Red Hat Update for System z Shawn Wells EMail: swells@redhat.com Phone: (+1) 443 534 0130 Lead, Linux on System z
Slide 1

Slide 2

Agenda Red Hat Intro & Company Overview Red Hat Technology Update Enterprise Linux Update Long Range Virtualization Plan Security/MLS/Common Criteria System z Specifics Hardware Exploitation Roadmap Summary & Close 2
Slide 3

Red Hat, Inc Headquarters: Raleigh, NC Founded 1993 Public 1999 (NYSE: RHT) Operating in 27 countries Over 2800 Employees worldwide Over 50% are engineers 85% Government/Commercial Linux Market Share 40+% Year over Year Growth (For 24 straight quarters) 3
Slide 4

4
Slide 5
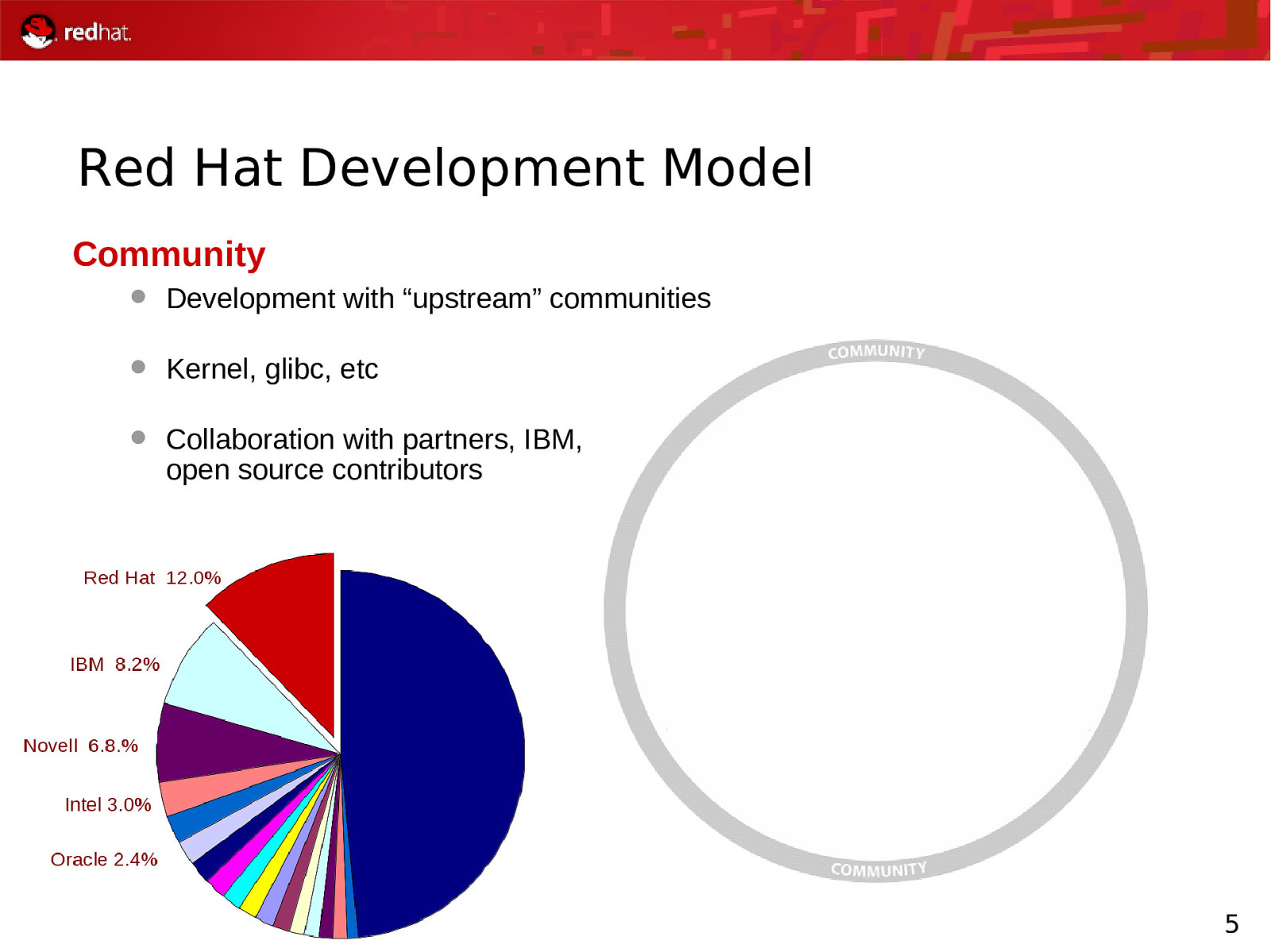
Red Hat Development Model Community Development with “upstream” communities Kernel, glibc, etc Collaboration with partners, IBM, open source contributors 5
Slide 6

Red Hat Development Model Fedora Rapid innovation Latest technologies Community Supported Released ~6mo cycles 6
Slide 7
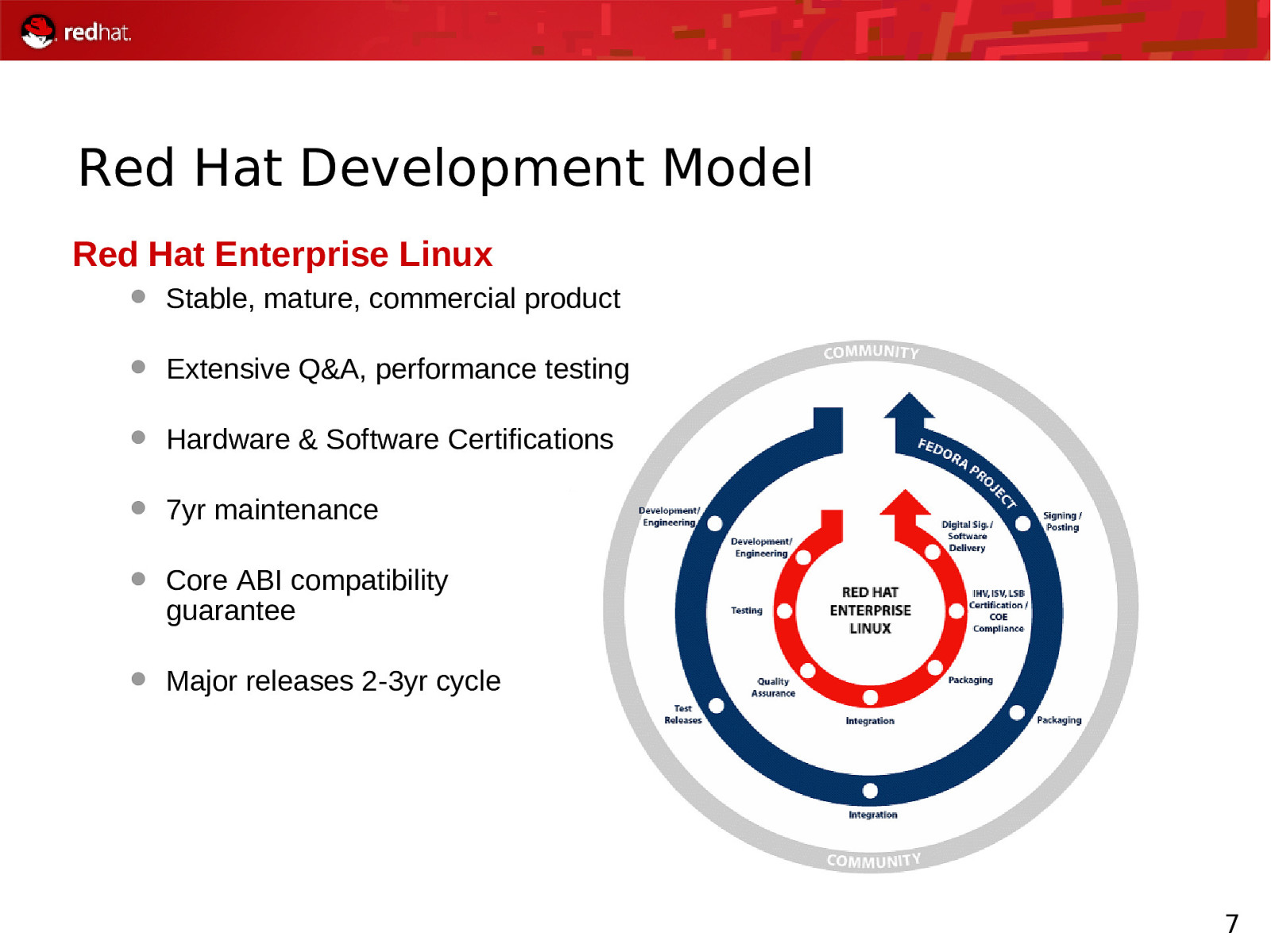
Red Hat Development Model Red Hat Enterprise Linux Stable, mature, commercial product Extensive Q&A, performance testing Hardware & Software Certifications 7yr maintenance Core ABI compatibility guarantee Major releases 2-3yr cycle 7
Slide 8

Fedora for System z http://unc.rdu.redhat.com/fc9-s390x/ 8
Slide 9
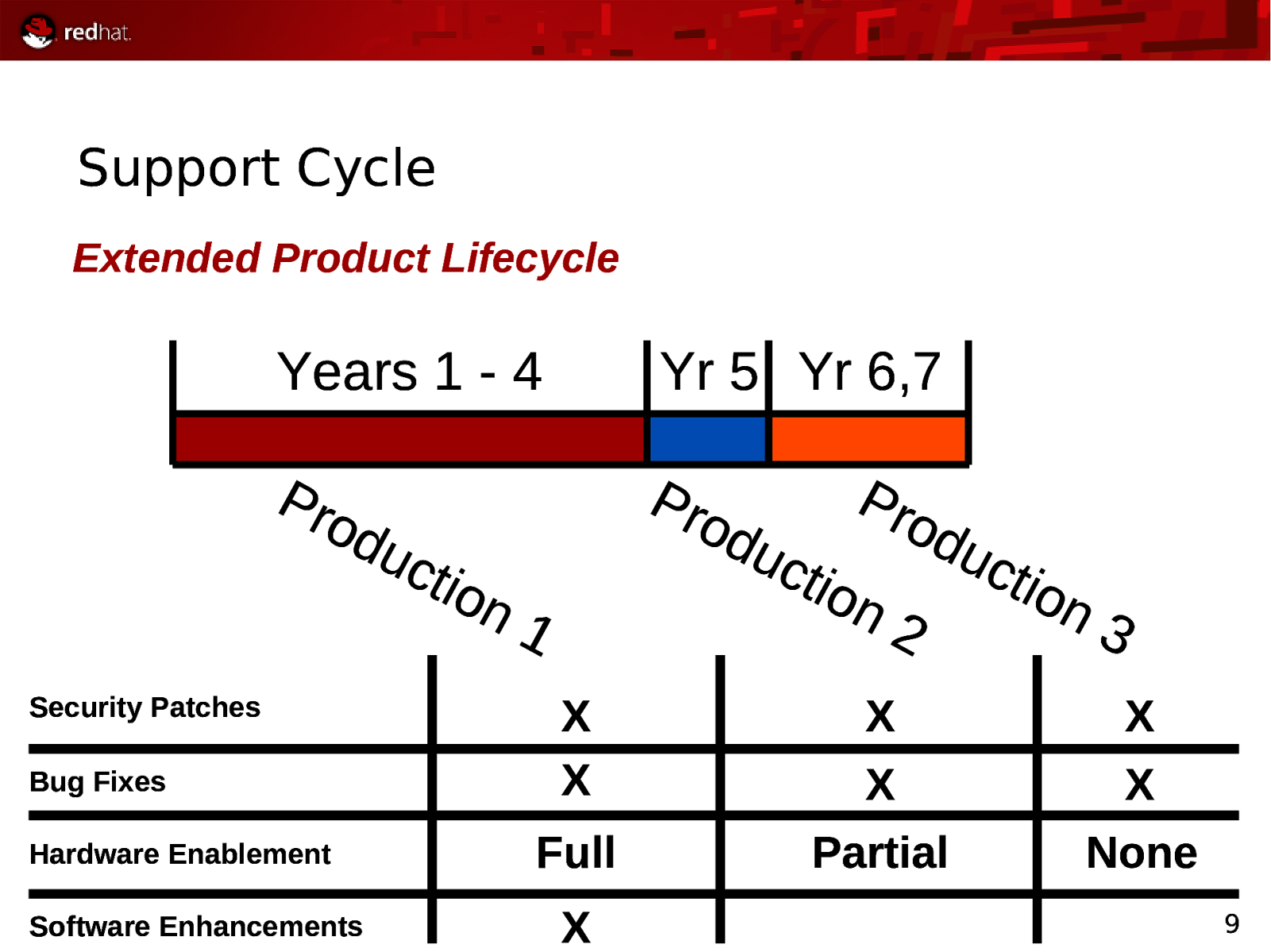
Support Cycle Extended Product Lifecycle Years 1 - 4 Yr 5 Yr 6,7 Pro d Pro d Security Patches Bug Fixes Hardware Enablement Software Enhancements uc tio n1 uc tio Pro d n2 uc tio n3 X X X X X X Full Partial None X 9
Slide 10
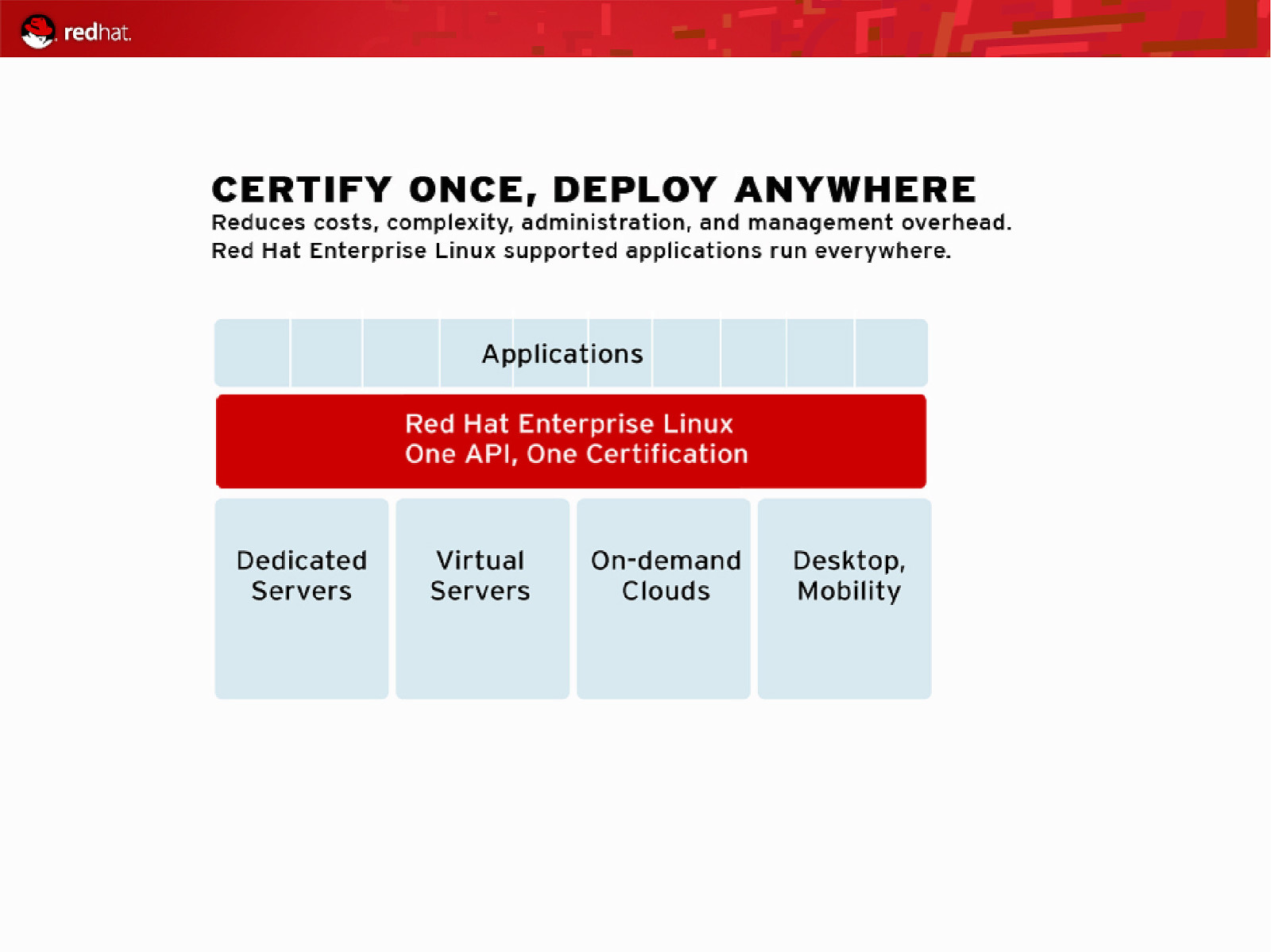
10
Slide 11

Red Hat Enterprise Linux Update
Slide 12

RHEL Kernel Updates High resolution timers (2.6.16) ● Provide fine resolution and accuracy depending on system configuration and capabilities - used for precise in-kernel timing Modular, on-the-fly switchable I/O schedulers (2.6.10) ● Only provided as a boot option in RHEL4 ● Improved algorithms (esp. for CFQ) ● Per-Queue selectable (previously system-wide) New Pipe implementation (2.6.11) ● 30-90% perf improvement in pipe bandwidth ● Circular buffer allow more buffering rather than blocking writers 12
Slide 13

Monitoring Features Inotify (2.6.13) ● New file system event monitoring mechanism (replaces dnotify) ● Ideal for security and performance monitoring Process Events Connector (2.6.15) ● Reports fork, exec, id change, and exit events for all processes to userspace ● Useful for accounting/auditing (e.g. ELSA), system activity monitoring, security, and resource management Blktrace ● Block queue IO tracing – monitor block device queue traffic (2.6.17) 13
Slide 14

File System Features EXT3 ● Ext3 block reservation & on-line growth (2.6.10 & RHEL4) ● Extended Attributes in the body of large inode ● Saves space and improves performance (2.6.11) ● Increases maximum ext3 file-system size from 8TB to 16TB (2.6.18) ACL support for NFSv3 and NFSv4 (2.6.13) NFS ● Support large reads and writes on the wire (2.6.16) ● Linux NFS client supports transfer sizes up to 1MB Device mapper multipath support 14
Slide 15
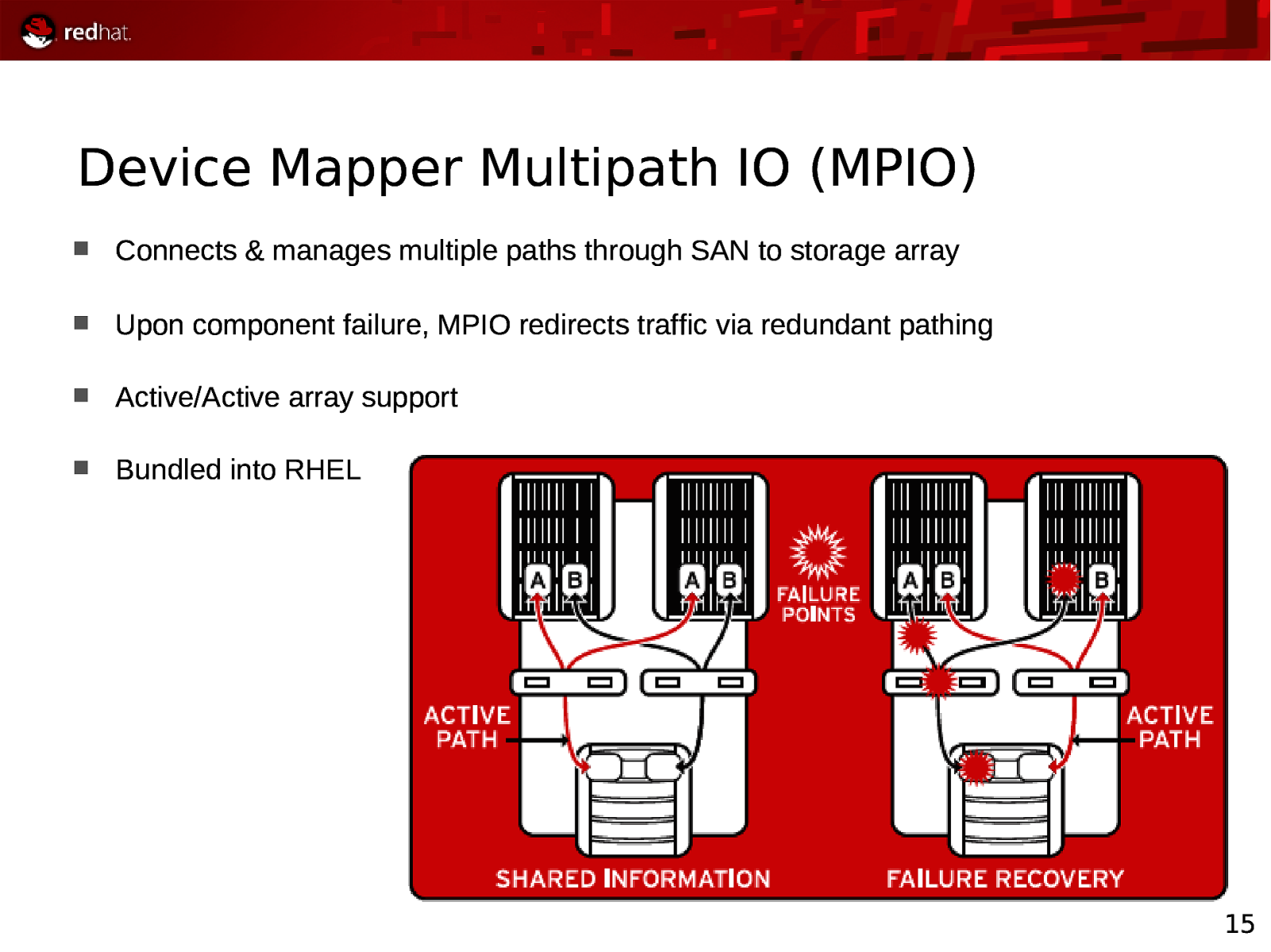
Device Mapper Multipath IO (MPIO) Connects & manages multiple paths through SAN to storage array Upon component failure, MPIO redirects traffic via redundant pathing Active/Active array support Bundled into RHEL 15
Slide 16

Security Features Address space randomization: ● Address randomization of multiple entities – including stack & mmap() region (used by shared libraries) (2.6.12; more complete implementation than in RHEL4) ● Greatly complicates and slows down hacker attacks Multilevel security (MLS) implementation for SELinux (2.6.12) ● Third policy scheme for SELinux, with RBAC & TE Audit subsytem ● Support for process-context based filtering (2.6.17) ● More filter rule comparators (2.6.17) TCP/UDP getpeersec ● Enable a security-aware application to retrieve the security context of an IPSec security association a particular TCP or UDP socket in using (2.6.17) 16
Slide 17

Networking Add nf_conntrack subsystem: (2.6.15) ● Common IPv4/IPv6 generic connection tracking subsystem ● Allows IPv6 to have a stateful firewall capability (not previously possible) ● Enables analysis of whole streams of packets, rather than only checking the headers of individual packets SELinux per-packet access controls ● Replaces old packet controls ● Add Secmark support to core networking ● Allows security subsystems to place security markings on network packets (2.6.18) IPv6 ● RFC 3484 compliant source address selection (2.6.15) ● Add support for Router Preference (RFC4191) (2.6.17) ● Add Router Reachability Probing (RFC4191) (2.6.17 17
Slide 18

Red Hat Enterprise Linux Future Virtualization Update
Slide 19
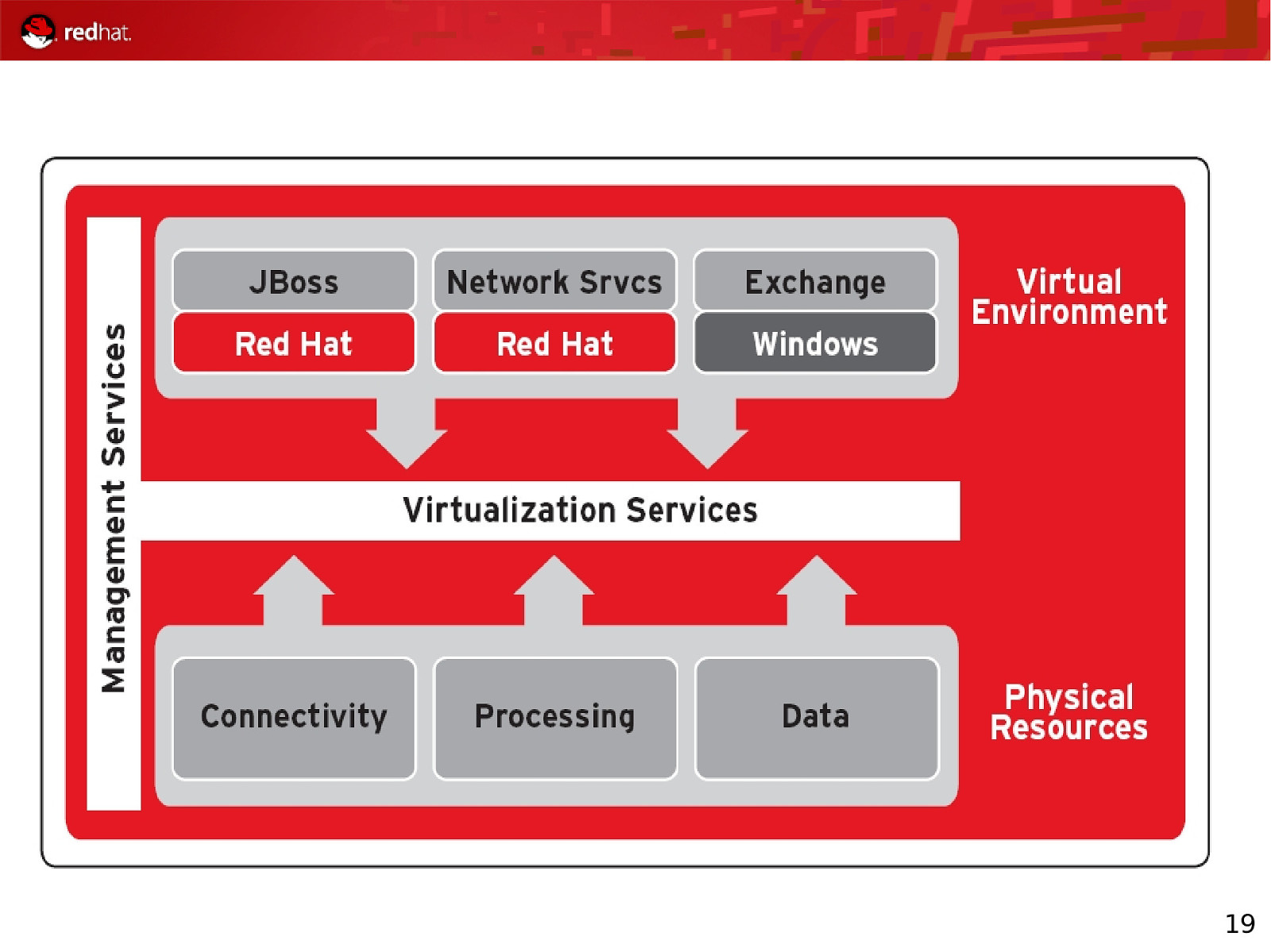
19
Slide 20
Introduction to libvirt API Hypervisor agnostic Stable API for tool/app development CIM providers; Python, C bindings, scriptable Allows authenticated/encrypted sessions to remote hypervisors Current support for Xen Hypervisor KVM Hypervisor QEMU Hypervisor 20
Slide 21
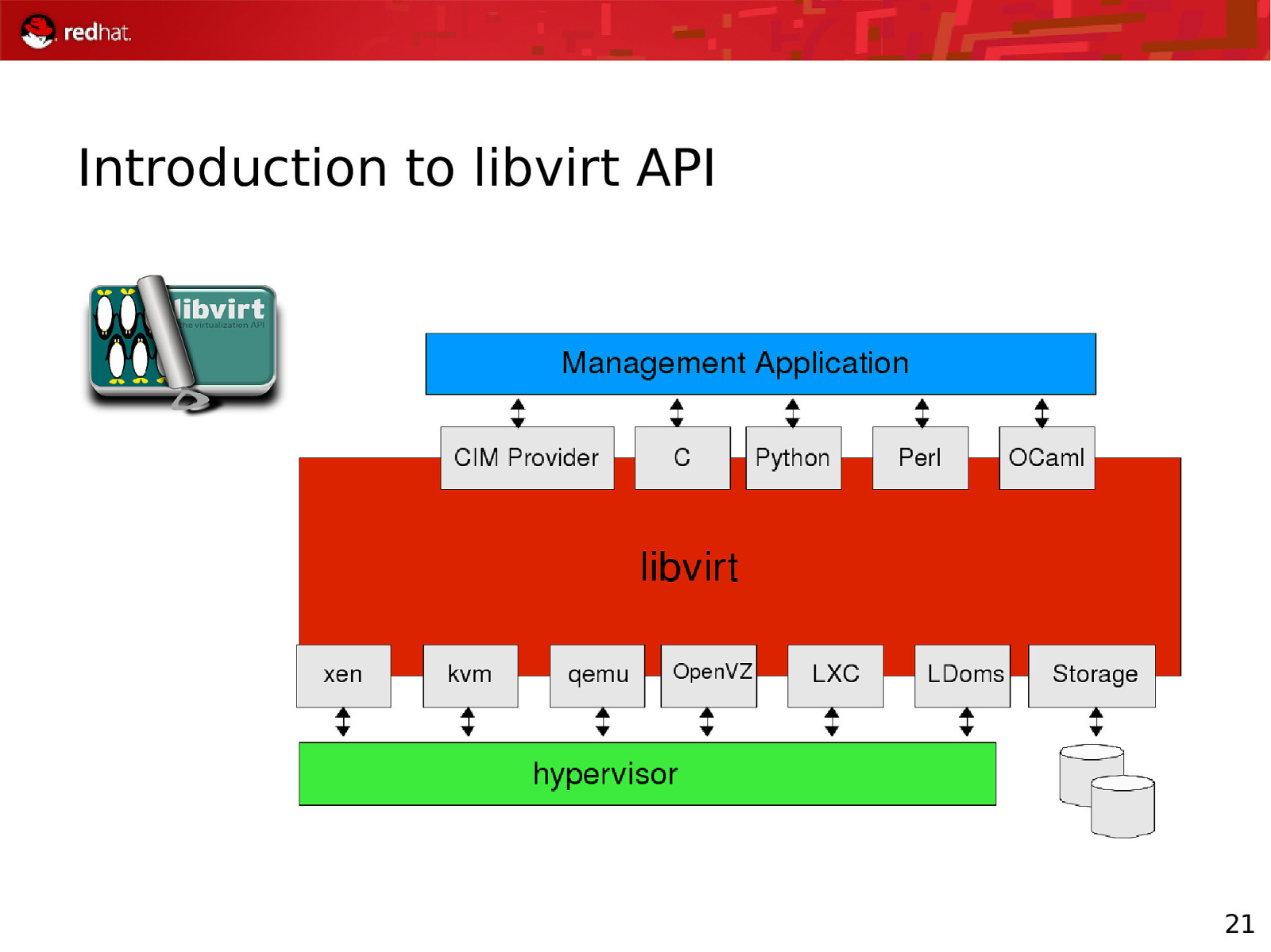
Introduction to libvirt API 21
Slide 22
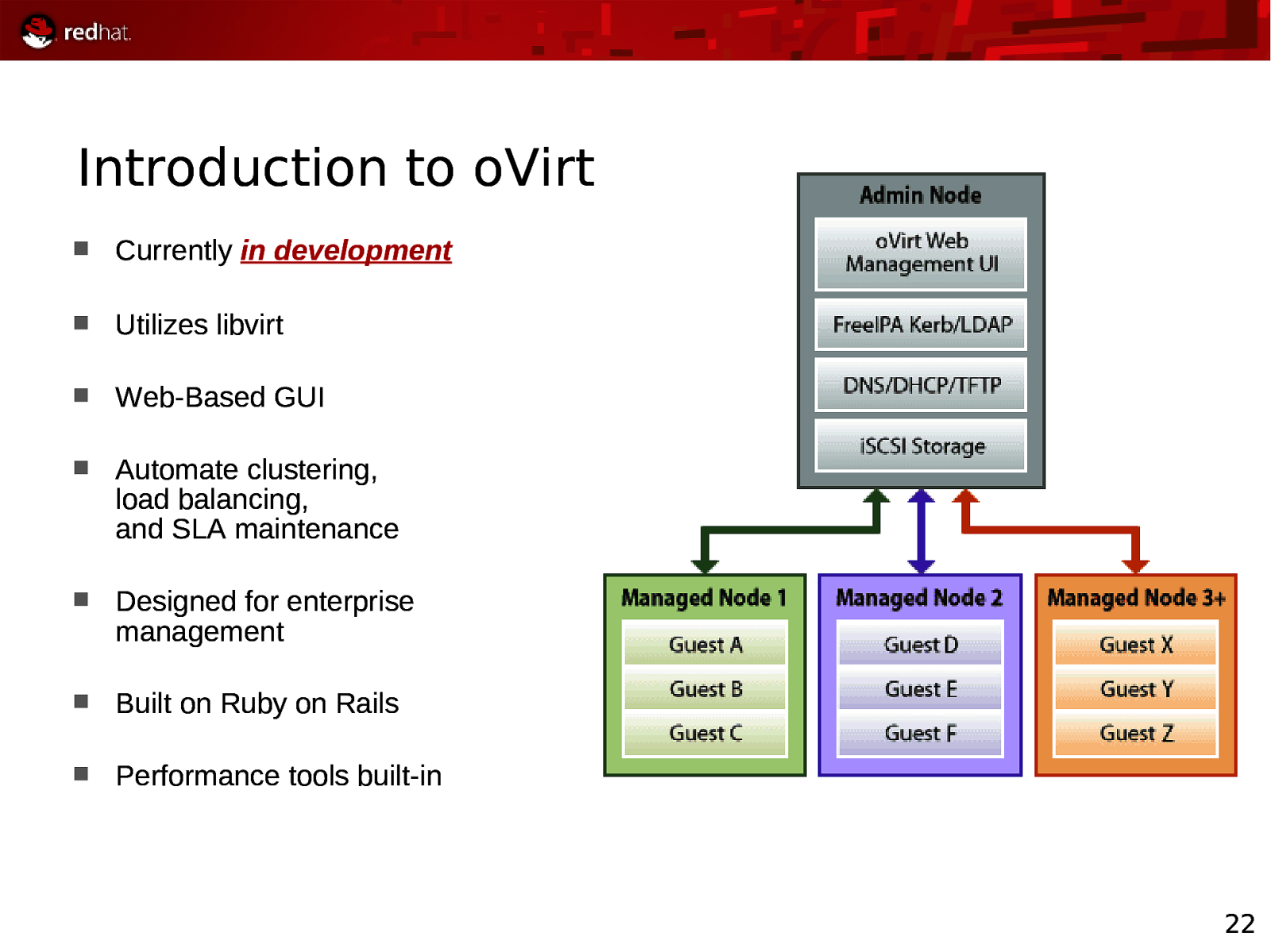
Introduction to oVirt Currently in development Utilizes libvirt Web-Based GUI Automate clustering, load balancing, and SLA maintenance Designed for enterprise management Built on Ruby on Rails Performance tools built-in 22
Slide 23

Red Hat Enterprise Linux Security Update
Slide 24

Red Hat Security Certifications ● ● ● ● ● NIAP/Common Criteria: The most evaluated operating system platform ● Red Hat Enterprise Linux 2.1 – EAL 2 (Completed: February 2004) ● Red Hat Enterprise Linux 3 EAL 3+/CAPP (Completed: August 2004) ● Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 EAL 4+/CAPP (Completed: February 2006) ● Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 EAL4+/CAPP/LSPP/RBAC (Completed: June 2007) DII-COE ● Red Hat Enterprise Linux 3 (Self-Certification Completed: October 2004) ● Red Hat Enterprise Linux: First Linux platform certified by DISA DCID 6/3 ● Currently PL3 & PL4: ask about kickstarts. ● Often a component in PL5 systems DISA SRRs / STIGs ● Ask about kickstarts. FIPS 140-2 ● Red Hat / NSS Cryptography Libraries certified Level 2 24
Slide 25

RHEL5 Security: NIST Standards Work Extensible Configuration Checklist Description Format (XCCDF) Enumeration for configuration requirements DISA FSO committed to deploying STIG as XCCDF Others working with NIST Security policy becomes one file 25
Slide 26

Red Hat Tomorrow: Here comes XCCDF XCCFD Format Language for describing policy “your password will be…” 26
Slide 27
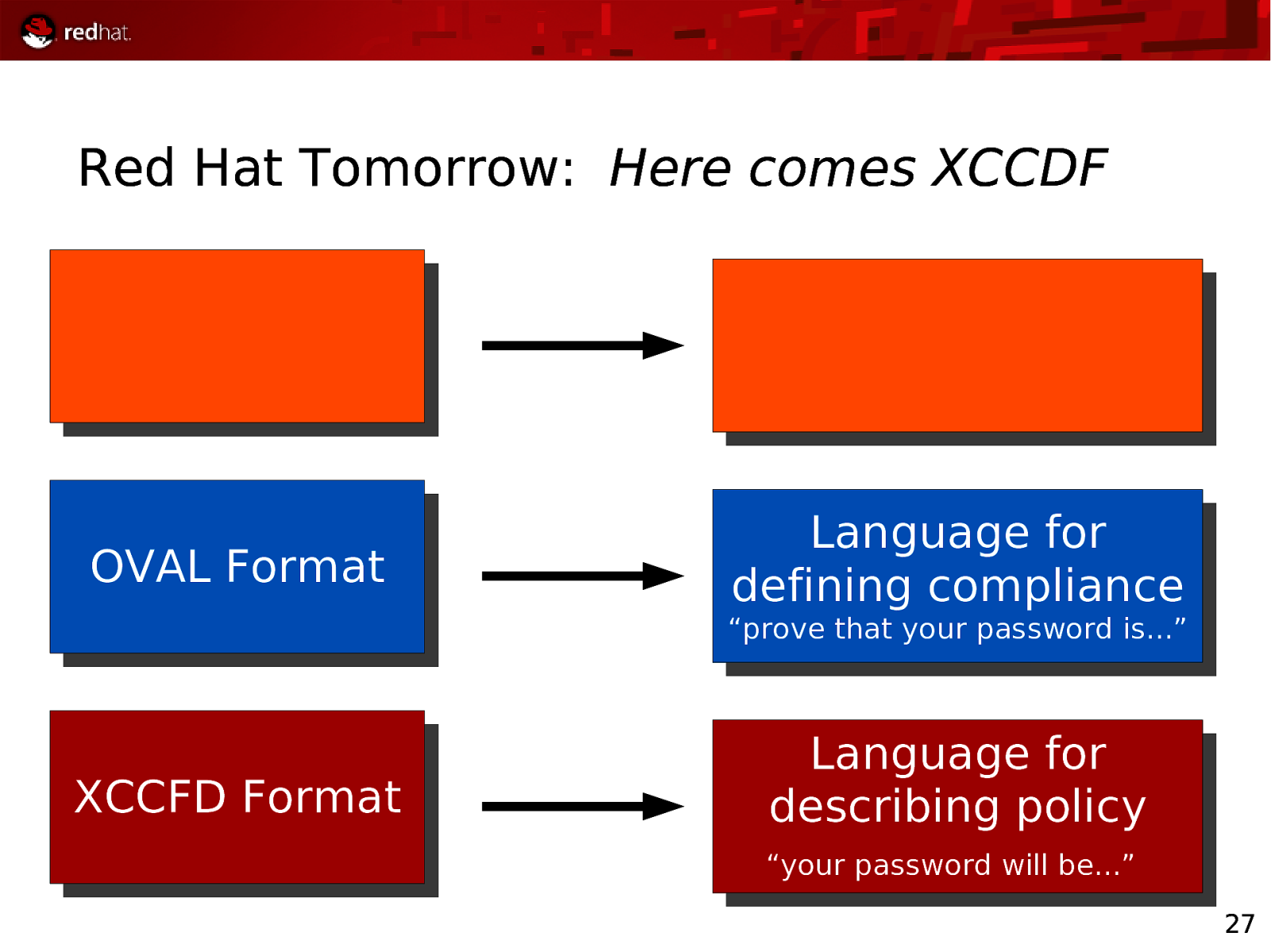
Red Hat Tomorrow: Here comes XCCDF OVAL Format Language for defining compliance “prove that your password is…” XCCFD Format Language for describing policy “your password will be…” 27
Slide 28
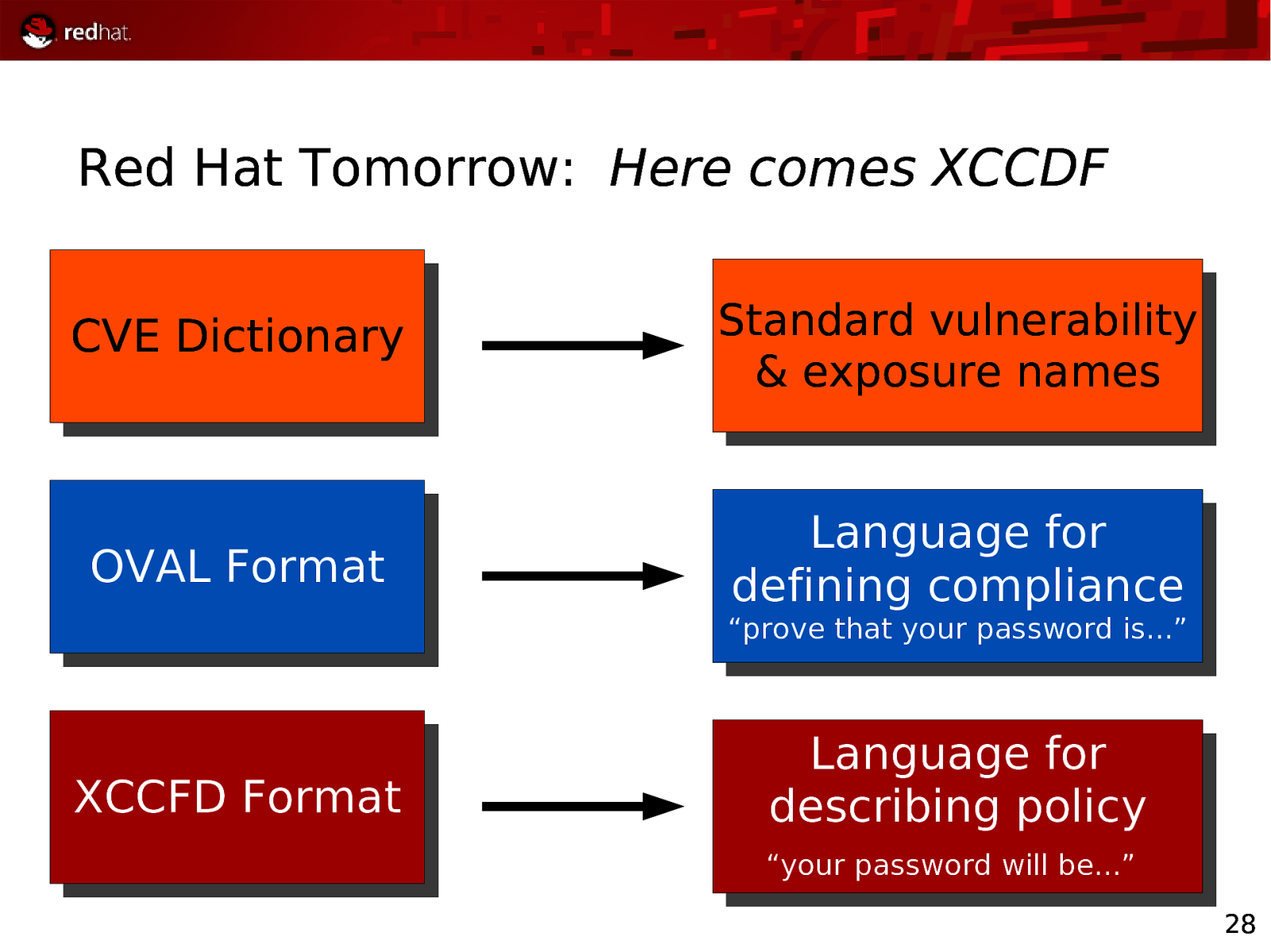
Red Hat Tomorrow: Here comes XCCDF CVE Dictionary Standard vulnerability & exposure names OVAL Format Language for defining compliance “prove that your password is…” XCCFD Format Language for describing policy “your password will be…” 28
Slide 29
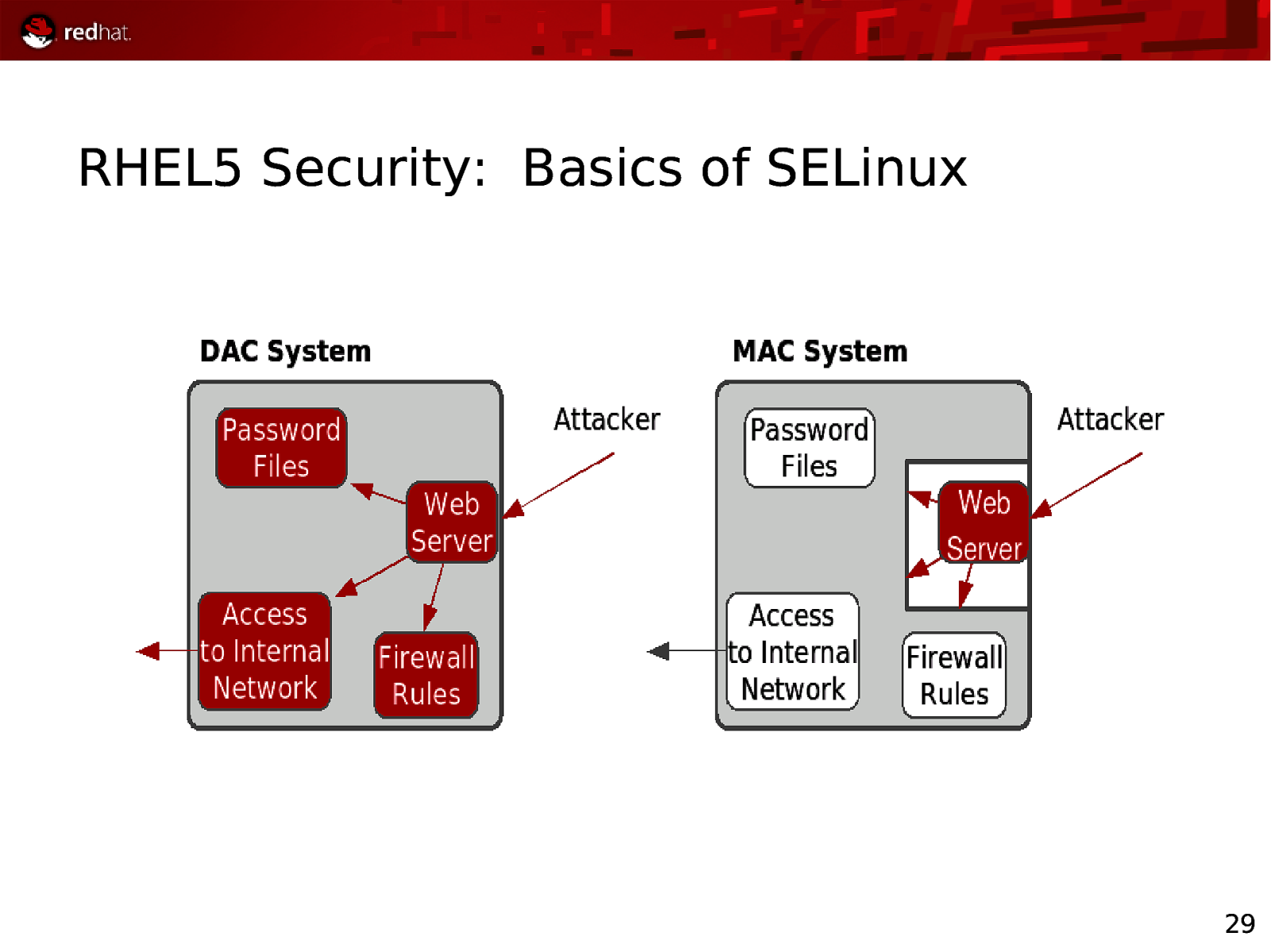
RHEL5 Security: Basics of SELinux 29
Slide 30
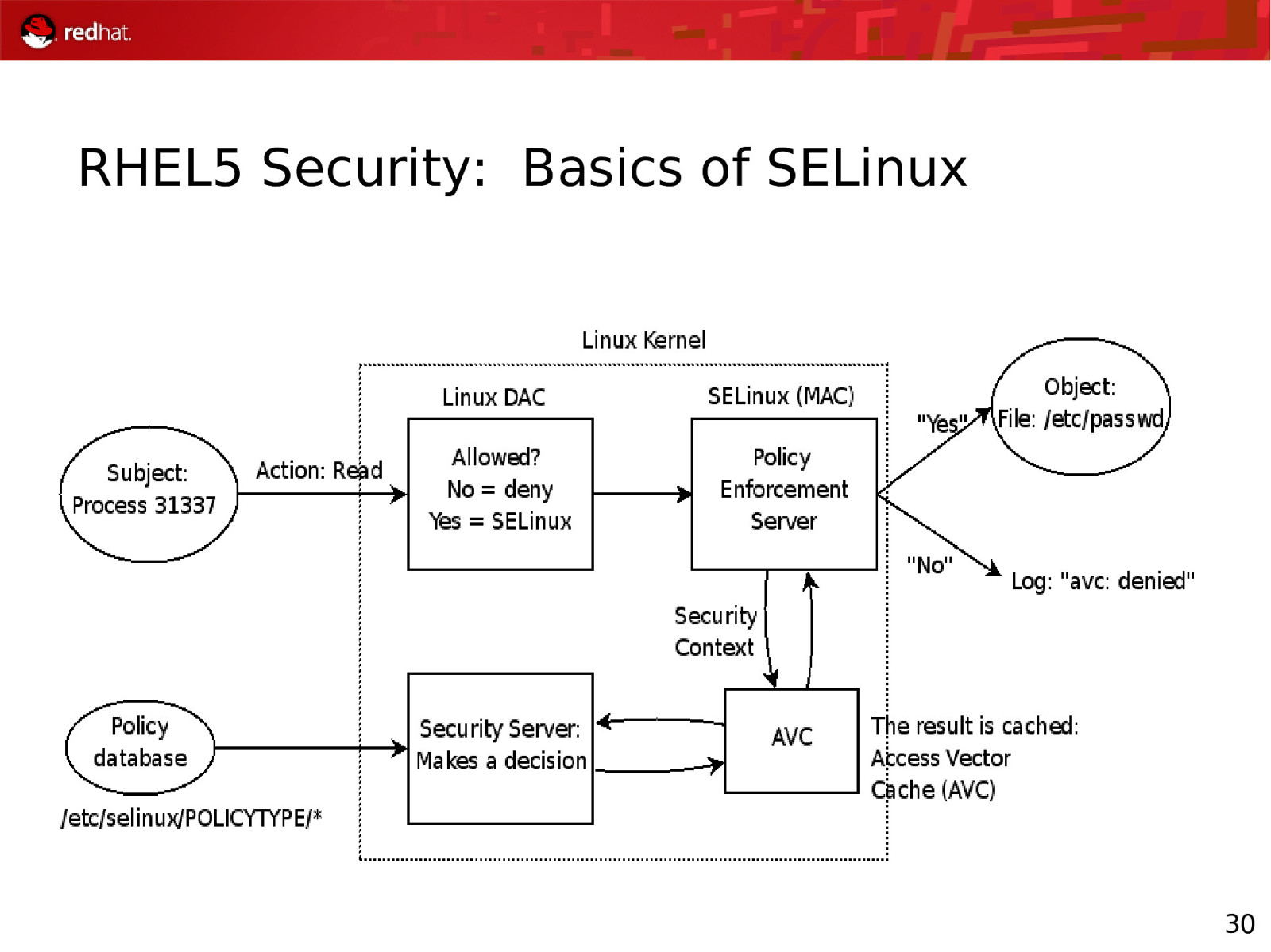
RHEL5 Security: Basics of SELinux 30
Slide 31

RHEL5 Security: SELinux Policies Targeted Policy (Default) Applications run unconfined unless explicitly defined policy exists Strict Policy All application actions explicitly allowed through SELinux, else actions denied MLS Polyinstantiated file systems Allows for different “views” based on clearance level 31
Slide 32

SELinux Contexts user_u:object_r:context_t Examples: Apache_u:ApacheBackup_r:ApacheDataFiles_t Apache_u:ApacheConfig_r:ApacheConfigFiles_t 32
Slide 33
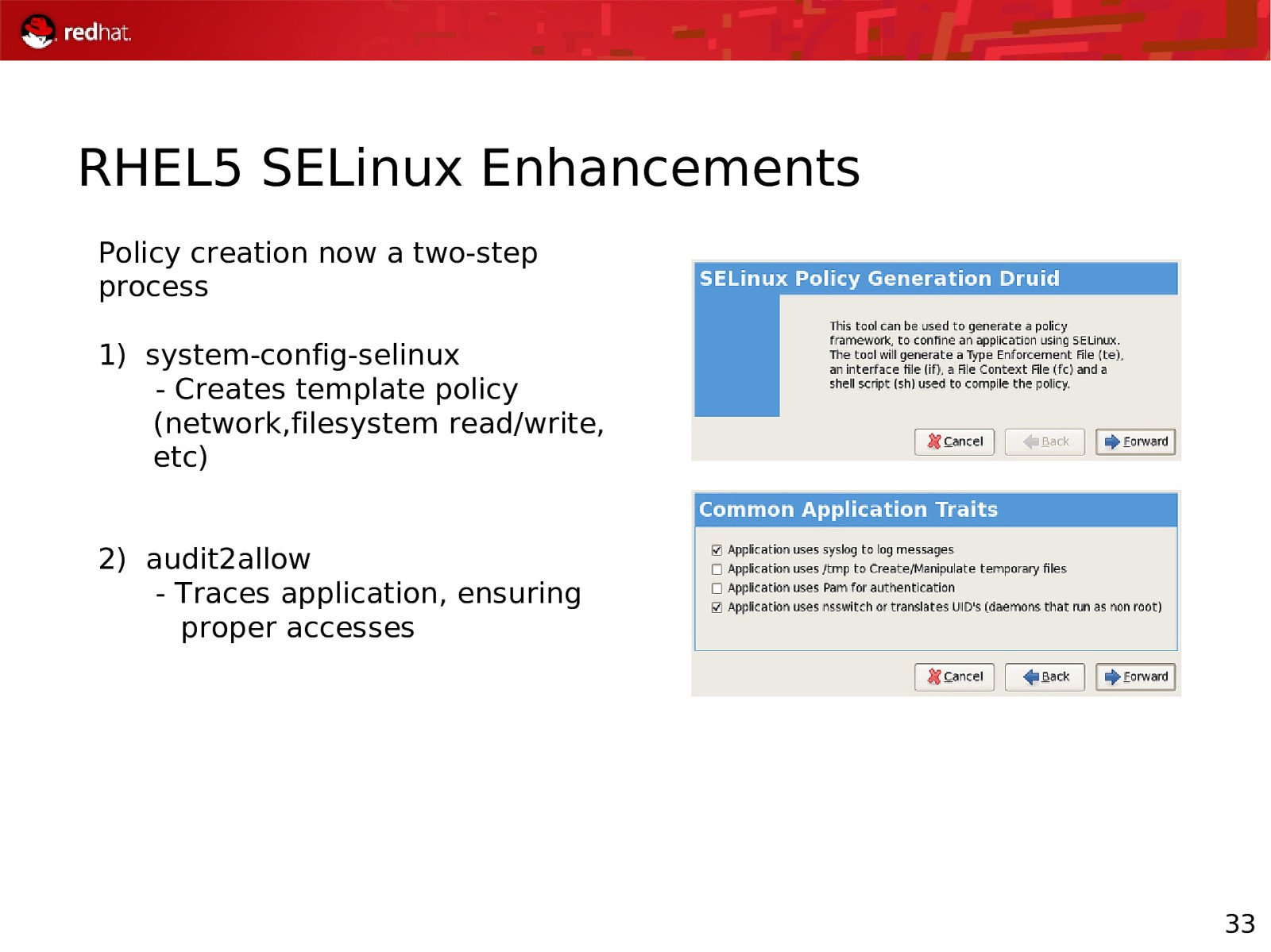
RHEL5 SELinux Enhancements Policy creation now a two-step process 1) system-config-selinux - Creates template policy (network,filesystem read/write, etc) 2) audit2allow - Traces application, ensuring proper accesses 33
Slide 34

RHEL5 SELinux Enhancements Loadable Policy Modules ● In the past, all policy changes had to be made to the policy source ● Required the entire policy re-compiled ● ● ● Requiring a full set of policy development tools on production systems. Modules allow for the creation of self-contained policy modules ● Safely linked together to create system policies ● Add policy on the fly ● Remove policy on the fly Framework to allow ISV/OEM partners to ship their own modular SELinux policy Further Information ● http://sepolicy-server.sourceforge.net/index.php?page=moduleoverview 34
Slide 35
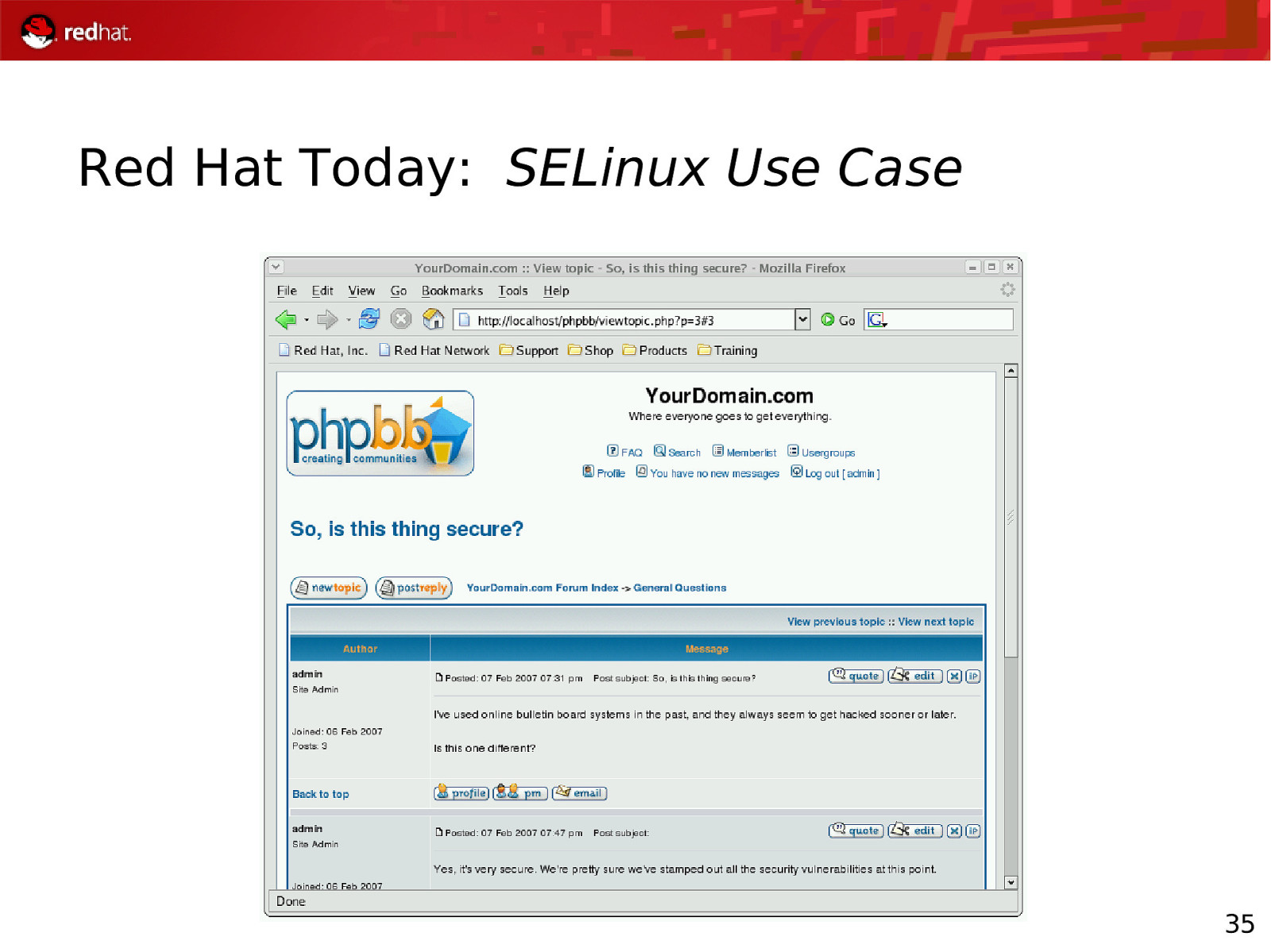
Red Hat Today: SELinux Use Case 35
Slide 36
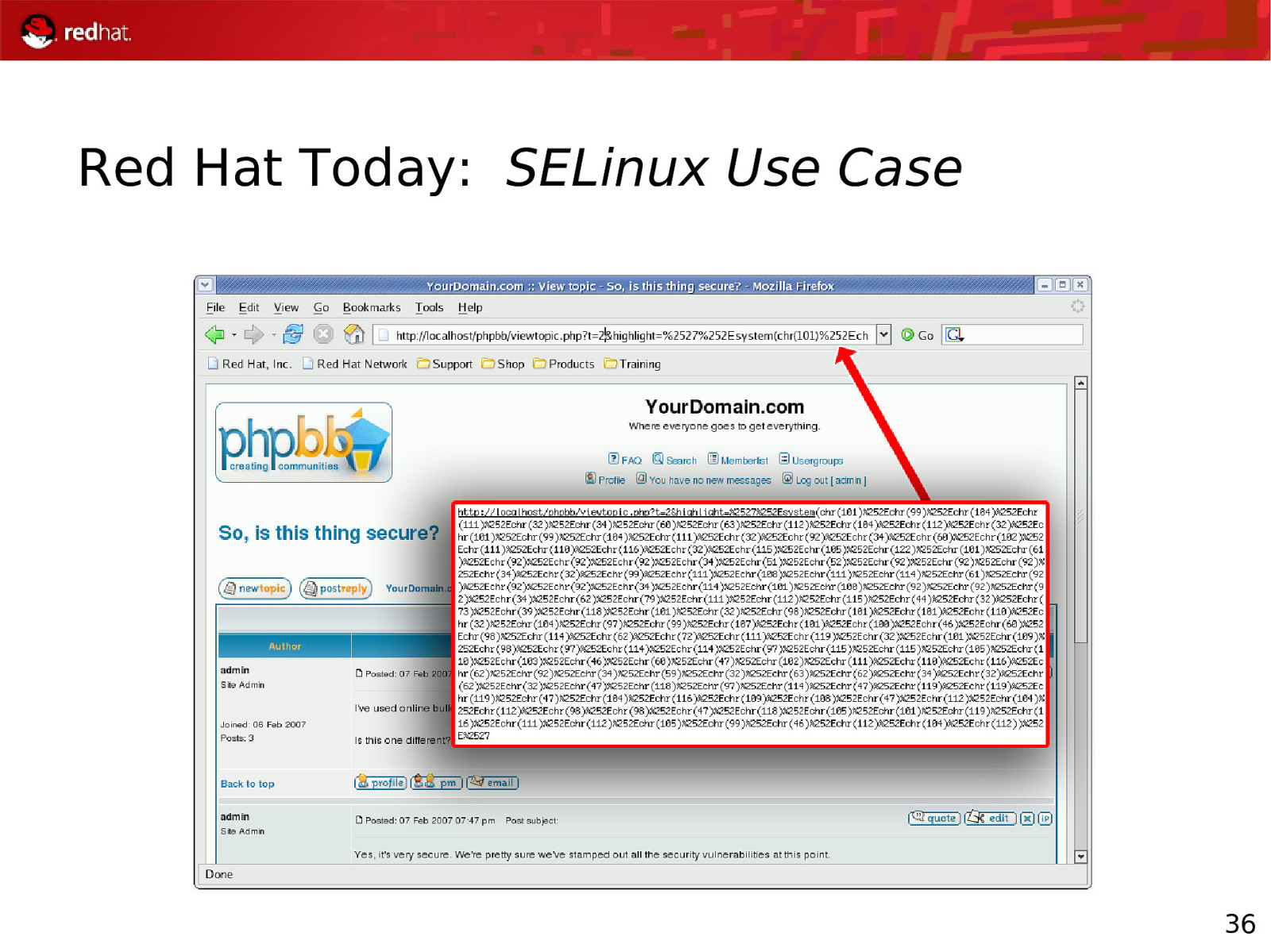
Red Hat Today: SELinux Use Case 36
Slide 37
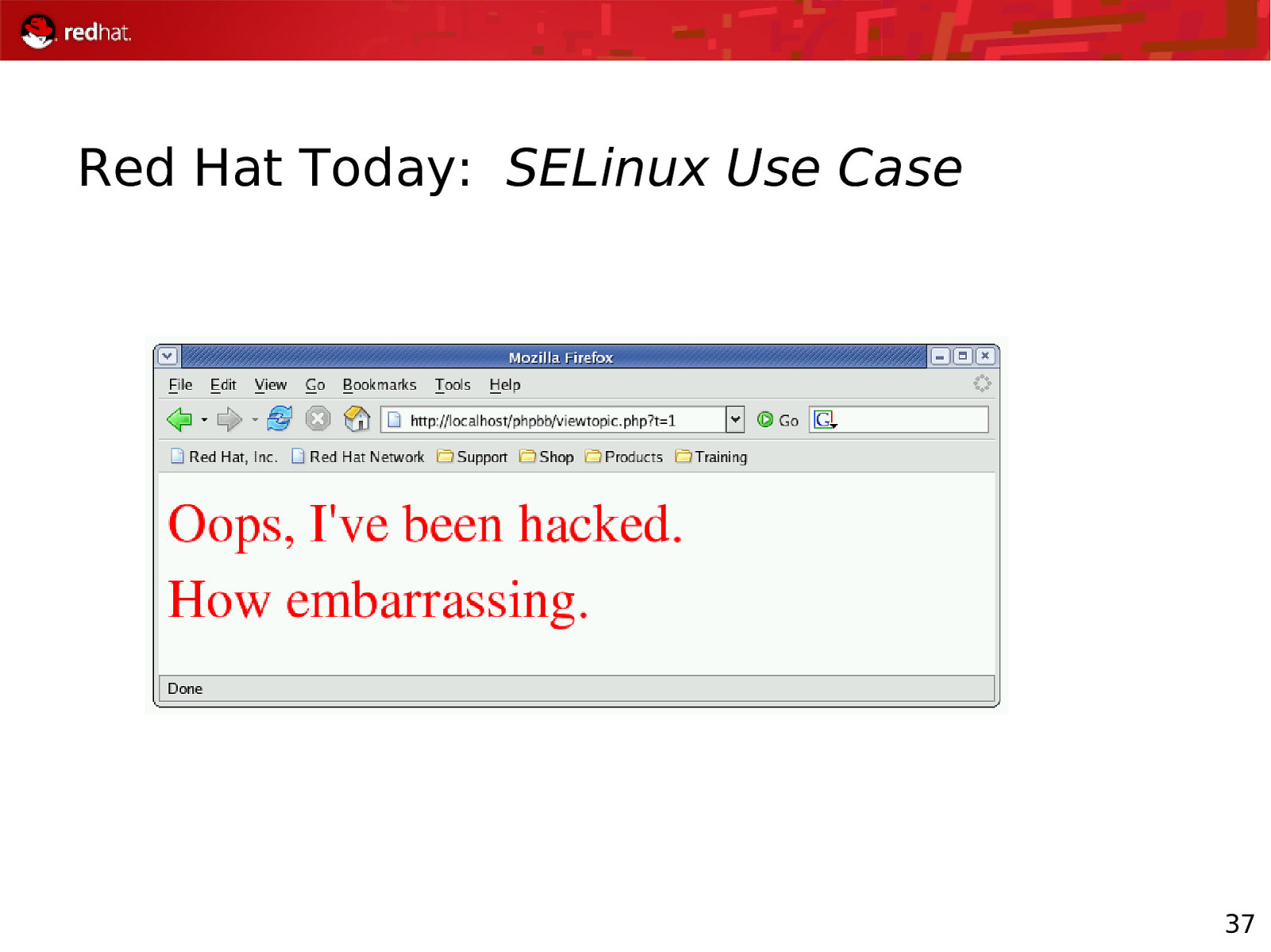
Red Hat Today: SELinux Use Case 37
Slide 38

Red Hat Today: RHEL Security Status SELinux Use Case Apache should not be allowed to overwrite content Therefore, Apache – and any program started by Apache – is not given write access to the data SELinux constrains the program, regardless of the user running executable The content is protected, even if the Apache PHP/CGI user owns the files When attacker uses the same exploit, with SELinux turned on: Mar 3 23:02:04 rhel4-u4-as kernel: audit(1170820924.171:108): avc: denied { write } for pid=26760 comm=”sh” name=”phpbb” dev=dm-0 ino=1114119 scontext=root:system_r:httpd_sys_script_t tcontext=root:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t tclass=dir 38
Slide 39

Red Hat Enterprise Linux System z Update
Slide 40

Red Hat Today: Announcements Red Hat / IBM Alliance Technical Perspective Dedicated Partner Managers IBM on-site kernel engineers at Red Hat Weekly calls with IBM System z Product Mgmt Emphasis on IBM access to code (making it easier to work together) Weekly reviews of open bugs & feature requests Proof of Concept Support Marketing & Sales Perspective Joint World-Wide Tour Marist, zNTP, T3, SHARE, zExpo, etc Business Perspective Dedicated staff from helpdesk to executive 40
Slide 41
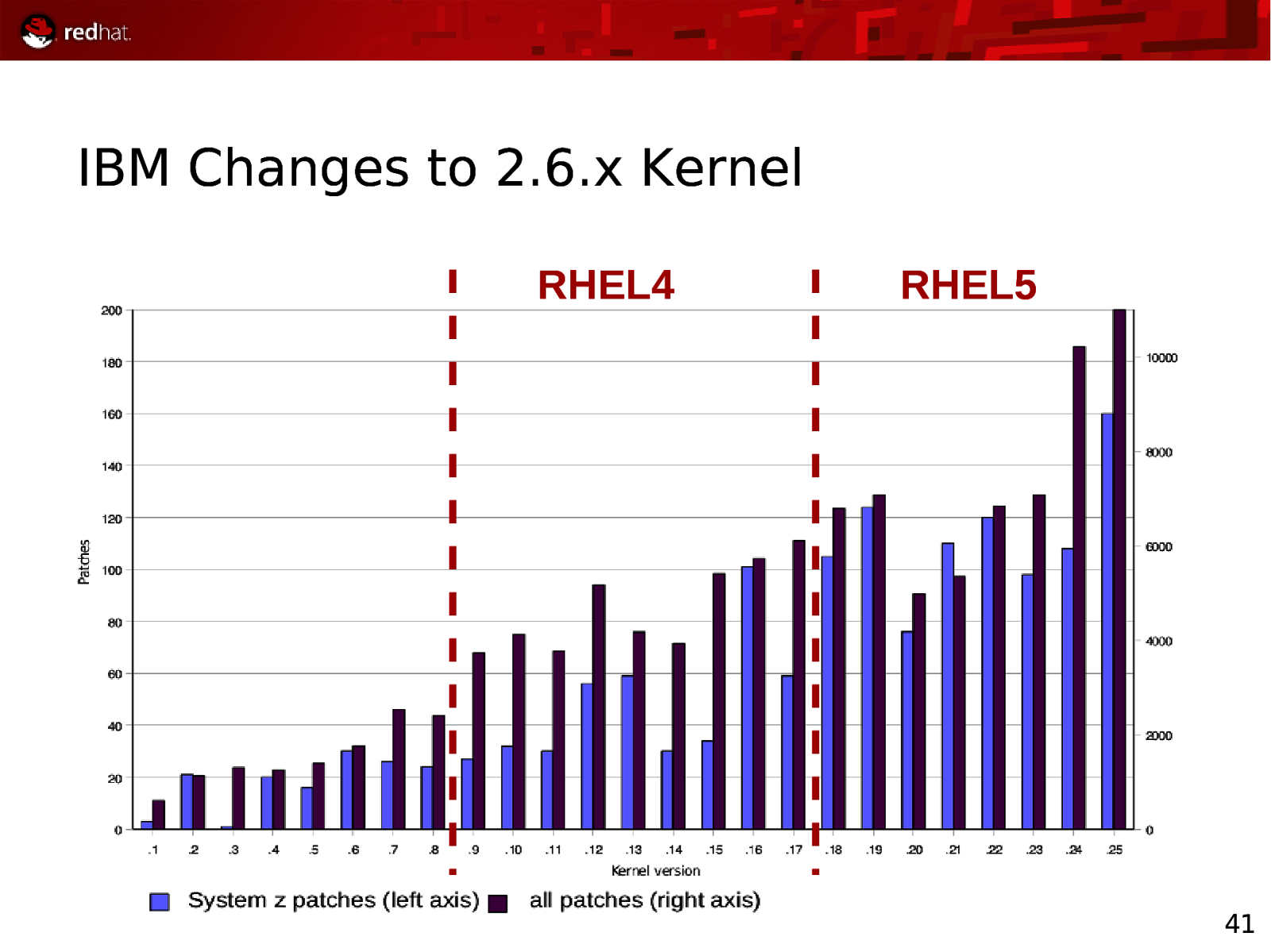
IBM Changes to 2.6.x Kernel RHEL4 RHEL5 41
Slide 42
Red Hat Today: RHEL Status Upstream of Code DASD Drive Updates zFCP Driver Updates zFCP multipathing support in RHEL5 installer Crypto2 Express Support Hugetblfs Layer-2 IPv6 support for Hipersockets Marketing Perspective Joint World-Wide Tour Marist, zNTP, T3, SHARE, zExpo, etc Sales Perspective Joint sales calls 42
Slide 43
Red Hat Today: RHEL Status RHEL 5.1 ● Improved z/VM scheduling ● Improved performance with key recompiled libraries RHEL 5.2 ● Support for new IBM z10 ● Improved IBM Director support to support fast connection to z/VM ● Improved Virtual Server Management ● Implementation of SCSI dump infrastructure ● Support for Dynamic CHPID reconfiguration ● Better network configuration tool support for System z network adapters ● Improved install experience with support for “ssh -X” with VNC ● Better network performance with skb scatter-gather support ● Implemented device-multipath support for xDR/GDPS RHEL 5.3 ● NSS, CPU Affinity, ETR support planned ● Suggestions? swells@redhat.com 43
Slide 44

Red Hat Today: RHEL Security Status Hardware Enablement In kernel crypto S/390 implementation of SHA-384 and SHA-512 digests Improved encryption performance (i.e. encrypted filesystems) libica library Support for updated OpenSSL, PKCS#11, GSKit, and kernel crypto APIs Device driver performance updates Crypto2 Express Support 44
Slide 45

Red Hat Enterprise Linux Update Red Hat Network
Slide 46
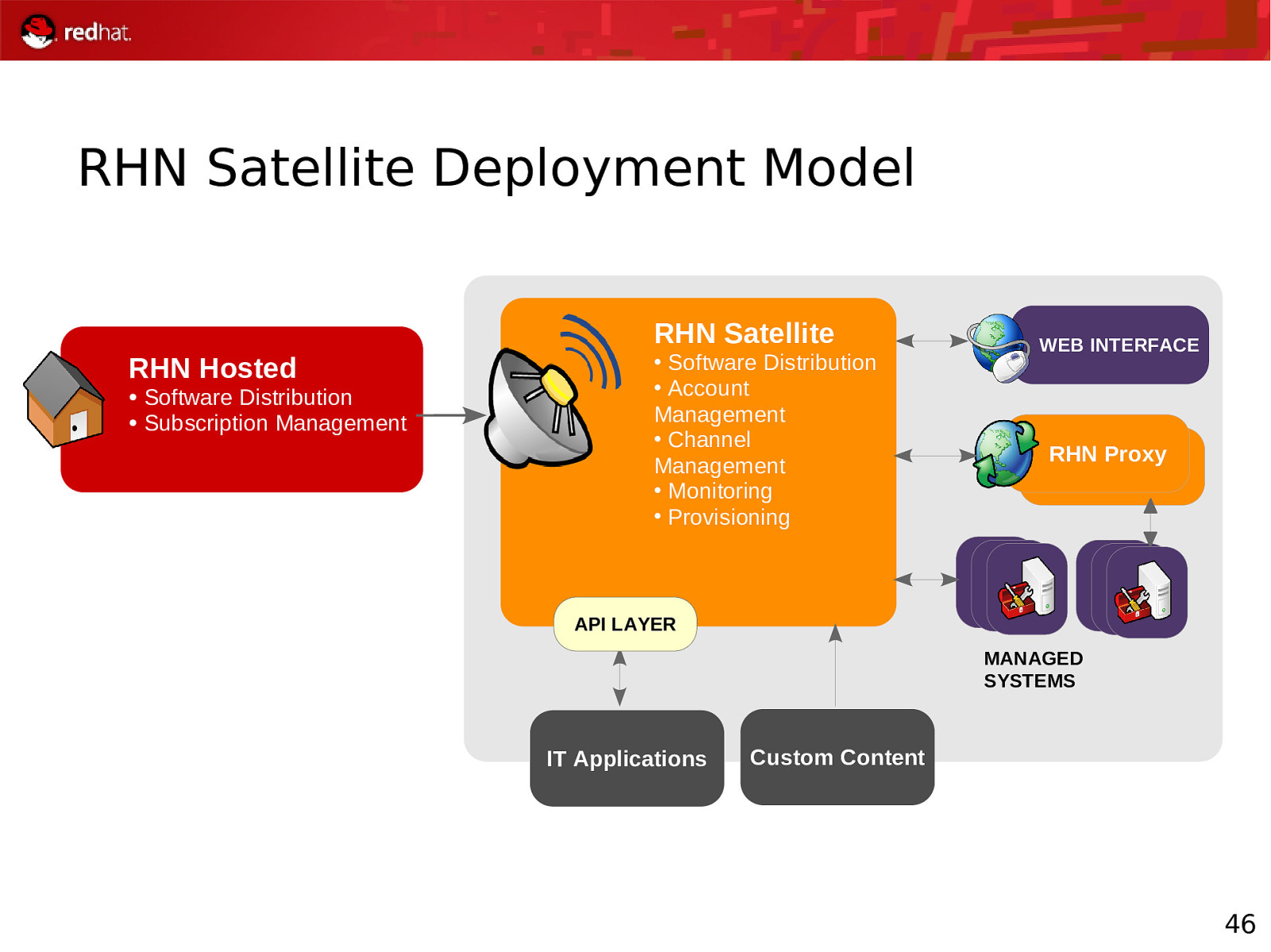
RHN Satellite Deployment Model RHN Satellite RHN Hosted ● ● Software Distribution Subscription Management • Software Distribution • Account Management • Channel Management • Monitoring • Provisioning WEB INTERFACE RHN Proxy API LAYER MANAGED SYSTEMS IT Applications Custom Content 46
Slide 47

What is Red Hat Network? Update 47
Slide 48

What is Red Hat Network? Update Manage 48
Slide 49
What is Red Hat Network? Update Manage Provision 49
Slide 50
What is Red Hat Network? Update Manage Provision Monitor 50
Slide 51
51
Slide 52
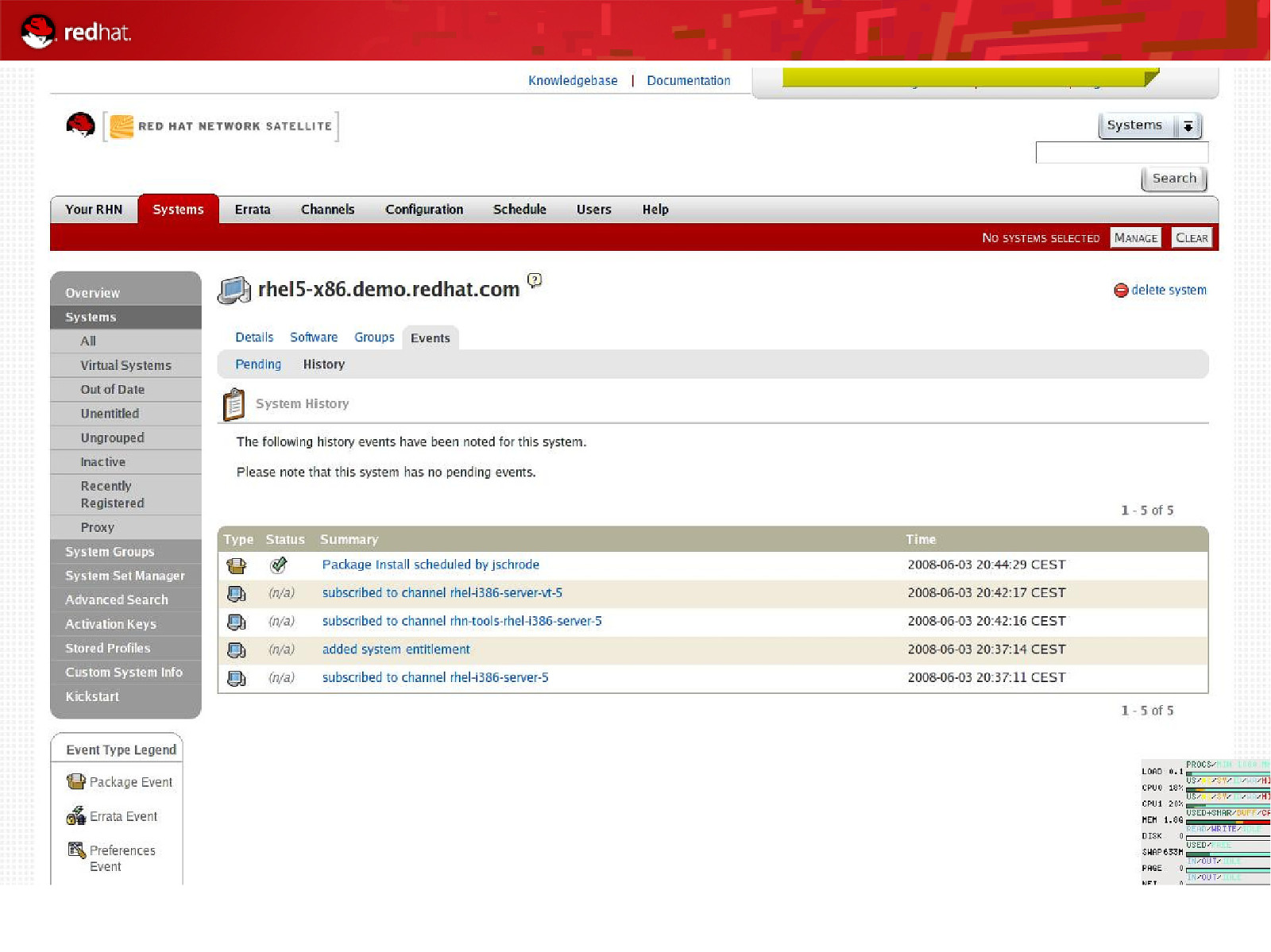
52
Slide 53
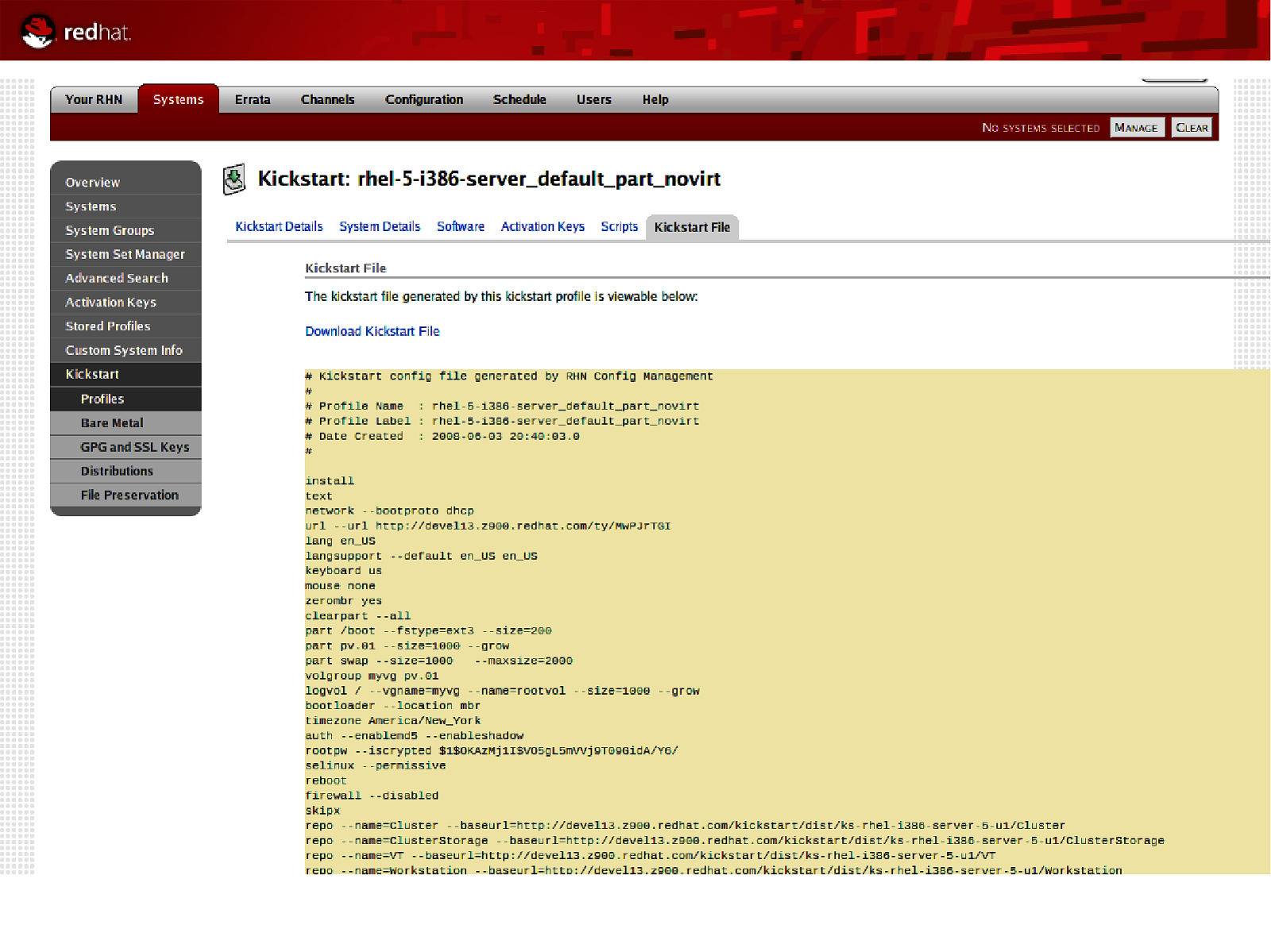
53
Slide 54

RHN Satellite Is Now Open Source http://spacewalk.redhat.com Announced at Red Hat Summit 2008 …. remember the Fedora -> RHEL model? 54
Slide 55

Open Discussion