access multiple environments. Single Sign-On (SSO) Method whereby the user can access multiple applications with a single login. Token Management Management of access tokens, which are used for token-based authentication such as APIs. Directory Management Managing the directories where identity profiles and access rights are stored and organized. Directory Synchronization Synchronizing between directories where access rights and identity profiles are stored and organized so that they are up-to-date in the various systems. For example, between Cloud and on-premises directories. AUTHENTICATION ACCESS MANAGEMENT DIRECTORY MANAGEMENT Description 21
Slide 22
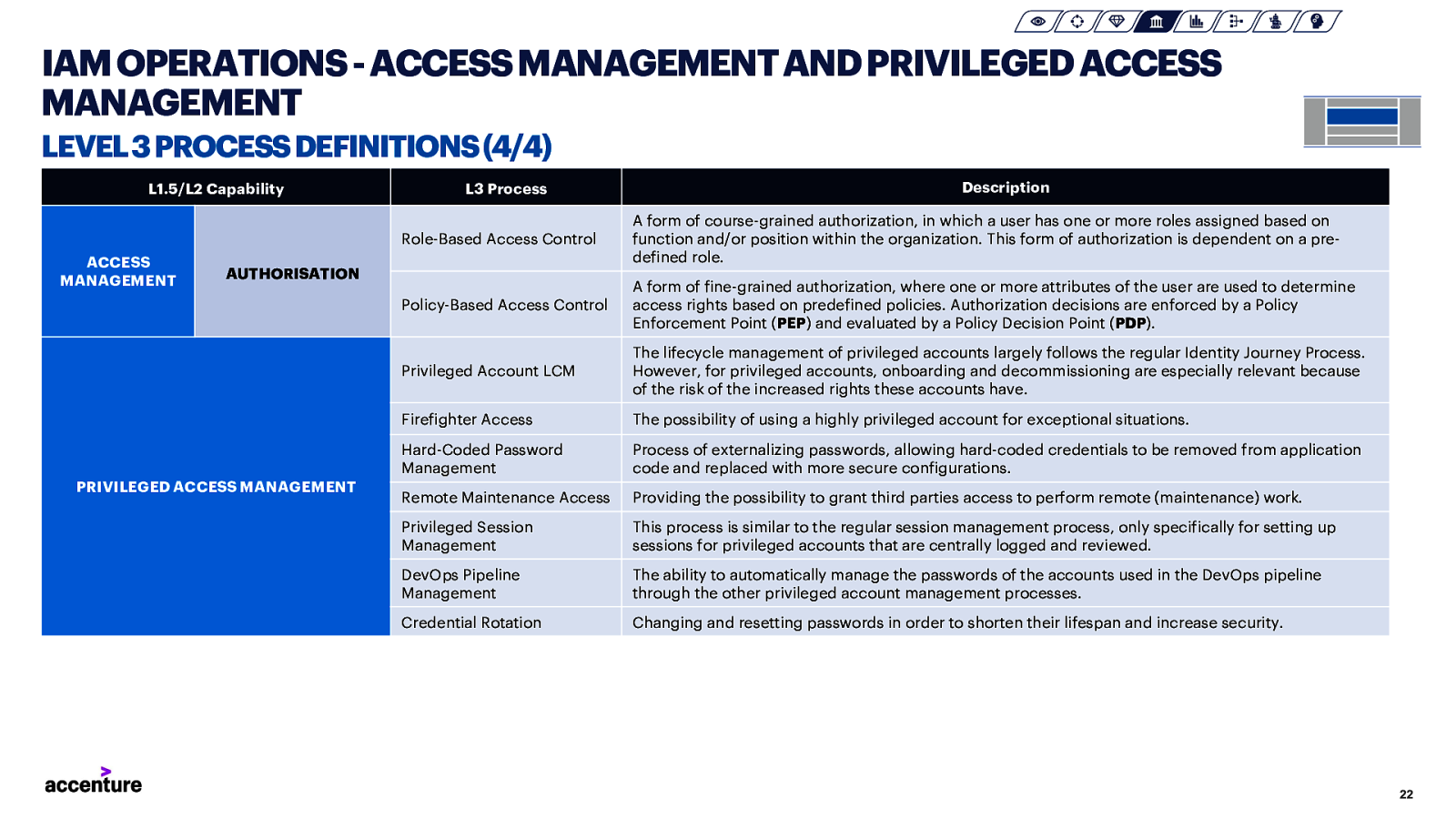
IAM OPERATIONS -ACCESS MANAGEMENT AND PRIVILEGED ACCESS MANAGEMENT LEVEL 3 PROCESS DEFINITIONS (4/4) L1.5/L2 Capability ACCESS MANAGEMENT L3 Process Role-Based Access Control A form of course-grained authorization, in which a user has one or more roles assigned based on function and/or position within the organization. This form of authorization is dependent on a predefined role. Policy-Based Access Control A form of fine-grained authorization, where one or more attributes of the user are used to determine access rights based on predefined policies. Authorization decisions are enforced by a Policy Enforcement Point (PEP) and evaluated by a Policy Decision Point (PDP). Privileged Account LCM The lifecycle management of privileged accounts largely follows the regular Identity Journey Process. However, for privileged accounts, onboarding and decommissioning are especially relevant because of the risk of the increased rights these accounts have. Firefighter Access The possibility of using a highly privileged account for exceptional situations. Hard-Coded Password Management Process of externalizing passwords, allowing hard-coded credentials to be removed from application code and replaced with more secure configurations. Remote Maintenance Access Providing the possibility to grant third parties access to perform remote (maintenance) work. Privileged Session Management This process is similar to the regular session management process, only specifically for setting up sessions for privileged accounts that are centrally logged and reviewed. DevOps Pipeline Management The ability to automatically manage the passwords of the accounts used in the DevOps pipeline through the other privileged account management processes. Credential Rotation Changing and resetting passwords in order to shorten their lifespan and increase security. AUTHORISATION PRIVILEGED ACCESS MANAGEMENT Description 22
Slide 23
CONTENTS IAM VISION Business Strategy & Vision Contents IAM Operating Model
- IAM Vison 3. Value drivers 4. IAM Capability Areas IAM Vision INTENT
- Operating Model Principles Operating Model Principles Value Drivers IAM Capability Areas
- Metrics 7. Technology & Vendors 8. People (Roles and sourcing) BLUEPRINT
- Governance & Processes Governance Processes & Metrics Technology People IAM Execution 23
Slide 24
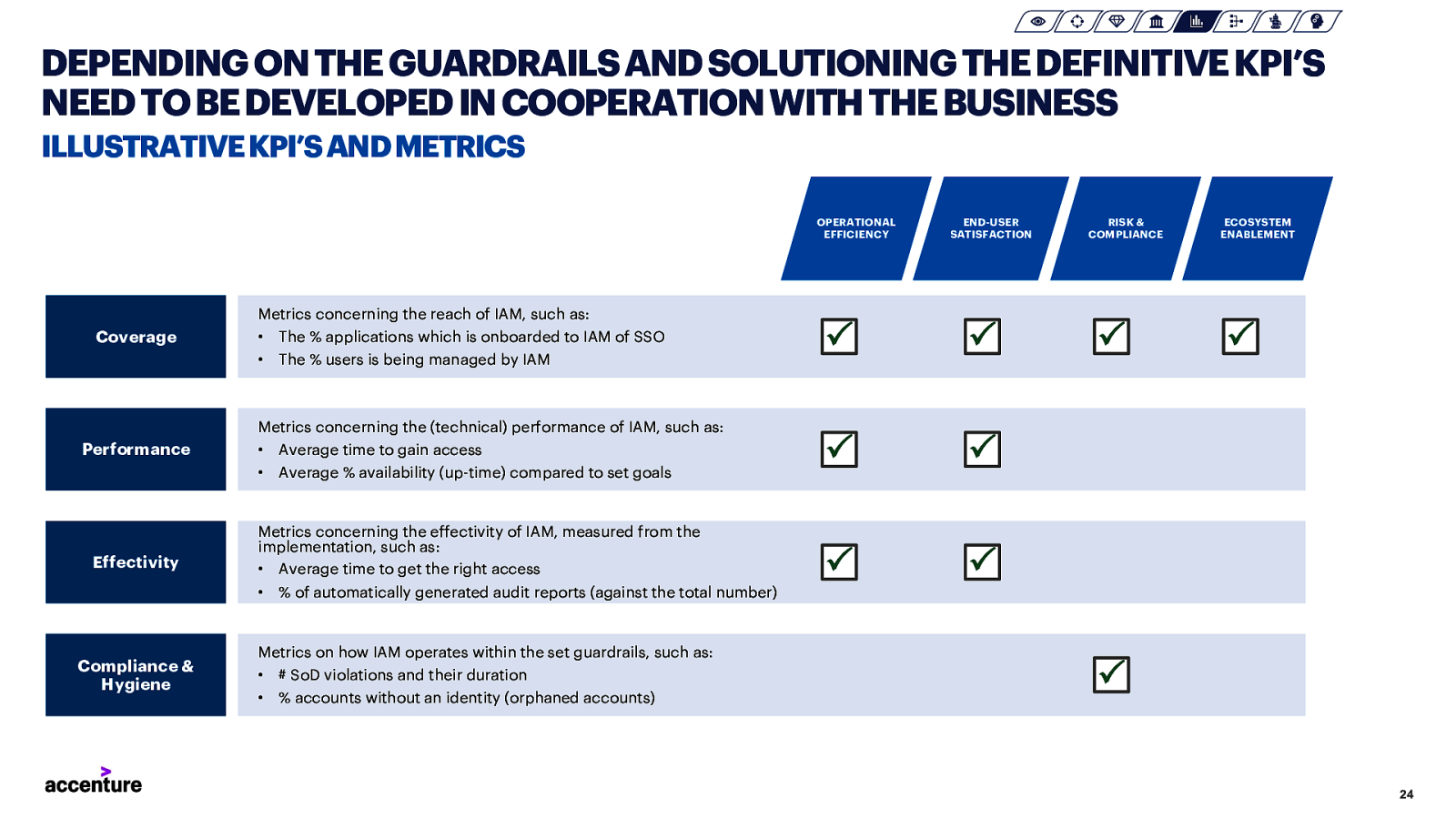
DEPENDING ON THE GUARDRAILS AND SOLUTIONING THE DEFINITIVE KPI’S NEED TO BE DEVELOPED IN COOPERATION WITH THE BUSINESS ILLUSTRATIVE KPI’S AND METRICS OPERATIONAL EFFICIENCY Metrics concerning the reach of IAM, such as: Coverage • • The % applications which is onboarded to IAM of SSO The % users is being managed by IAM Metrics concerning the (technical) performance of IAM, such as: Performance Effectivity • • Metrics concerning the effectivity of IAM, measured from the implementation, such as: • Average time to get the right access • Compliance & Hygiene Average time to gain access Average % availability (up-time) compared to set goals P P P P P P RISK & COMPLIANCE P ECOSYSTEM ENABLEMENT P % of automatically generated audit reports (against the total number) Metrics on how IAM operates within the set guardrails, such as: • # SoD violations and their duration • END-USER SATISFACTION % accounts without an identity (orphaned accounts) P 24
Slide 25
CONTENTS IAM CAPABILITY MODEL Business Strategy & Vision Contents IAM Operating Model
- IAM Vison 3. Value drivers 4. IAM Capability Areas IAM Vision INTENT
- Operating Model Principles Operating Model Principles Value Drivers IAM Capability Areas
- Metrics 7. Technology & Vendors 8. People (Roles and sourcing) BLUEPRINT
- Governance & Processes Governance Processes & Metrics Technology People IAM Execution 25
Slide 26
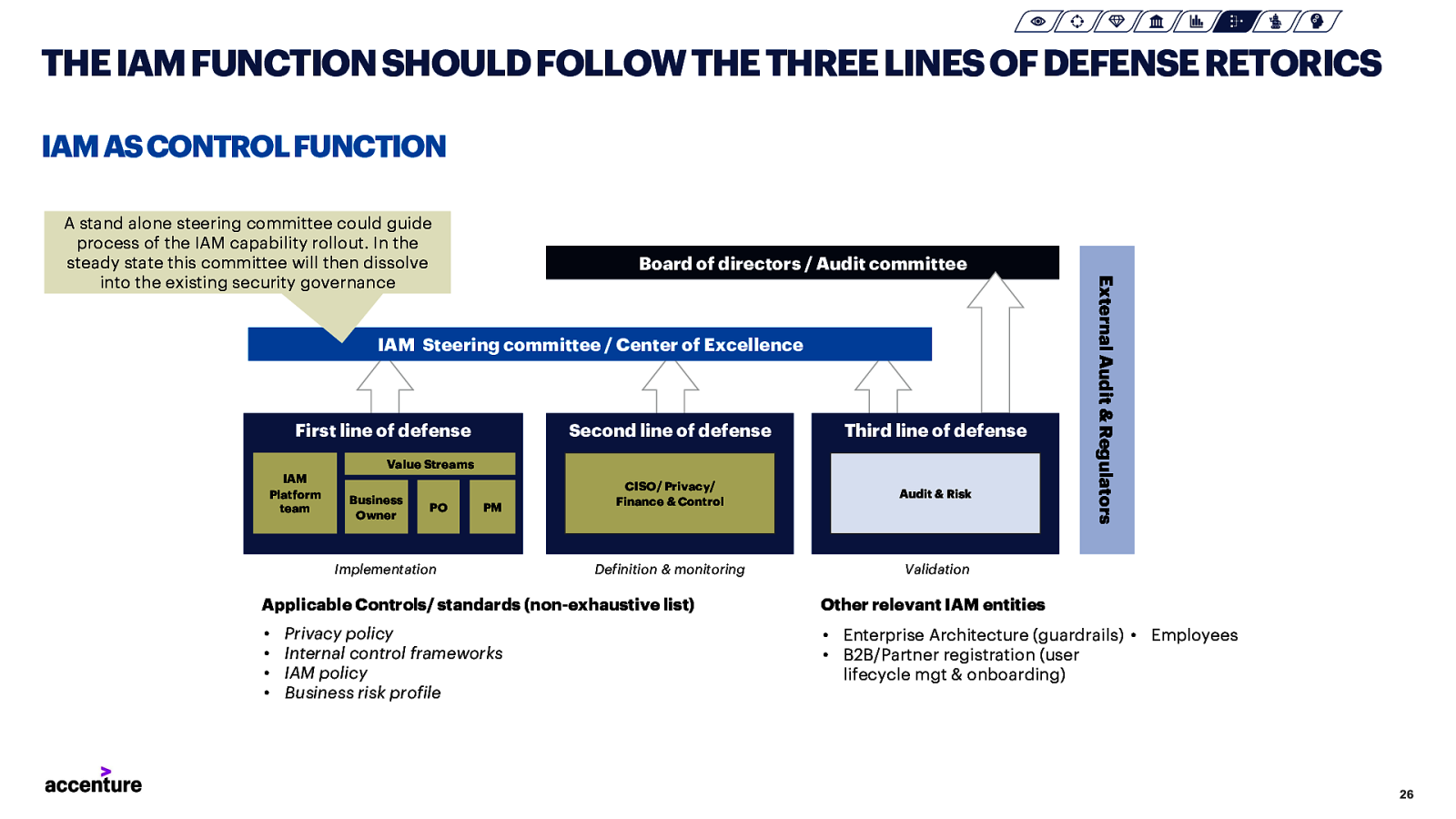
THE IAMFUNCTION SHOULD FOLLOW THE THREE LINES OF DEFENSERETORICS IAM AS CONTROL FUNCTION A stand alone steering committee could guide process of the IAM capability rollout. In the steady state this committee will then dissolve into the existing security governance Board of directors / Audit committee First line of defense Second line of defense Third line of defense CISO/ Privacy/ Finance & Control Audit & Risk Definition & monitoring Validation Value Streams IAM Platform team Business Owner PO PM Implementation External Audit & Regulators IAM Steering committee / Center of Excellence Applicable Controls/ standards (non-exhaustive list) Other relevant IAM entities • • • • • Enterprise Architecture (guardrails) • Employees • B2B/Partner registration (user lifecycle mgt & onboarding) Privacy policy Internal control frameworks IAM policy Business risk profile 26
Slide 27
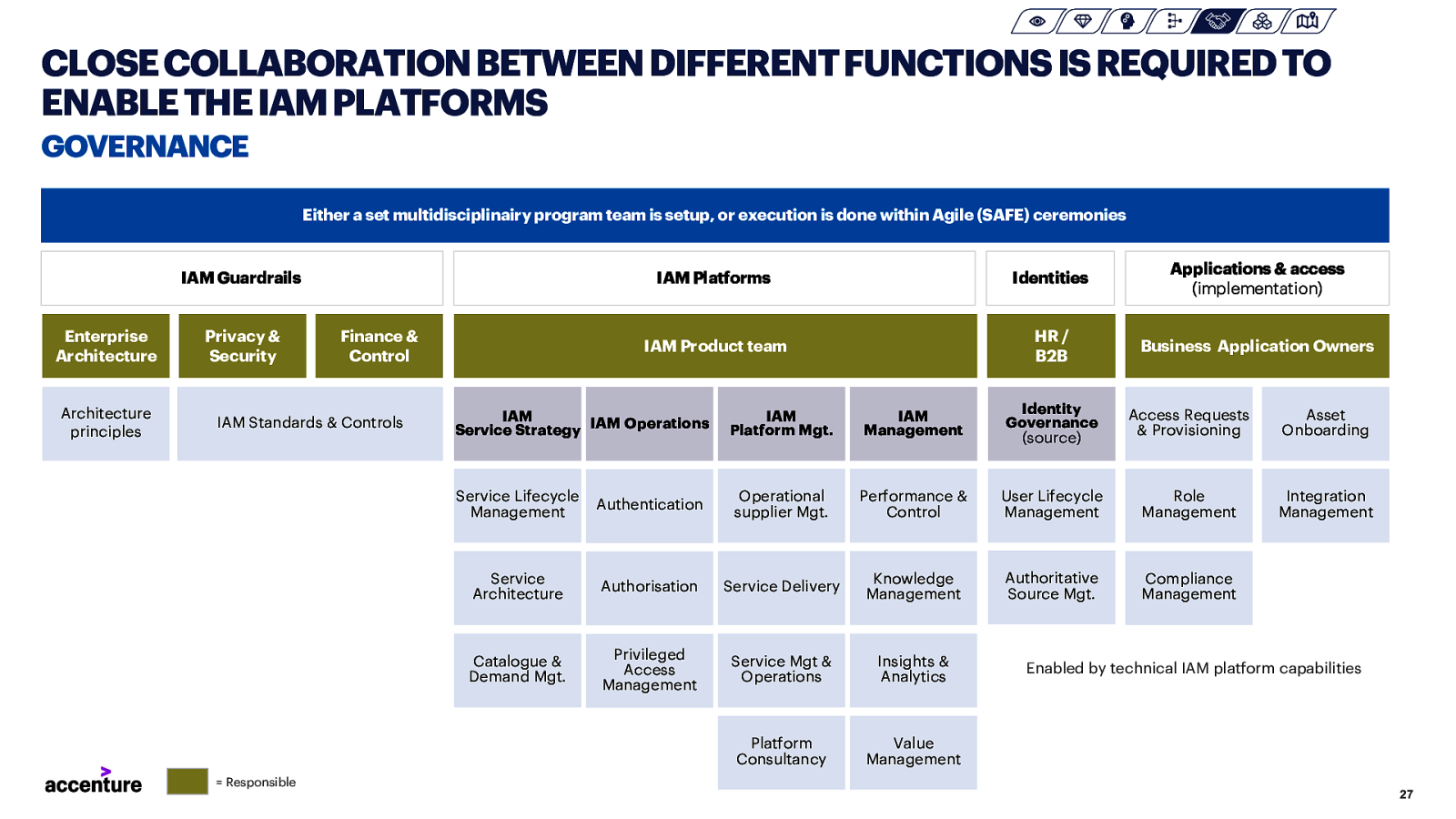
CLOSE COLLABORATIONBETWEEN DIFFERENT FUNCTIONSIS REQUIREDTO ENABLETHEIAMPLATFORMS GOVERNANCE Either a set multidisciplinairy program team is setup, or execution is done within Agile (SAFE) ceremonies IAM Guardrails Enterprise Architecture Architecture principles Privacy & Security Finance & Control IAM Standards & Controls = Responsible IAM Platforms Identities Applications & access (implementation) IAM Product team HR / B2B Business Application Owners IAM Service Strategy IAM Operations IAM Platform Mgt. IAM Management Identity Governance (source) Access Requests & Provisioning Asset Onboarding Service Lifecycle Management Authentication Operational supplier Mgt. Performance & Control User Lifecycle Management Role Management Integration Management Service Architecture Authorisation Service Delivery Knowledge Management Authoritative Source Mgt. Compliance Management Catalogue & Demand Mgt. Privileged Access Management Service Mgt & Operations Insights & Analytics Platform Consultancy Value Management Enabled by technical IAM platform capabilities 27
Slide 28
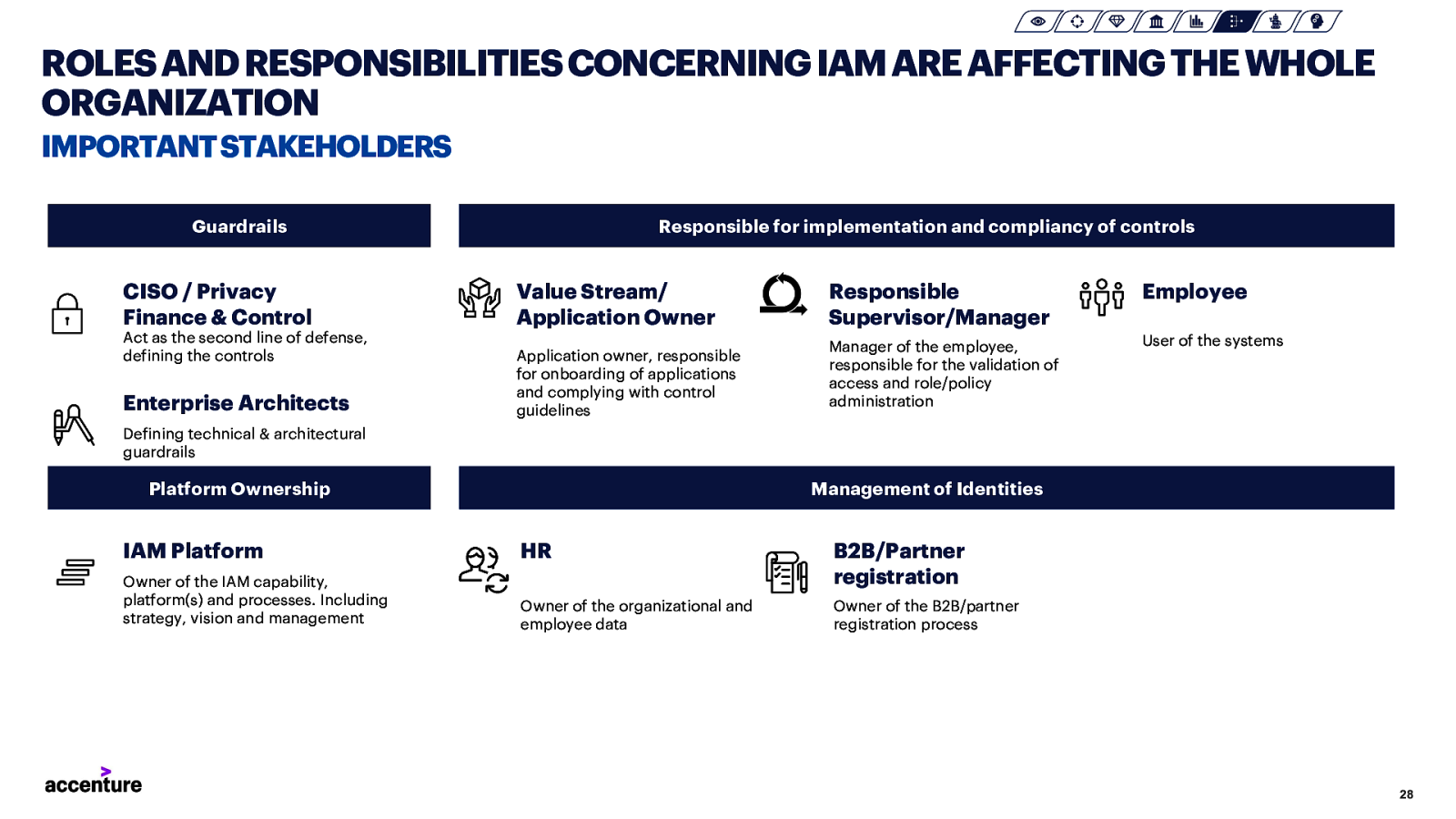
ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES CONCERNING IAM ARE AFFECTING THE WHOLE ORGANIZATION IMPORTANT STAKEHOLDERS Guardrails CISO / Privacy Finance & Control Act as the second line of defense, defining the controls Enterprise Architects Responsible for implementation and compliancy of controls Value Stream/ Application Owner Application owner, responsible for onboarding of applications and complying with control guidelines Responsible Supervisor/Manager Employee Manager of the employee, responsible for the validation of access and role/policy administration User of the systems Defining technical & architectural guardrails Platform Ownership Management of Identities IAM Platform HR Owner of the IAM capability, platform(s) and processes. Including strategy, vision and management B2B/Partner registration Owner of the organizational and employee data Owner of the B2B/partner registration process 28
Slide 29
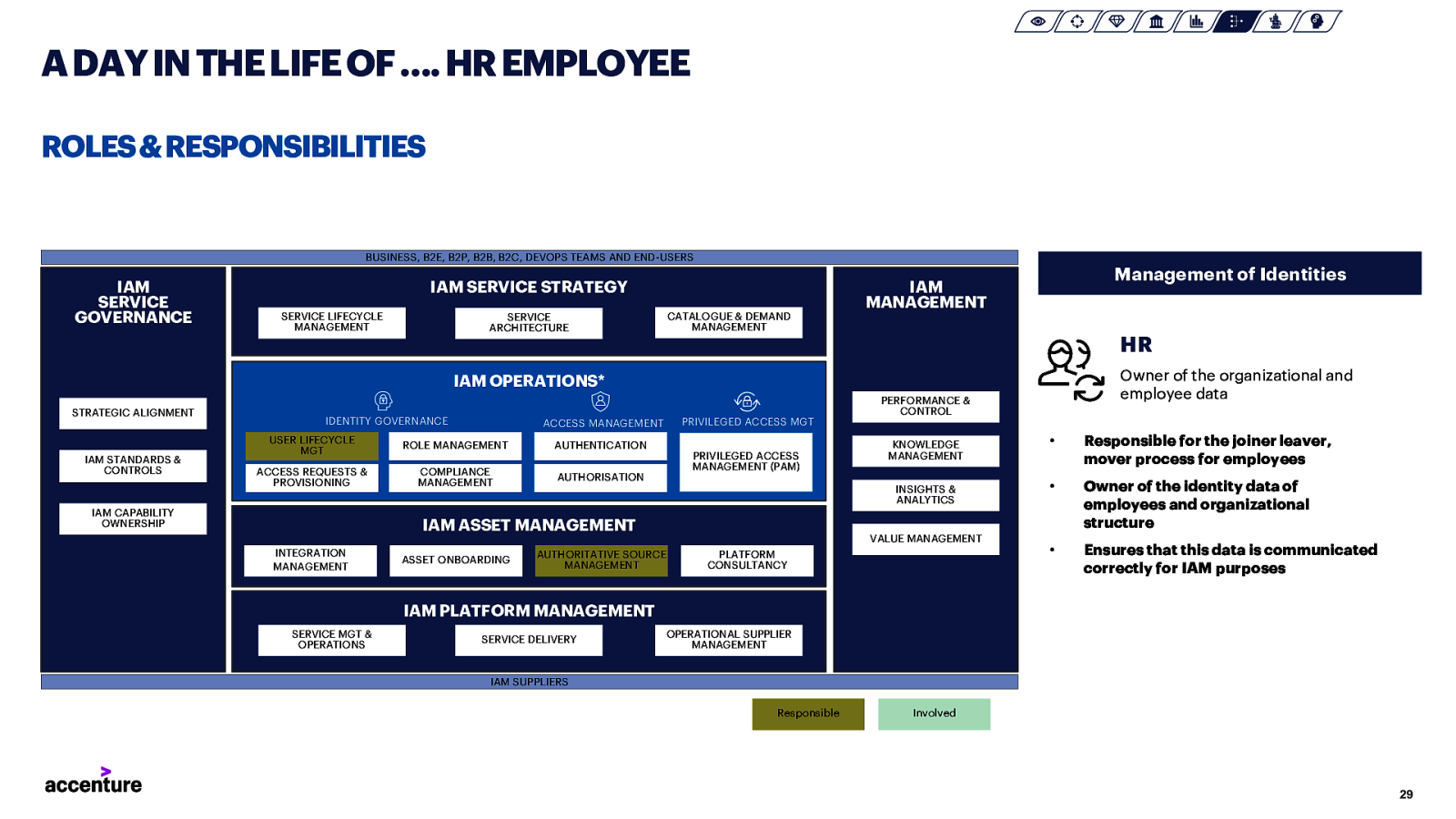
A DAY IN THE LIFE OF …. HR EMPLOYEE ROLES & RESPONSIBILITIES BUSINESS, B2E, B2P, B2B, B2C, DEVOPS TEAMS AND END-USERS IAM SERVICE GOVERNANCE IAM SERVICE STRATEGY SERVICE LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT Management of Identities IAM MANAGEMENT CATALOGUE & DEMAND MANAGEMENT SERVICE ARCHITECTURE HR Owner of the organizational and employee data IAM OPERATIONS* STRATEGIC ALIGNMENT IAM STANDARDS & CONTROLS IDENTITY GOVERNANCE ROLE MANAGEMENT ACCESS REQUESTS & PROVISIONING COMPLIANCE MANAGEMENT IAM CAPABILITY OWNERSHIP PRIVILEGED ACCESS MGT ACCESS MANAGEMENT USER LIFECYCLE MGT AUTHENTICATION PRIVILEGED ACCESS MANAGEMENT (PAM) AUTHORISATION ASSET ONBOARDING KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT INSIGHTS & ANALYTICS IAM ASSET MANAGEMENT INTEGRATION MANAGEMENT PERFORMANCE & CONTROL VALUE MANAGEMENT AUTHORITATIVE SOURCE MANAGEMENT PLATFORM CONSULTANCY • Responsible for the joiner leaver, mover process for employees • Owner of the identity data of employees and organizational structure • Ensures that this data is communicated correctly for IAM purposes IAM PLATFORM MANAGEMENT SERVICE MGT & OPERATIONS SERVICE DELIVERY OPERATIONAL SUPPLIER MANAGEMENT IAM SUPPLIERS Responsible Involved 29
Slide 30
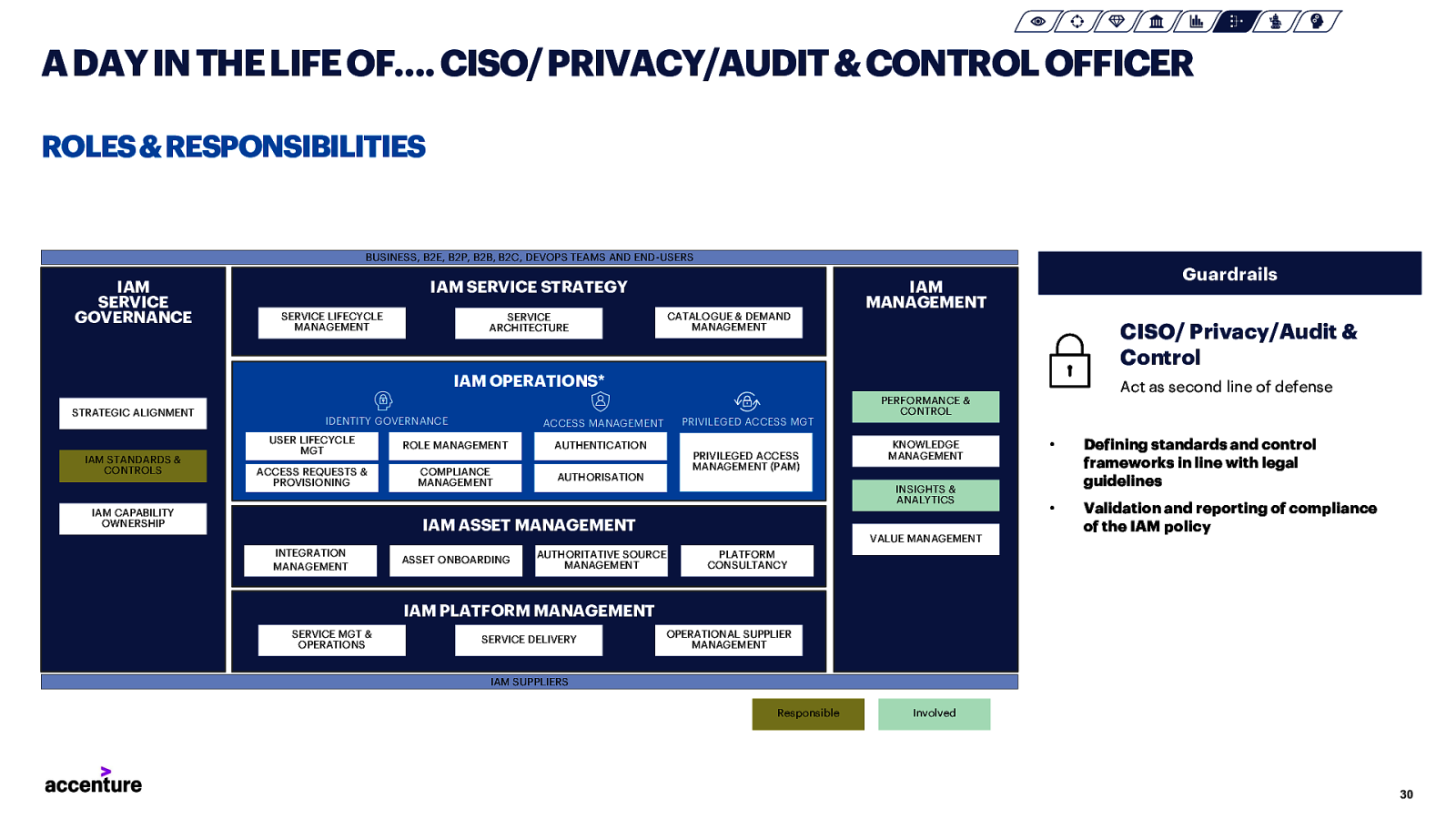
A DAY IN THE LIFE OF…. CISO/ PRIVACY/AUDIT & CONTROL OFFICER ROLES & RESPONSIBILITIES BUSINESS, B2E, B2P, B2B, B2C, DEVOPS TEAMS AND END-USERS IAM SERVICE GOVERNANCE IAM SERVICE STRATEGY SERVICE LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT Guardrails IAM MANAGEMENT CATALOGUE & DEMAND MANAGEMENT SERVICE ARCHITECTURE CISO/ Privacy/Audit & Control IAM OPERATIONS* STRATEGIC ALIGNMENT IAM STANDARDS & CONTROLS IDENTITY GOVERNANCE PRIVILEGED ACCESS MGT ACCESS MANAGEMENT USER LIFECYCLE MGT ROLE MANAGEMENT ACCESS REQUESTS & PROVISIONING COMPLIANCE MANAGEMENT IAM CAPABILITY OWNERSHIP Act as second line of defense AUTHENTICATION PRIVILEGED ACCESS MANAGEMENT (PAM) AUTHORISATION ASSET ONBOARDING KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT INSIGHTS & ANALYTICS IAM ASSET MANAGEMENT INTEGRATION MANAGEMENT PERFORMANCE & CONTROL VALUE MANAGEMENT AUTHORITATIVE SOURCE MANAGEMENT • Defining standards and control frameworks in line with legal guidelines • Validation and reporting of compliance of the IAM policy PLATFORM CONSULTANCY IAM PLATFORM MANAGEMENT SERVICE MGT & OPERATIONS SERVICE DELIVERY OPERATIONAL SUPPLIER MANAGEMENT IAM SUPPLIERS Responsible Involved 30
Slide 31
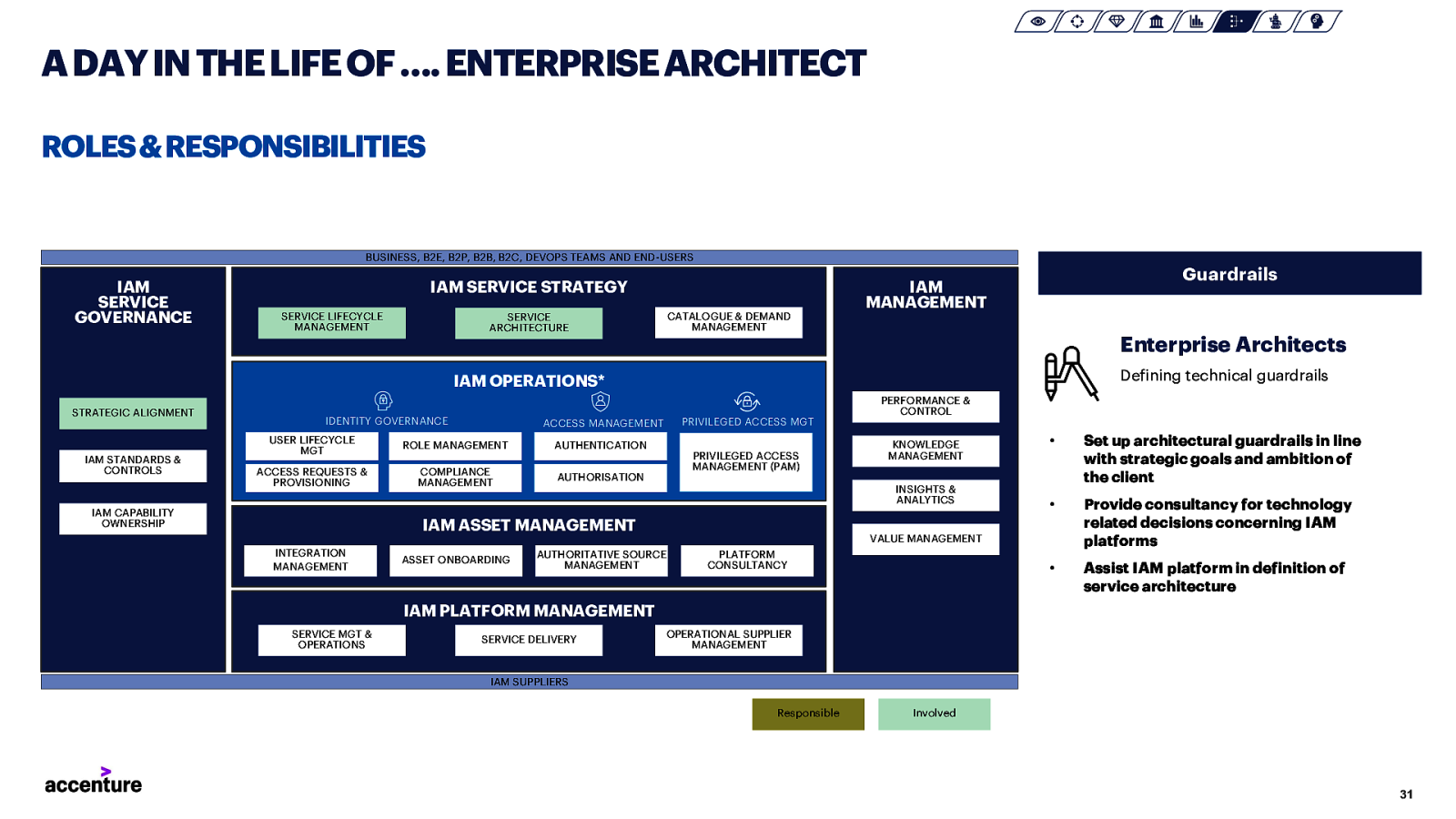
A DAY IN THE LIFE OF …. ENTERPRISE ARCHITECT ROLES & RESPONSIBILITIES BUSINESS, B2E, B2P, B2B, B2C, DEVOPS TEAMS AND END-USERS IAM SERVICE GOVERNANCE IAM SERVICE STRATEGY SERVICE LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT Guardrails IAM MANAGEMENT CATALOGUE & DEMAND MANAGEMENT SERVICE ARCHITECTURE Enterprise Architects Defining technical guardrails IAM OPERATIONS* STRATEGIC ALIGNMENT IAM STANDARDS & CONTROLS IDENTITY GOVERNANCE ROLE MANAGEMENT ACCESS REQUESTS & PROVISIONING COMPLIANCE MANAGEMENT IAM CAPABILITY OWNERSHIP PRIVILEGED ACCESS MGT ACCESS MANAGEMENT USER LIFECYCLE MGT AUTHENTICATION PRIVILEGED ACCESS MANAGEMENT (PAM) AUTHORISATION ASSET ONBOARDING KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT INSIGHTS & ANALYTICS IAM ASSET MANAGEMENT INTEGRATION MANAGEMENT PERFORMANCE & CONTROL • Set up architectural guardrails in line with strategic goals and ambition of the client • Provide consultancy for technology related decisions concerning IAM platforms • Assist IAM platform in definition of service architecture VALUE MANAGEMENT AUTHORITATIVE SOURCE MANAGEMENT PLATFORM CONSULTANCY IAM PLATFORM MANAGEMENT SERVICE MGT & OPERATIONS SERVICE DELIVERY OPERATIONAL SUPPLIER MANAGEMENT IAM SUPPLIERS Responsible Involved 31
Slide 32
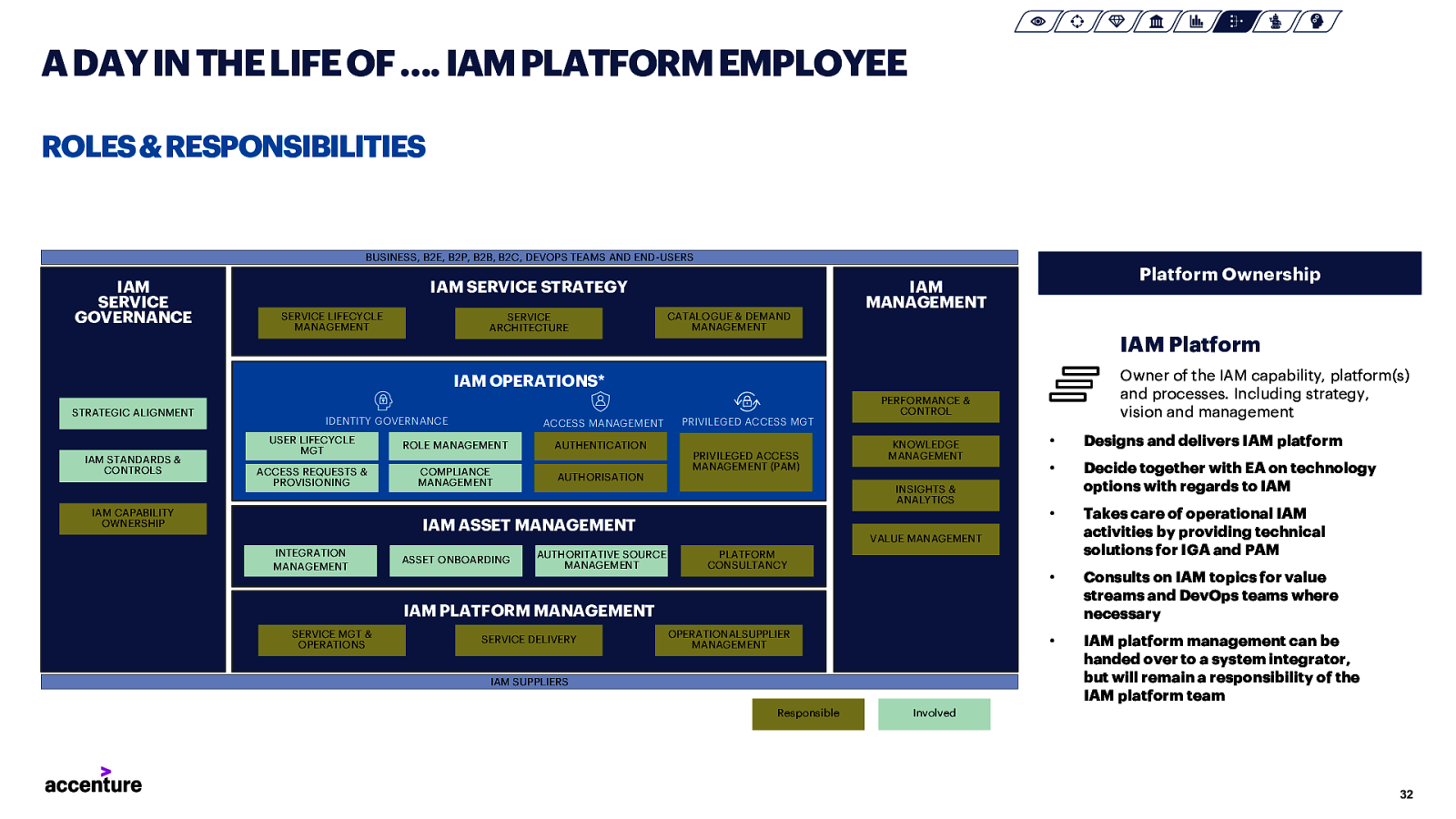
A DAY IN THE LIFE OF …. IAM PLATFORM EMPLOYEE ROLES & RESPONSIBILITIES BUSINESS, B2E, B2P, B2B, B2C, DEVOPS TEAMS AND END-USERS IAM SERVICE GOVERNANCE IAM SERVICE STRATEGY SERVICE LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SERVICE ARCHITECTURE Platform Ownership IAM MANAGEMENT CATALOGUE & DEMAND MANAGEMENT IAM Platform Owner of the IAM capability, platform(s) and processes. Including strategy, vision and management IAM OPERATIONS* STRATEGIC ALIGNMENT IAM STANDARDS & CONTROLS IDENTITY GOVERNANCE ACCESS MANAGEMENT USER LIFECYCLE MGT ROLE MANAGEMENT ACCESS REQUESTS & PROVISIONING COMPLIANCE MANAGEMENT IAM CAPABILITY OWNERSHIP PRIVILEGED ACCESS MGT AUTHENTICATION AUTHORISATION PRIVILEGED ACCESS MANAGEMENT (PAM) ASSET ONBOARDING KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT INSIGHTS & ANALYTICS IAM ASSET MANAGEMENT INTEGRATION MANAGEMENT PERFORMANCE & CONTROL AUTHORITATIVE SOURCE MANAGEMENT • Designs and delivers IAM platform • Decide together with EA on technology options with regards to IAM • Takes care of operational IAM activities by providing technical solutions for IGA and PAM • Consults on IAM topics for value streams and DevOps teams where necessary • IAM platform management can be handed over to a system integrator, but will remain a responsibility of the IAM platform team VALUE MANAGEMENT PLATFORM CONSULTANCY IAM PLATFORM MANAGEMENT SERVICE MGT & OPERATIONS SERVICE DELIVERY OPERATIONALSUPPLIER MANAGEMENT IAM SUPPLIERS Responsible Involved 32
Slide 33
A DAY IN THE LIFE OF …. B2B/PARTNER REGISTRATION EMPLOYEE ROLES & RESPONSIBILITIES BUSINESS, B2E, B2P, B2B, B2C, DEVOPS TEAMS AND END-USERS IAM SERVICE GOVERNANCE IAM SERVICE STRATEGY SERVICE LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT Management of Identities IAM MANAGEMENT CATALOGUE & DEMAND MANAGEMENT SERVICE ARCHITECTURE B2B/Partner registration Owner of the B2B/partner registration process IAM OPERATIONS* STRATEGIC ALIGNMENT IAM STANDARDS & CONTROLS IDENTITY GOVERNANCE ROLE MANAGEMENT ACCESS REQUESTS & PROVISIONING COMPLIANCE MANAGEMENT IAM CAPABILITY OWNERSHIP PRIVILEGED ACCESS MGT ACCESS MANAGEMENT USER LIFECYCLE MGT AUTHENTICATION PRIVILEGED ACCESS MANAGEMENT (PAM) AUTHORISATION ASSET ONBOARDING KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT Facilitates the on and offboarding process for new B2B/Partner companies, including creation of the super user • Transfers the responsibility of onboarding and registering B2B/partners’ employees to their respective superuser • Responsible for correct usage of B2B/Partner data related to IAM VALUE MANAGEMENT AUTHORITATIVE SOURCE MANAGEMENT PLATFORM CONSULTANCY IAM PLATFORM MANAGEMENT SERVICE MGT & OPERATIONS • INSIGHTS & ANALYTICS IAM ASSET MANAGEMENT INTEGRATION MANAGEMENT PERFORMANCE & CONTROL SERVICE DELIVERY OPERATIONAL SUPPLIER MANAGEMENT IAM SUPPLIERS Responsible Involved 33
Slide 34
A DAY IN THE LIFE OF …. APPLICATION OWNER ROLES & RESPONSIBILITIES BUSINESS, B2E, B2P, B2B, B2C, DEVOPS TEAMS AND END-USERS IAM SERVICE GOVERNANCE IAM SERVICE STRATEGY SERVICE LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT Implementation Controls IAM MANAGEMENT CATALOGUE & DEMAND MANAGEMENT SERVICE ARCHITECTURE Value Stream/ Application Owner IAM OPERATIONS* STRATEGIC ALIGNMENT IAM STANDARDS & CONTROLS IDENTITY GOVERNANCE ROLE MANAGEMENT ACCESS REQUESTS & PROVISIONING COMPLIANCE MANAGEMENT IAM CAPABILITY OWNERSHIP PRIVILEGED ACCESS MGT ACCESS MANAGEMENT USER LIFECYCLE MGT AUTHENTICATION PRIVILEGED ACCESS MANAGEMENT (PAM) AUTHORISATION INTEGRATION MANAGEMENT ASSET ONBOARDING KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT INSIGHTS & ANALYTICS IAM ASSET MANAGEMENT VALUE MANAGEMENT AUTHORITATIVE SOURCE MANAGEMENT PLATFORM CONSULTANCY IAM PLATFORM MANAGEMENT SERVICE MGT & OPERATIONS SERVICE DELIVERY Onboarding of applications and complying with control guidelines PERFORMANCE & CONTROL • Defining and maintaining the roles and policies regarding access to the platform • Defining and maintaining the possible authorisations to the platform • Validation of (additional) access to the platform and take part in the audit cycles (certification) • Responsible for the onboarding and integration of applications with the IAM platform(s) • Request standard building blocks and align with IAM platform team using the service catalogue / portal OPERATIONAL SUPPLIER MANAGEMENT IAM SUPPLIERS Responsible Involved 34
Slide 35
A DAY IN THE LIFE OF …. USER ROLES & RESPONSIBILITIES BUSINESS, B2E, B2P, B2B, B2C, DEVOPS TEAMS AND END-USERS IAM SERVICE GOVERNANCE IAM SERVICE STRATEGY SERVICE LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT Implementation Controls IAM MANAGEMENT CATALOGUE & DEMAND MANAGEMENT SERVICE ARCHITECTURE Employee User of systems IAM OPERATIONS* STRATEGIC ALIGNMENT IAM STANDARDS & CONTROLS IDENTITY GOVERNANCE ROLE MANAGEMENT ACCESS REQUESTS & PROVISIONING COMPLIANCE MANAGEMENT IAM CAPABILITY OWNERSHIP PRIVILEGED ACCESS MGT ACCESS MANAGEMENT USER LIFECYCLE MGT AUTHENTICATION PRIVILEGED ACCESS MANAGEMENT (PAM) AUTHORISATION ASSET ONBOARDING KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT INSIGHTS & ANALYTICS IAM ASSET MANAGEMENT INTEGRATION MANAGEMENT PERFORMANCE & CONTROL • Make use of self service for i.e. requesting access and passwordresets VALUE MANAGEMENT AUTHORITATIVE SOURCE MANAGEMENT PLATFORM CONSULTANCY IAM PLATFORM MANAGEMENT SERVICE MGT & OPERATIONS SERVICE DELIVERY OPERATIONAL SUPPLIER MANAGEMENT IAM SUPPLIERS Responsible Involved 35
Slide 36
A DAY IN THE LIFE OF …. RESPONSIBLE SUPERVISOR/MANAGER ROLES & RESPONSIBILITIES BUSINESS, B2E, B2P, B2B, B2C, DEVOPS TEAMS AND END-USERS IAM SERVICE GOVERNANCE IAM SERVICE STRATEGY SERVICE LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT Implementation Controls IAM MANAGEMENT CATALOGUE & DEMAND MANAGEMENT SERVICE ARCHITECTURE Responsible Supervisor/Manager IAM OPERATIONS* STRATEGIC ALIGNMENT IAM STANDARDS & CONTROLS IDENTITY GOVERNANCE ROLE MANAGEMENT ACCESS REQUESTS & PROVISIONING COMPLIANCE MANAGEMENT IAM CAPABILITY OWNERSHIP PRIVILEGED ACCESS MGT ACCESS MANAGEMENT USER LIFECYCLE MGT AUTHENTICATION PRIVILEGED ACCESS MANAGEMENT (PAM) AUTHORISATION ASSET ONBOARDING KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT • Defining and maintaining the roles and policies, which can be of different levels, depending on the required access of the respective teams • Request access for new employees in his/her team • Validation of (additional) access to the platform and take part in the audit cycles (certification) • Supports in defining the roles and policies INSIGHTS & ANALYTICS IAM ASSET MANAGEMENT INTEGRATION MANAGEMENT Manager of the employee PERFORMANCE & CONTROL VALUE MANAGEMENT AUTHORITATIVE SOURCE MANAGEMENT PLATFORM CONSULTANCY IAM PLATFORM MANAGEMENT SERVICE MGT & OPERATIONS SERVICE DELIVERY OPERATIONAL SUPPLIER MANAGEMENT IAM SUPPLIERS Responsible Involved 36
Slide 37
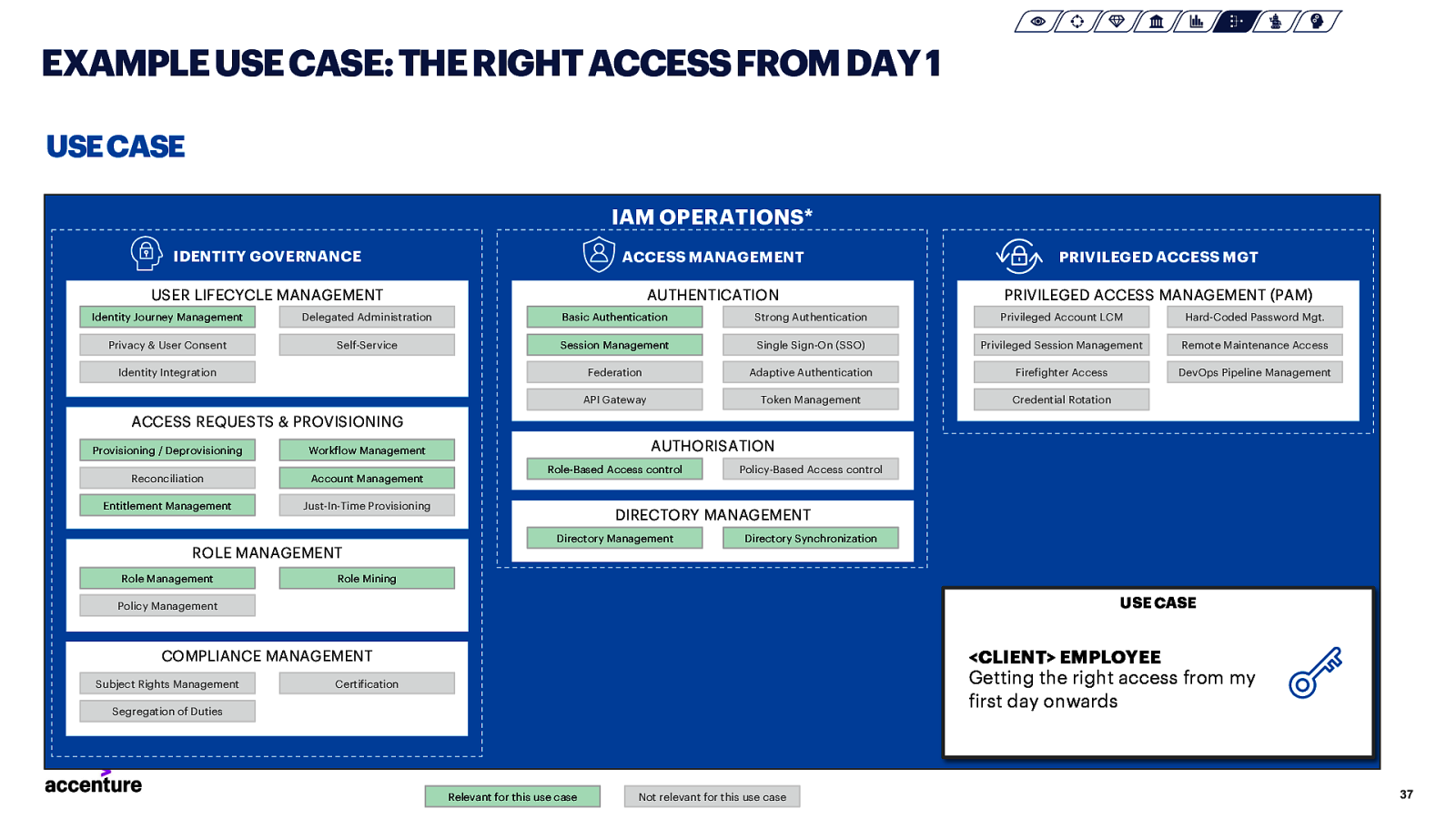
EXAMPLE USE CASE: THE RIGHT ACCESS FROM DAY 1 USE CASE IAM OPERATIONS* IDENTITY GOVERNANCE ACCESS MANAGEMENT USER LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT AUTHENTICATION PRIVILEGED ACCESS MGT PRIVILEGED ACCESS MANAGEMENT (PAM) Identity Journey Management Delegated Administration Basic Authentication Strong Authentication Privileged Account LCM Hard-Coded Password Mgt. Privacy & User Consent Self-Service Session Management Single Sign-On (SSO) Privileged Session Management Remote Maintenance Access Federation Adaptive Authentication Firefighter Access DevOps Pipeline Management API Gateway Token Management Credential Rotation Identity Integration ACCESS REQUESTS & PROVISIONING Provisioning / Deprovisioning AUTHORISATION Workflow Management Reconciliation Account Management Entitlement Management Just-In-Time Provisioning Role-Based Access control Policy-Based Access control DIRECTORY MANAGEMENT Directory Management Directory Synchronization ROLE MANAGEMENT Role Management Role Mining USE CASE Policy Management <CLIENT> EMPLOYEE Getting the right access from my first day onwards COMPLIANCE MANAGEMENT Subject Rights Management Certification Segregation of Duties Relevant for this use case Not relevant for this use case 37
Slide 38

CONTENTS IAM CAPABILITY MODEL Business Strategy & Vision Contents IAM Operating Model
- IAM Vison 3. Value drivers 4. IAM Capability Areas IAM Vision INTENT
- Operating Model Principles Operating Model Principles Value Drivers IAM Capability Areas
- Metrics 7. Technology & Vendors 8. People (Roles and sourcing) BLUEPRINT
- Governance & Processes Governance Processes & Metrics Technology People IAM Execution 38
Slide 39
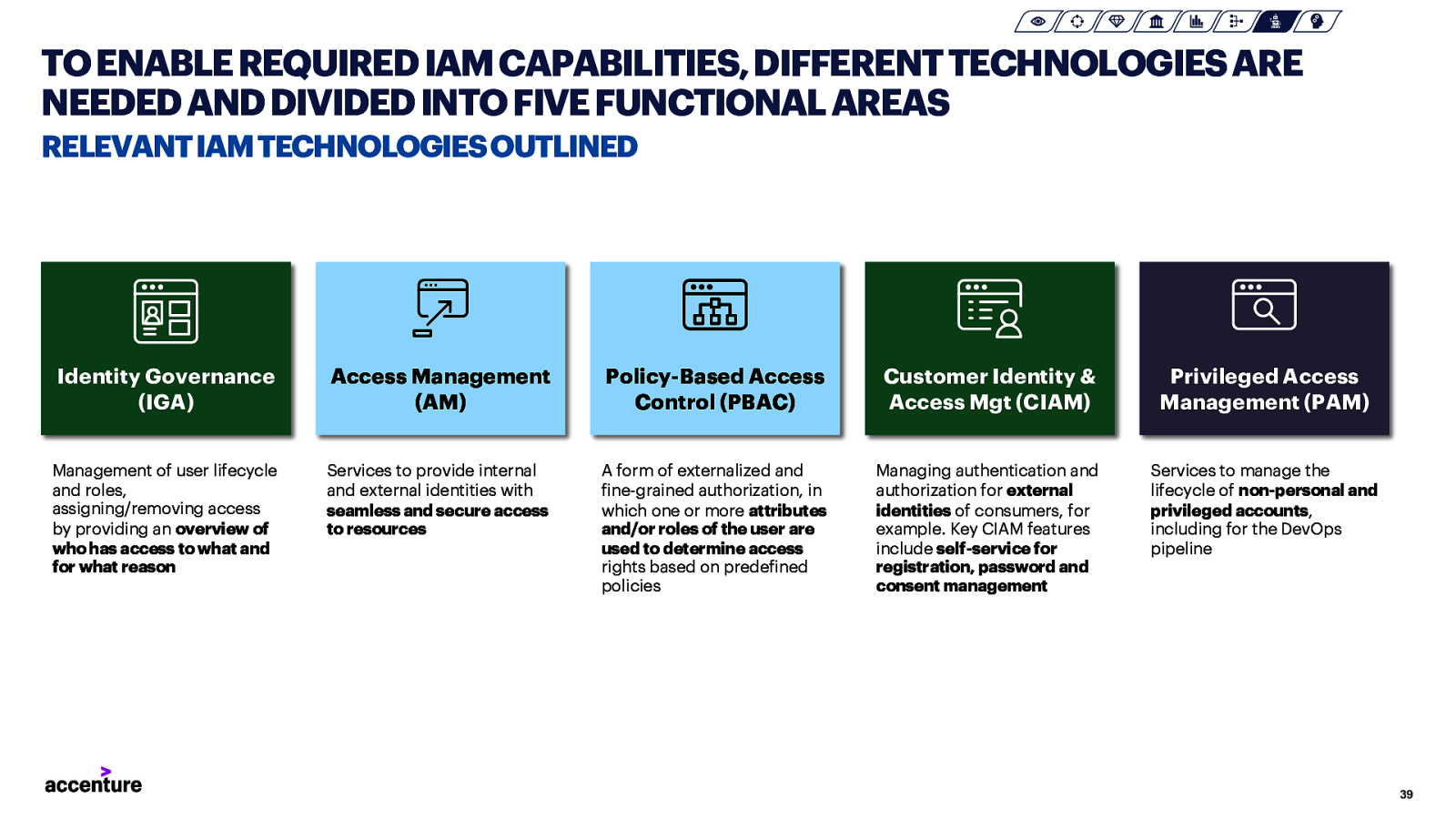
TO ENABLE REQUIRED IAM CAPABILITIES, DIFFERENT TECHNOLOGIES ARE NEEDED AND DIVIDED INTO FIVE FUNCTIONAL AREAS RELEVANT IAM TECHNOLOGIES OUTLINED Identity Governance (IGA) Access Management (AM) Policy-Based Access Control (PBAC) Customer Identity & Access Mgt (CIAM) Privileged Access Management (PAM) Management of user lifecycle and roles, assigning/removing access by providing an overview of who has access to what and for what reason Services to provide internal and external identities with seamless and secure access to resources A form of externalized and fine-grained authorization, in which one or more attributes and/or roles of the user are used to determine access rights based on predefined policies Managing authentication and authorization for external identities of consumers, for example. Key CIAM features include self-service for registration, password and consent management Services to manage the lifecycle of non-personal and privileged accounts, including for the DevOps pipeline 39
Slide 40
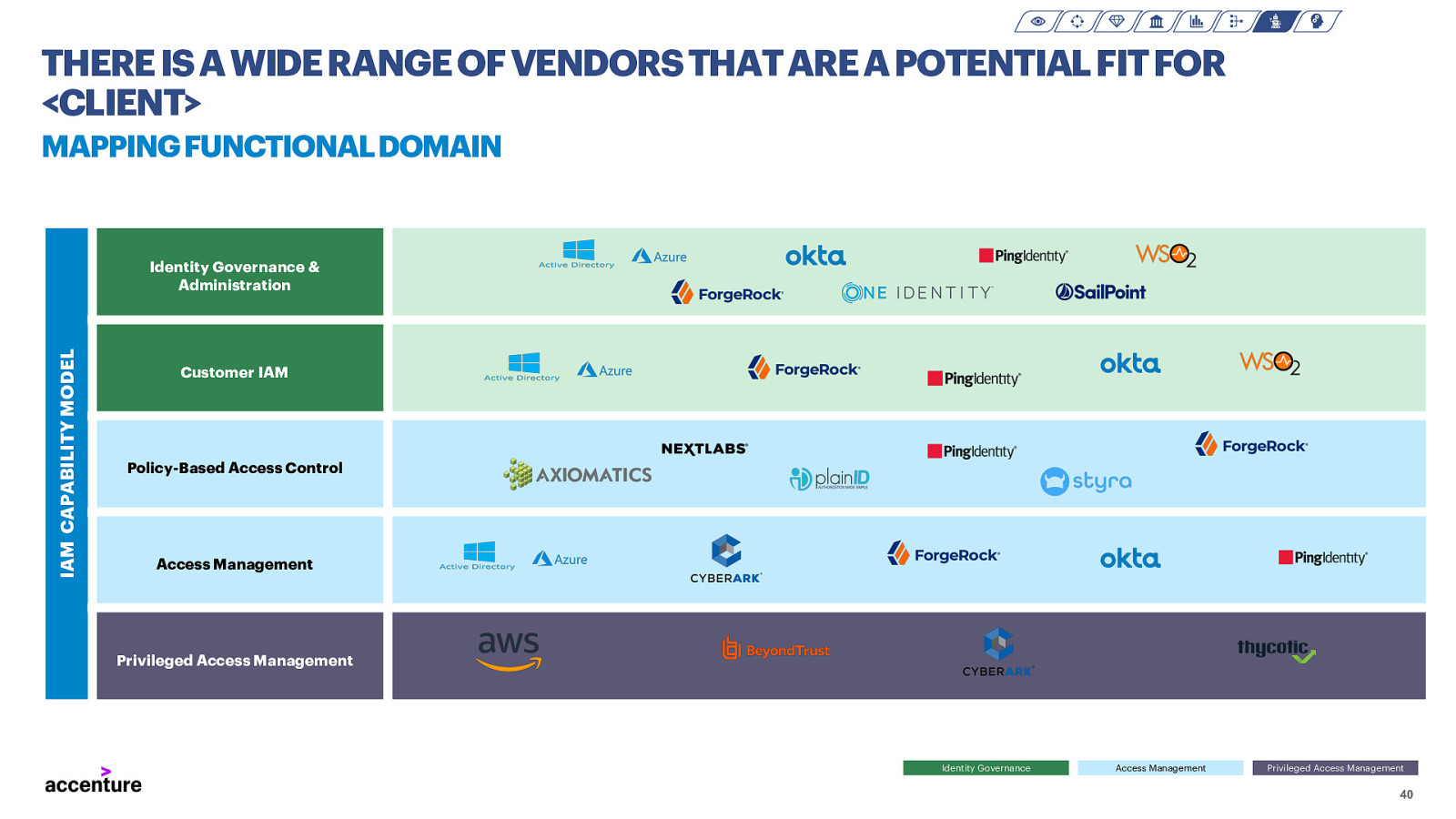
THERE IS A WIDE RANGE OF VENDORS THAT ARE A POTENTIAL FIT FOR <CLIENT> MAPPING FUNCTIONAL DOMAIN IAM CAPABILITY MODEL Identity Governance & Administration Customer IAM Policy-Based Access Control Access Management Privileged Access Management Identity Governance Access Management Privileged Access Management 40
Slide 41
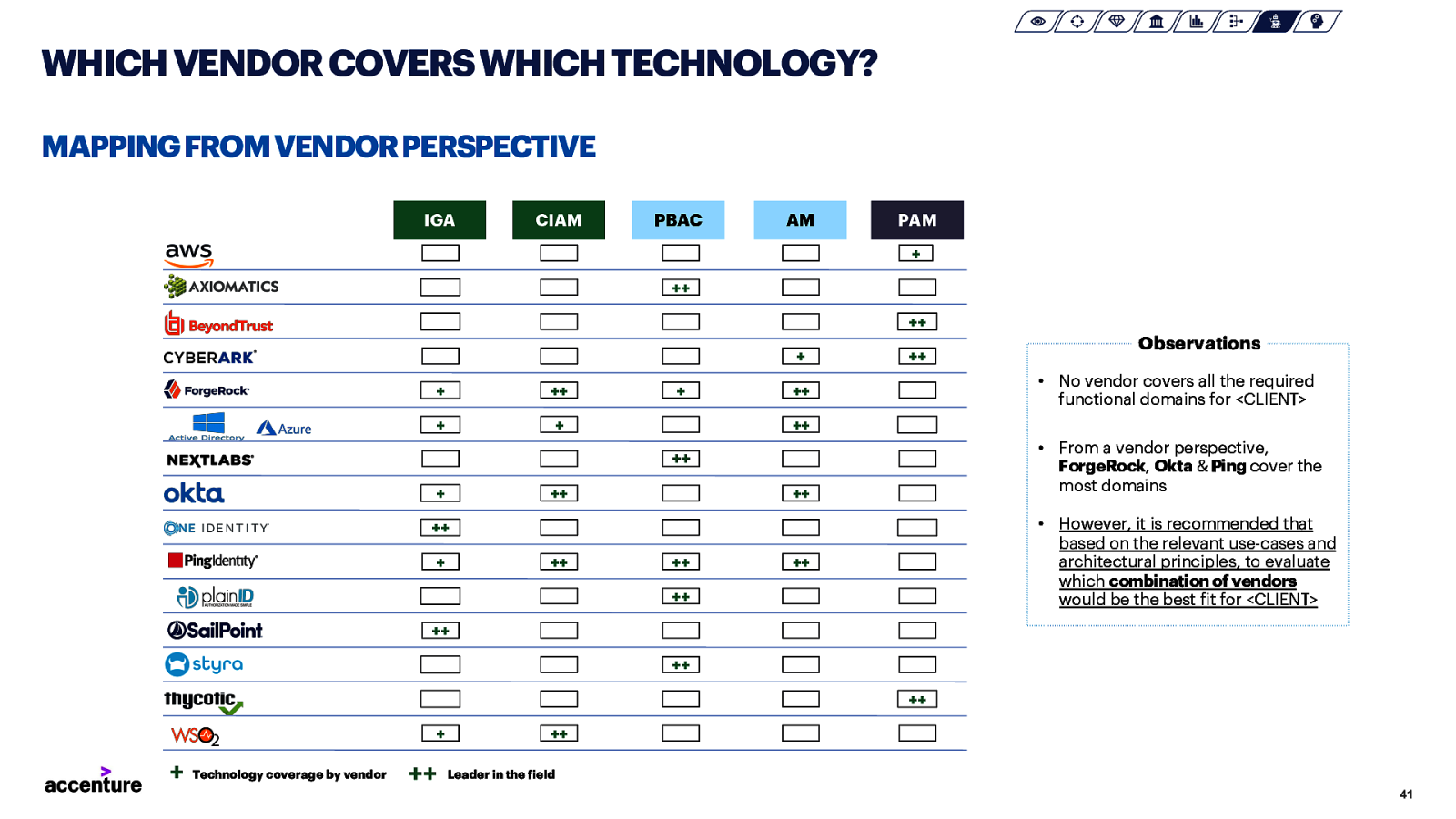
WHICH VENDOR COVERS WHICH TECHNOLOGY? MAPPING FROM VENDOR PERSPECTIVE IGA CIAM PBAC AM PAM + ++ ++ + + ++ + + + ++ • No vendor covers all the required functional domains for <CLIENT> ++ ++ • From a vendor perspective, ForgeRock, Okta & Ping cover the most domains ++ + ++ ++ • However, it is recommended that based on the relevant use-cases and architectural principles, to evaluate which combination of vendors would be the best fit for <CLIENT> ++ + ++ Observations ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ + + Technology coverage by vendor ++ ++ Leader in the field 41
Slide 42
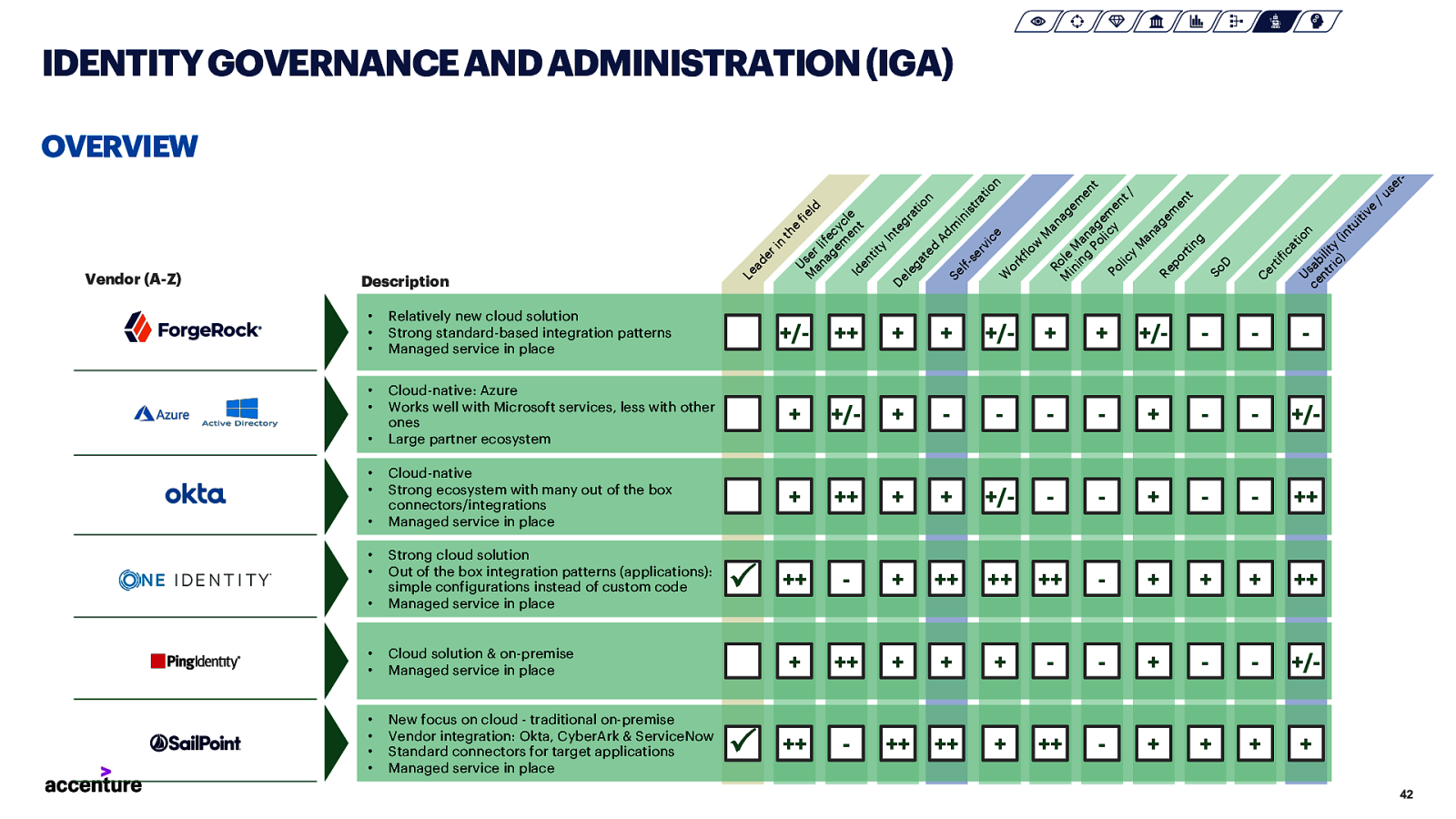
IDENTITY GOVERNANCE AND ADMINISTRATION (IGA) C er tif ic at io Us n ce ab nt ili ric ty ) (in tu iti ve ++ + + +/- + + +/-
Cloud-native: Azure Works well with Microsoft services, less with other ones Large partner ecosystem + +/- +
+/- Cloud-native Strong ecosystem with many out of the box connectors/integrations Managed service in place + ++ + + +/-
++ ++
++ ++ ++
++ + ++ + + +
+/- ++
++ ++ + ++
• • • Relatively new cloud solution Strong standard-based integration patterns Managed service in place • • • • • • • • • Strong cloud solution Out of the box integration patterns (applications): simple configurations instead of custom code Managed service in place • • Cloud solution & on-premise Managed service in place • • • • New focus on cloud - traditional on-premise Vendor integration: Okta, CyberArk & ServiceNow Standard connectors for target applications Managed service in place P P /u th e Us fie M er ld an li ag fe c em yc en le Id t en tit y In te De gr le at ga io te n d Ad m Se in lfis se tr at rv io ic n e W or kf lo w M an R ag M ole in M em in a en g na Po g t e lic m Po y en lic t/ y M an ag Re em po en rt t in g So D +/- Description Le ad er in Vendor (A-Z) se r- OVERVIEW 42
Slide 43
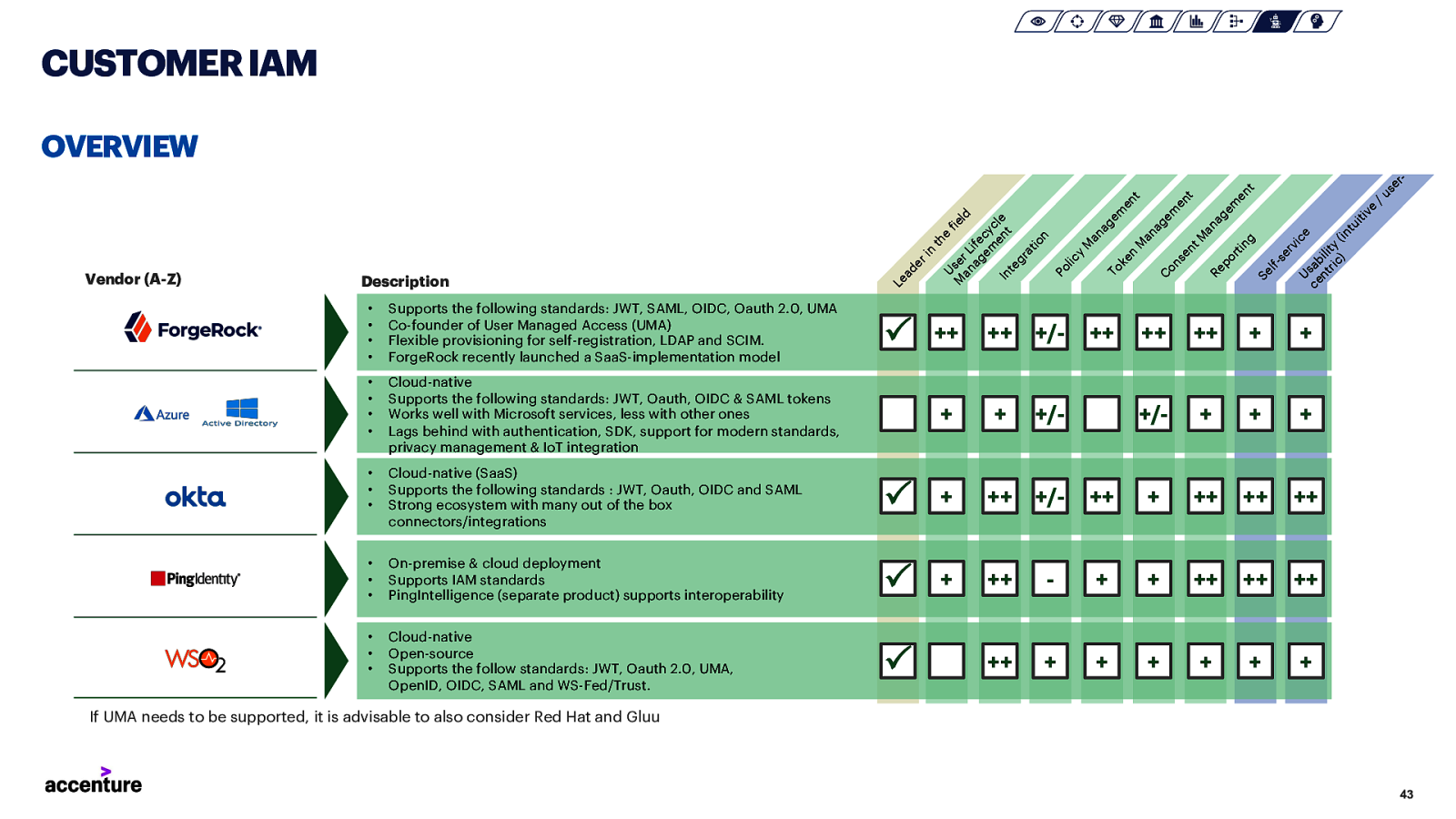
CUSTOMER IAM Description • • • • Supports the following standards: JWT, SAML, OIDC, Oauth 2.0, UMA Co-founder of User Managed Access (UMA) Flexible provisioning for self-registration, LDAP and SCIM. ForgeRock recently launched a SaaS-implementation model • • • • Cloud-native Supports the following standards: JWT, Oauth, OIDC & SAML tokens Works well with Microsoft services, less with other ones Lags behind with authentication, SDK, support for modern standards, privacy management & IoT integration • • • Cloud-native (SaaS) Supports the following standards : JWT, Oauth, OIDC and SAML Strong ecosystem with many out of the box connectors/integrations • • • • • • Le ad er in Vendor (A-Z) th e Us fie M er ld an L ag ife em cy en cle In t te gr at io n Po lic y M an ag To em ke en n t M an ag C em on en se t nt M an Re ag po em rt en in g t Se lfse rv ic Us e ce ab nt ili ric ty ) (in tu iti ve /u se r- OVERVIEW P ++ ++ +/- + + +/- P + ++ +/- On-premise & cloud deployment Supports IAM standards PingIntelligence (separate product) supports interoperability P + ++ Cloud-native Open-source Supports the follow standards: JWT, Oauth 2.0, UMA, OpenID, OIDC, SAML and WS-Fed/Trust. P ++ ++ ++ ++ + + +/- + + + ++ + ++ ++ ++
++ ++ ++ + + + + + + If UMA needs to be supported, it is advisable to also consider Red Hat and Gluu 43
Slide 44

ACCESS MANAGEMENT Vendor (A-Z) Description • Recently entered the access management domain with the acquisition of Idaptive, which offers SSO and strong authentication • • • Beginning cloud solution Strong standard-based integration patterns Managed service in place • • • • Le ad er in th e U fie M ser ld an li ag fe c em yc en le Si t ng le Si gn -O Fe n de ra tio n AP IG at ew ay To ke n M an Us ag ce ab em nt ili en ric ty t ) (in tu iti ve /u se r- OVERVIEW +/- + +
P + ++ ++ ++ ++ +/- Cloud-native Works well with Microsoft services, less with other ones Large partner ecosystem Managed service in place P +/- + + + + +/- • • • Cloud-native Strong ecosystem with many out of the box connectors/integrations Managed service in place P + + + ++ + ++ • • Cloud solution and strong on-premise Managed service in place P + + ++ ++ ++ + 44
Slide 45
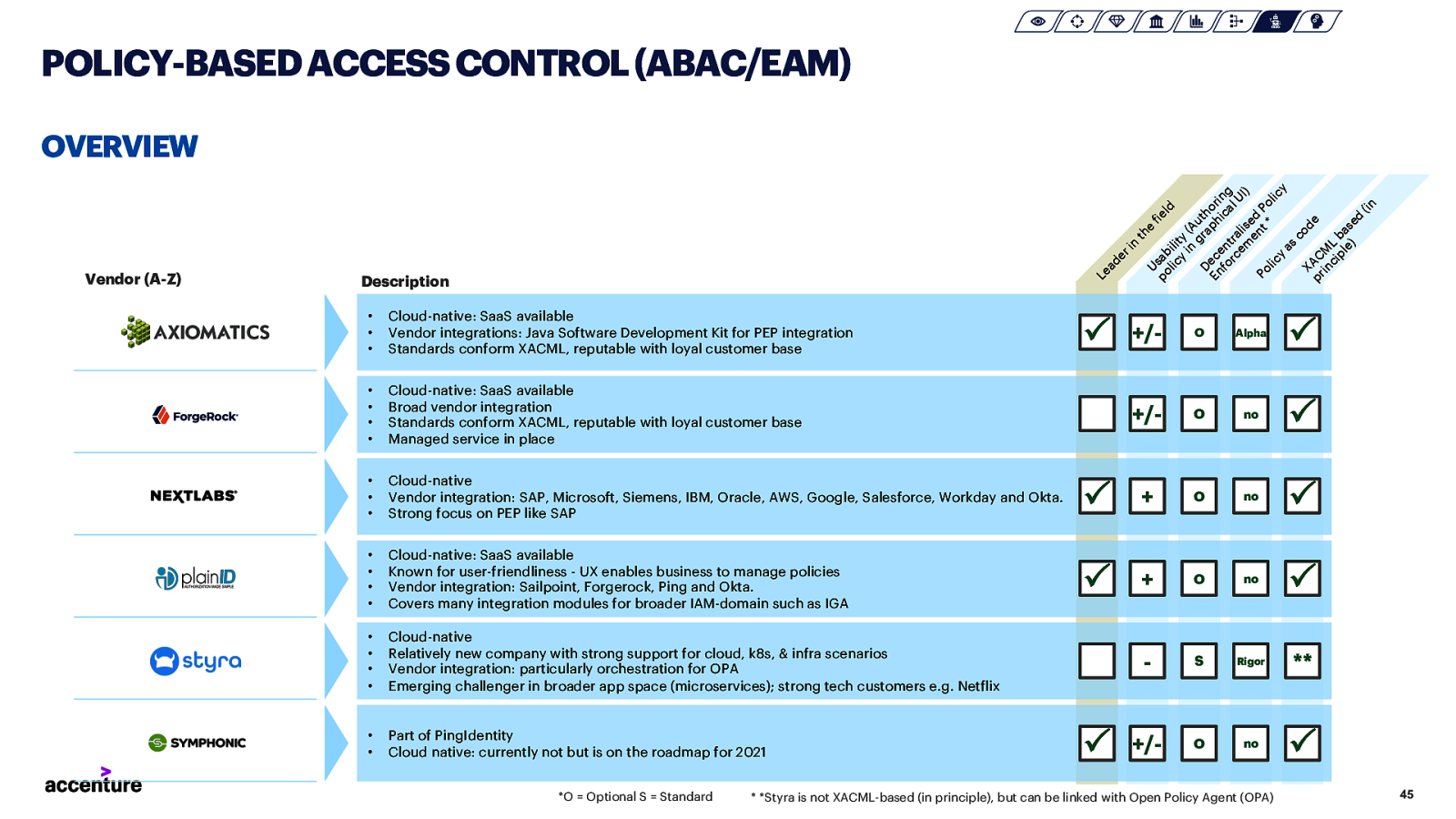
POLICY-BASED ACCESS CONTROL (ABAC/EAM) Vendor (A-Z) Le ad er in th e U fie po sab ld lic ili y ty in (A gr u t De ap ho En c hi rin fo en ca g rc tra lU em lis I) en ed Po t * Po lic lic y y as co X de pr AC in M ci L pl ba e) se d (in OVERVIEW Description • • • Cloud-native: SaaS available Vendor integrations: Java Software Development Kit for PEP integration Standards conform XACML, reputable with loyal customer base • • • • Cloud-native: SaaS available Broad vendor integration Standards conform XACML, reputable with loyal customer base Managed service in place • • • Cloud-native Vendor integration: SAP, Microsoft, Siemens, IBM, Oracle, AWS, Google, Salesforce, Workday and Okta. Strong focus on PEP like SAP • • • • Cloud-native: SaaS available Known for user-friendliness - UX enables business to manage policies Vendor integration: Sailpoint, Forgerock, Ping and Okta. Covers many integration modules for broader IAM-domain such as IGA • • • • Cloud-native Relatively new company with strong support for cloud, k8s, & infra scenarios Vendor integration: particularly orchestration for OPA Emerging challenger in broader app space (microservices); strong tech customers e.g. Netflix • • Part of PingIdentity Cloud native: currently not but is on the roadmap for 2021 *O = Optional S = Standard P +/- O Alpha P +/- O no P P + O no P P + O no P
S Rigor ** +/- O no P P
- *Styra is not XACML-based (in principle), but can be linked with Open Policy Agent (OPA) 45
Slide 46
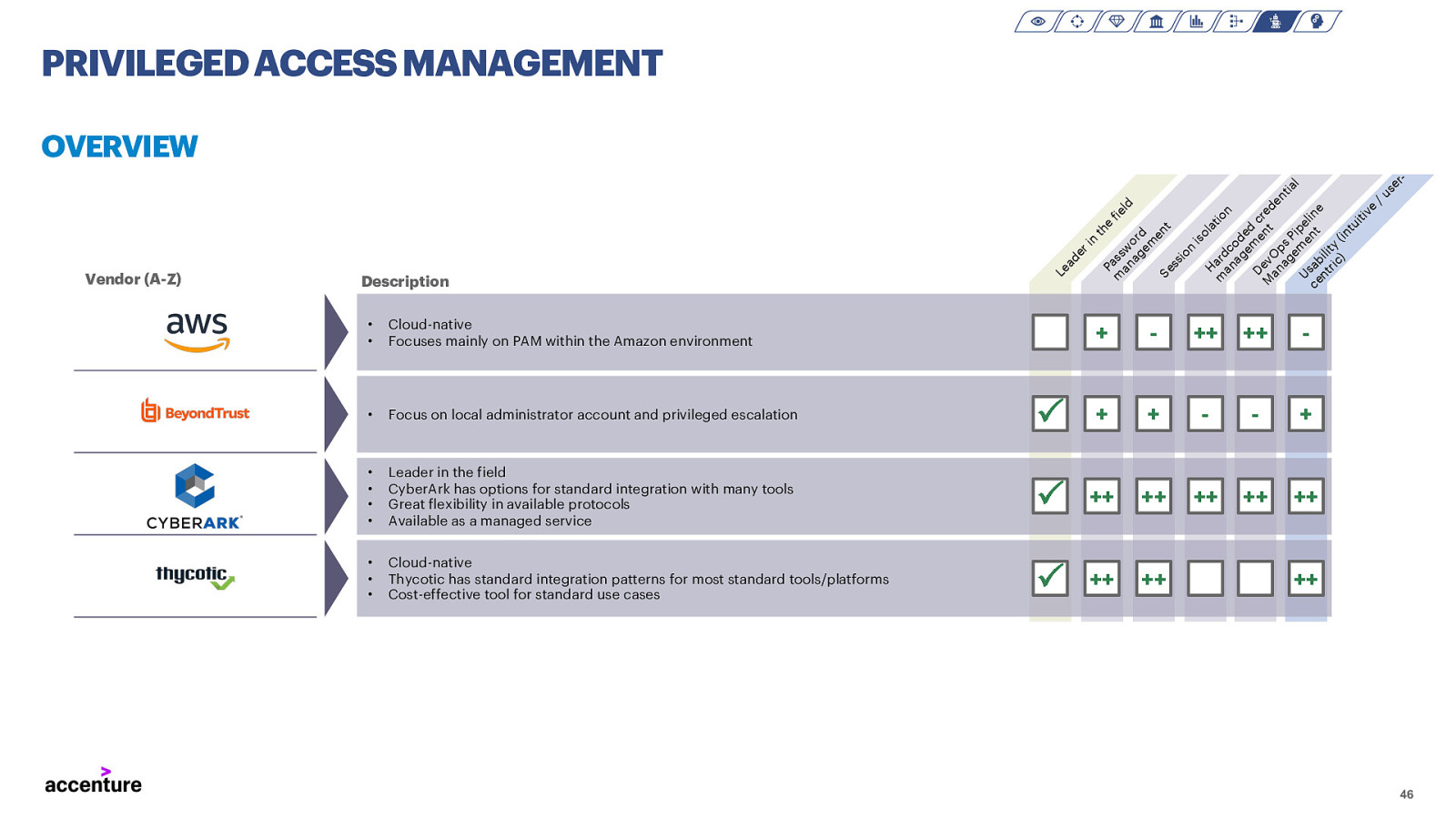
PRIVILEGED ACCESS MANAGEMENT Vendor (A-Z) Description • • Cloud-native Focuses mainly on PAM within the Amazon environment • Focus on local administrator account and privileged escalation • • • • • • • Le ad er in th Pa e fie m ss an w ld o ag rd em en Se t ss io n is ol H at a io m rd n an c ag od em ed D e c M evO nt red an p en ag s tia em Pip l Us en eli ce ab n t e nt ili ric ty ) (in tu iti ve /u se r- OVERVIEW +
++ ++
P + +
Leader in the field CyberArk has options for standard integration with many tools Great flexibility in available protocols Available as a managed service P ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ Cloud-native Thycotic has standard integration patterns for most standard tools/platforms Cost-effective tool for standard use cases P ++ ++ ++ 46
Slide 47
CONTENTS IAM CAPABILITY MODEL Business Strategy & Vision Contents IAM Operating Model
- IAM Vison 3. Value drivers 4. IAM Capability Areas IAM Vision INTENT
- Operating Model Principles Operating Model Principles Value Drivers IAM Capability Areas
- Metrics 7. Technology & Vendors 8. People (Roles and sourcing) BLUEPRINT
- Governance & Processes Governance Processes & Metrics Technology People IAM Execution 47
Slide 48
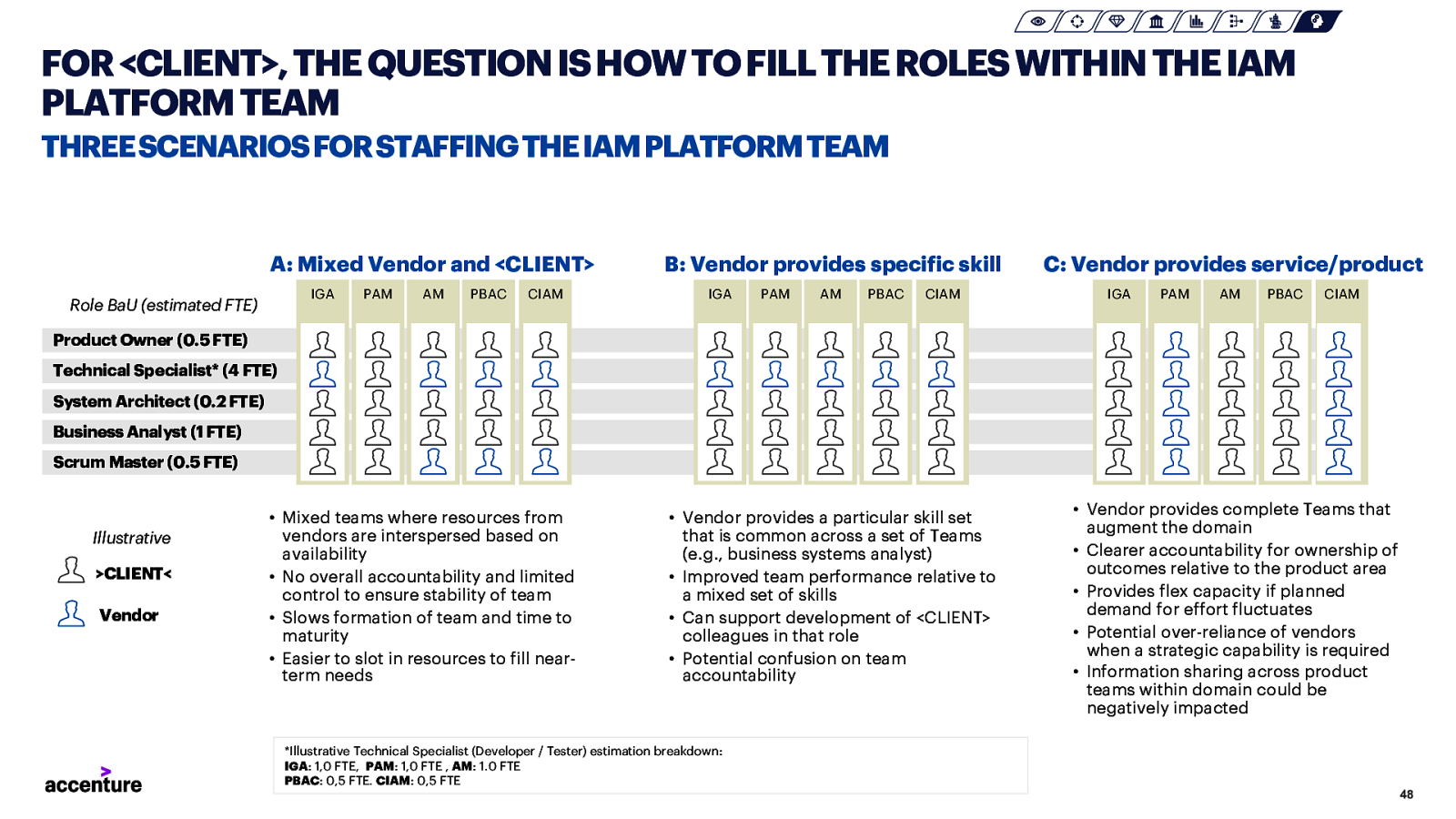
FOR <CLIENT>, THE QUESTION IS HOW TO FILL THE ROLES WITHIN THE IAM PLATFORM TEAM THREE SCENARIOS FOR STAFFING THE IAM PLATFORM TEAM A: Mixed Vendor and <CLIENT> IGA Role BaU (estimated FTE) PAM AM PBAC CIAM B: Vendor provides specific skill IGA PAM AM PBAC CIAM C: Vendor provides service/product IGA PAM AM PBAC CIAM Product Owner (0.5 FTE) Technical Specialist* (4 FTE) System Architect (0.2 FTE) Business Analyst (1 FTE) Scrum Master (0.5 FTE) Illustrative >CLIENT< Vendor • Mixed teams where resources from vendors are interspersed based on availability • No overall accountability and limited control to ensure stability of team • Slows formation of team and time to maturity • Easier to slot in resources to fill nearterm needs • Vendor provides a particular skill set that is common across a set of Teams (e.g., business systems analyst) • Improved team performance relative to a mixed set of skills • Can support development of <CLIENT> colleagues in that role • Potential confusion on team accountability *Illustrative Technical Specialist (Developer / Tester) estimation breakdown: IGA: 1,0 FTE, PAM: 1,0 FTE , AM: 1.0 FTE PBAC: 0,5 FTE. CIAM: 0,5 FTE • Vendor provides complete Teams that augment the domain • Clearer accountability for ownership of outcomes relative to the product area • Provides flex capacity if planned demand for effort fluctuates • Potential over-reliance of vendors when a strategic capability is required • Information sharing across product teams within domain could be negatively impacted 48
Slide 49

APPENDIX 49
Slide 50
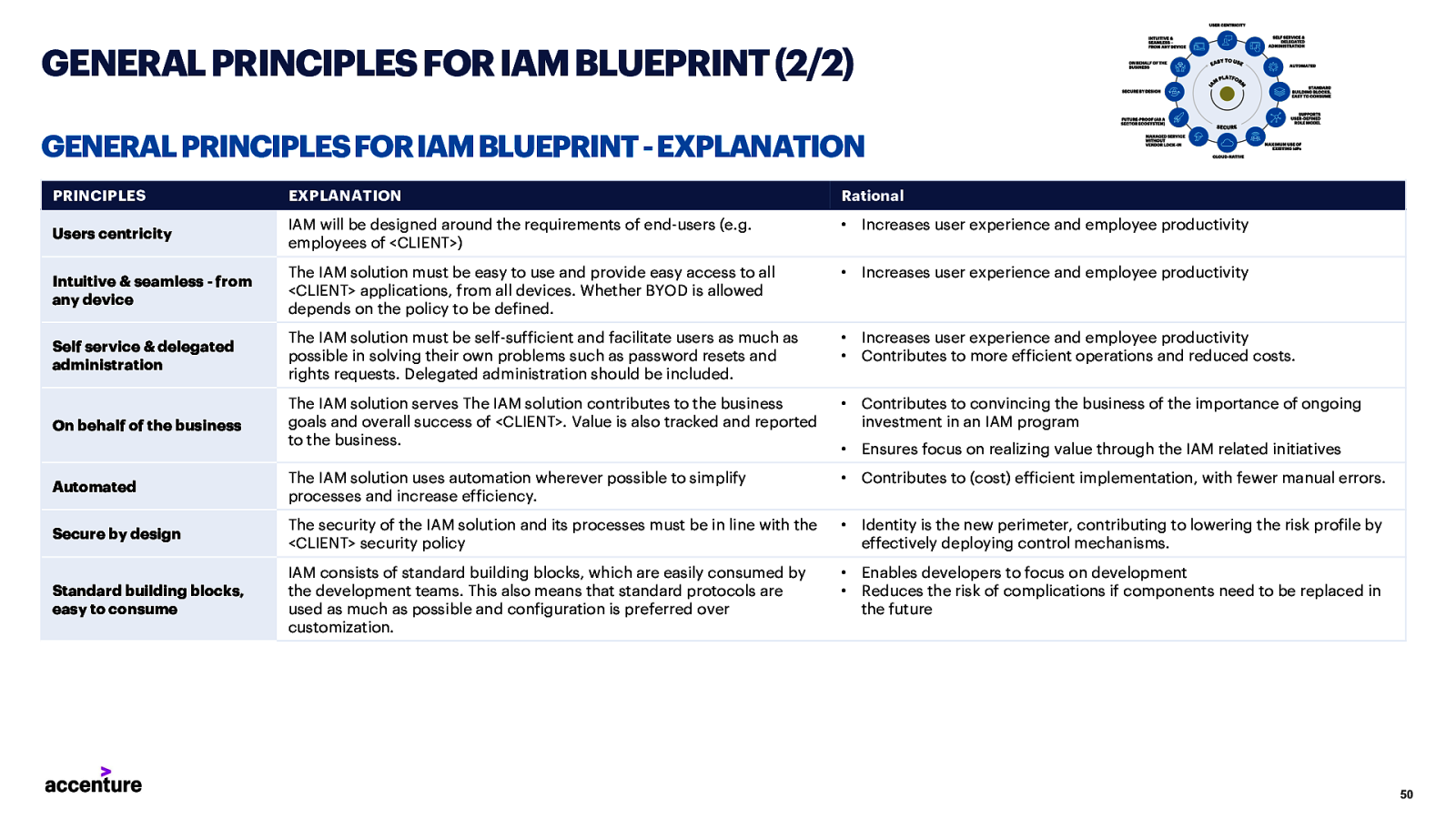
GENERAL PRINCIPLES FOR IAMBLUEPRINT (2/2) GENERAL PRINCIPLES FOR IAMBLUEPRINT -EXPLANATION PRINCIPLES EXPLANATION Rational Users centricity IAM will be designed around the requirements of end-users (e.g. employees of <CLIENT>) • Increases user experience and employee productivity Intuitive & seamless - from any device The IAM solution must be easy to use and provide easy access to all <CLIENT> applications, from all devices. Whether BYOD is allowed depends on the policy to be defined. • Increases user experience and employee productivity Self service & delegated administration The IAM solution must be self-sufficient and facilitate users as much as possible in solving their own problems such as password resets and rights requests. Delegated administration should be included. • • Increases user experience and employee productivity Contributes to more efficient operations and reduced costs. • On behalf of the business The IAM solution serves The IAM solution contributes to the business goals and overall success of <CLIENT>. Value is also tracked and reported to the business. Contributes to convincing the business of the importance of ongoing investment in an IAM program • Ensures focus on realizing value through the IAM related initiatives Automated The IAM solution uses automation wherever possible to simplify processes and increase efficiency. • Contributes to (cost) efficient implementation, with fewer manual errors. Secure by design The security of the IAM solution and its processes must be in line with the <CLIENT> security policy • Identity is the new perimeter, contributing to lowering the risk profile by effectively deploying control mechanisms. Standard building blocks, easy to consume IAM consists of standard building blocks, which are easily consumed by the development teams. This also means that standard protocols are used as much as possible and configuration is preferred over customization. • • Enables developers to focus on development Reduces the risk of complications if components need to be replaced in the future 50
Slide 51

GENERAL PRINCIPLES FOR IAMBLUEPRINT (2/2) DETAILEDEXPLANATION PRINCIPLES EXPLANATION Rational • Facilitates central role within the digitization of the energy sector and ensures sustainable development of IAM platforms. Future-proof as an ecosystem The IAM platform will be developed to support a future ecosystem within the sector. This means that current and future innovations in the market (of both identities, IAM, Applications and underlying infrastructure) will be used as much as possible and that this will also be secured in the development of the roadmap. Supports user-defined role model IAM must be able to identify both the identity of the acting entity (organization, person, system) and the capacity in which it is acting, taking into account that a user may be acting in another capacity at another point in time. • • Contributes to compliance. There may be requirements (e.g. license or accreditation) for assuming capacities. Managed Service without vendor lock-in Where possible, services surrounding IAM are arranged as a managed service. A vendor-agnostic design ensures that in the future certain components can be (relatively) easily disconnected. • • Contributes to more efficient operations. Ensures that <CLIENT> can focus on its core business, as devising and implementing solutions itself requires a lot of <CLIENT> capacity. Making maximum use of existing IdPs IAM should support integration with IdPs that are, or appear to be, market standards in order to facilitate its end users as much as possible. • • Contributes to cost-efficiency and digital enablement Should prevent additional work of self-maintenance and/or development. The IAM solution must enable cloud services (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, BPaaS) and be cloud-based itself. • Contributes to cost elasticity and scalability - ability to scale up or down cloud services depending on demand Contributes to agility - ability to quickly and safely integrate (new) cloud services. Cloud – Native • 51