Get the Hype on System z Current & Future Linux on System z Technology Thursday September 24th 2009
Slide 1

Slide 2

Agenda Part 1: Current Technology Review of RHEL 5.4, released Tuesday 2-SEPT Inclusion of Named Saved Segments (NSS) Updated fiber channel drivers & utilities Rebasing of s390utils to version 1.8.1 Tentative roadmap for RHEL 6 for System z An update on CMM2 (i.e. CMMA) development activities via the CMM-Lite technology Part 2: Future Technology What technologies are the joint IBM and Red Hat Linux on System z teams working on? Storage Networking Usability Crypto Misc 2
Slide 3
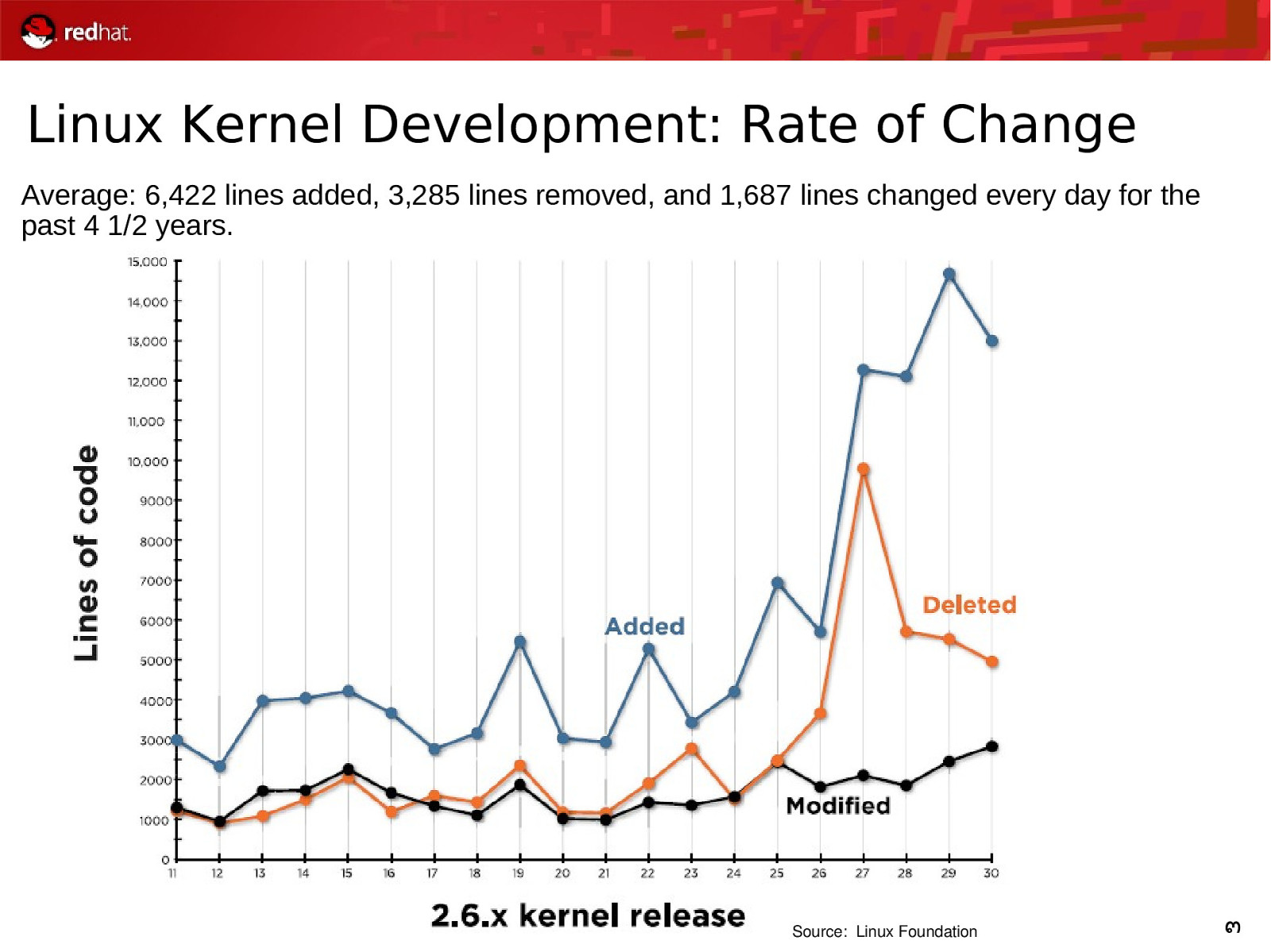
Linux Kernel Development: Rate of Change Average: 6,422 lines added, 3,285 lines removed, and 1,687 lines changed every day for the past 4 1/2 years. Source: Linux Foundation 3
Slide 4
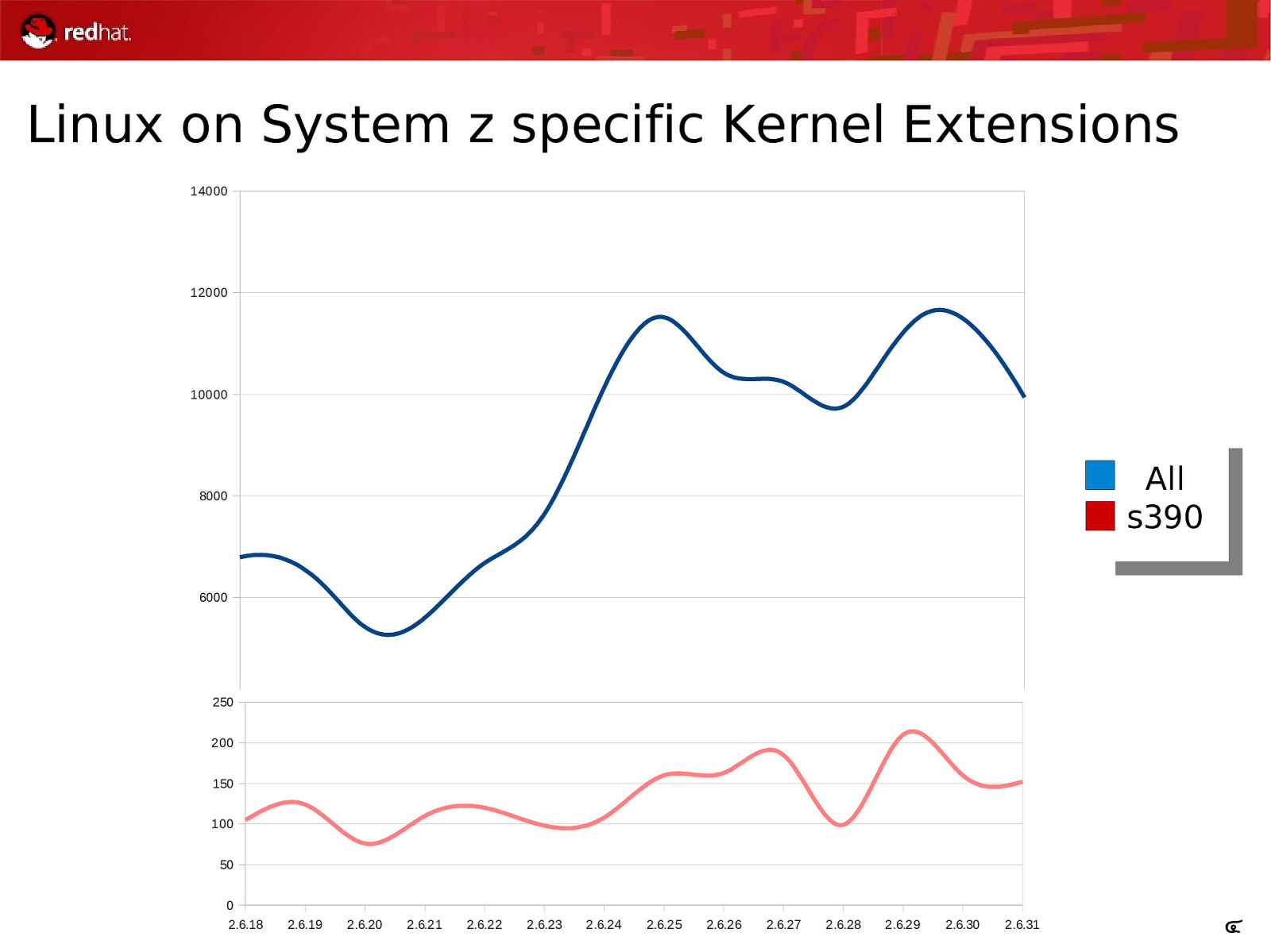
Linux on System z specific Kernel Extensions 14000 12000 10000 All s390 8000 6000 4000 250 200 150 2000 100 50 00 2.6.18 2.6.18 2.6.19 2.6.19 2.6.20 2.6.20 2.6.21 2.6.21 2.6.22 2.6.22 2.6.23 2.6.23 2.6.24 2.6.24 2.6.25 2.6.25 2.6.26 2.6.26 2.6.27 2.6.27 2.6.28 2.6.28 2.6.29 2.6.29 2.6.30 2.6.30 2.6.31 2.6.31 4
Slide 5
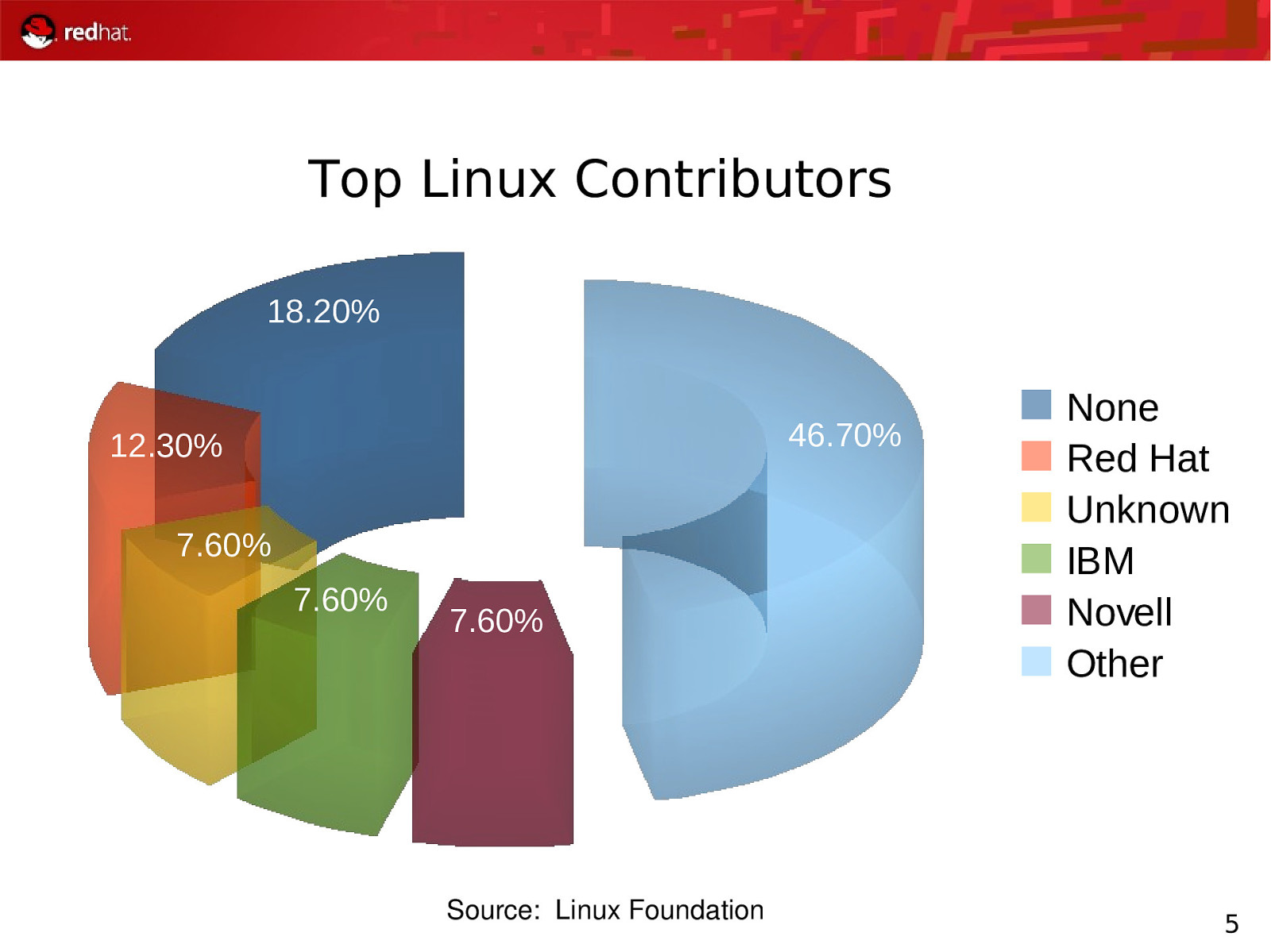
Top Linux Contributors 18.20% 46.70% 12.30% 7.60% 7.60% 7.60% Source: Linux Foundation None Red Hat Unknown IBM Novell Other 5
Slide 6

IBM collaborates with the Linux community …has been an active participant since 1999 …is one of the leading commercial contributors to Linux …has over 600 full-time developers working with Linux and open source Linux Kernel & Subsystem Development Expanding the Open Source Ecosystem Kernel Base Kernel Base Apache Apache Security Security Eclipse Eclipse Systems Mgmt Systems Mgmt Mozilla Firefox Mozilla Firefox Virtualization Virtualization OpenOffice.org , OpenOffice.org , Filesystems, Filesystems, and more… and more… and more… and more… Foster and Protect the Ecosystem The Linux The Linux Foundation Foundation Promoting Open Standards & Community Collaboration Linux Standards Linux Standards Base Base Common Criteria Common Criteria certification, certification, and more… and more… Software Software Freedom Freedom Law Center Law Center Free Software Free Software Foundation (FSF), Foundation (FSF), and more… and more… 6
Slide 7
The IBM Linux Development Process IBM Linux on System z Development contributes in the following areas Kernel s390-tools Open Source Tools (e.g. eclipse, ooprofile) GCC, GLIBC, Binutils Upstream Kernel Developer DeveloperWorks Works Website Website Community Customer Customer 7
Slide 8

Red Hat Development Model Community Development with “upstream” communities Kernel, glibc, etc Collaboration with partners, IBM, open source contributors 8
Slide 9
Red Hat Development Model Fedora Rapid innovation Latest technologies Community Supported Released ~6mo cycles 9
Slide 10
Red Hat Development Model Red Hat Enterprise Linux Stable, mature, commercial product Extensive Q&A, performance testing Hardware & Software Certifications 7-10 year maintenance Core ABI compatibility guarantee Major releases 2-3yr cycle 10
Slide 11

Fedora for System z Opens Linux on System z development to entire Open Source community, not just IBM, Red Hat, and Novell. Linux for System z now follows same development process as every other platform, allowing for faster Q&A, faster feature inclusion, and increased stability http://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Architectures/s390x 11
Slide 12
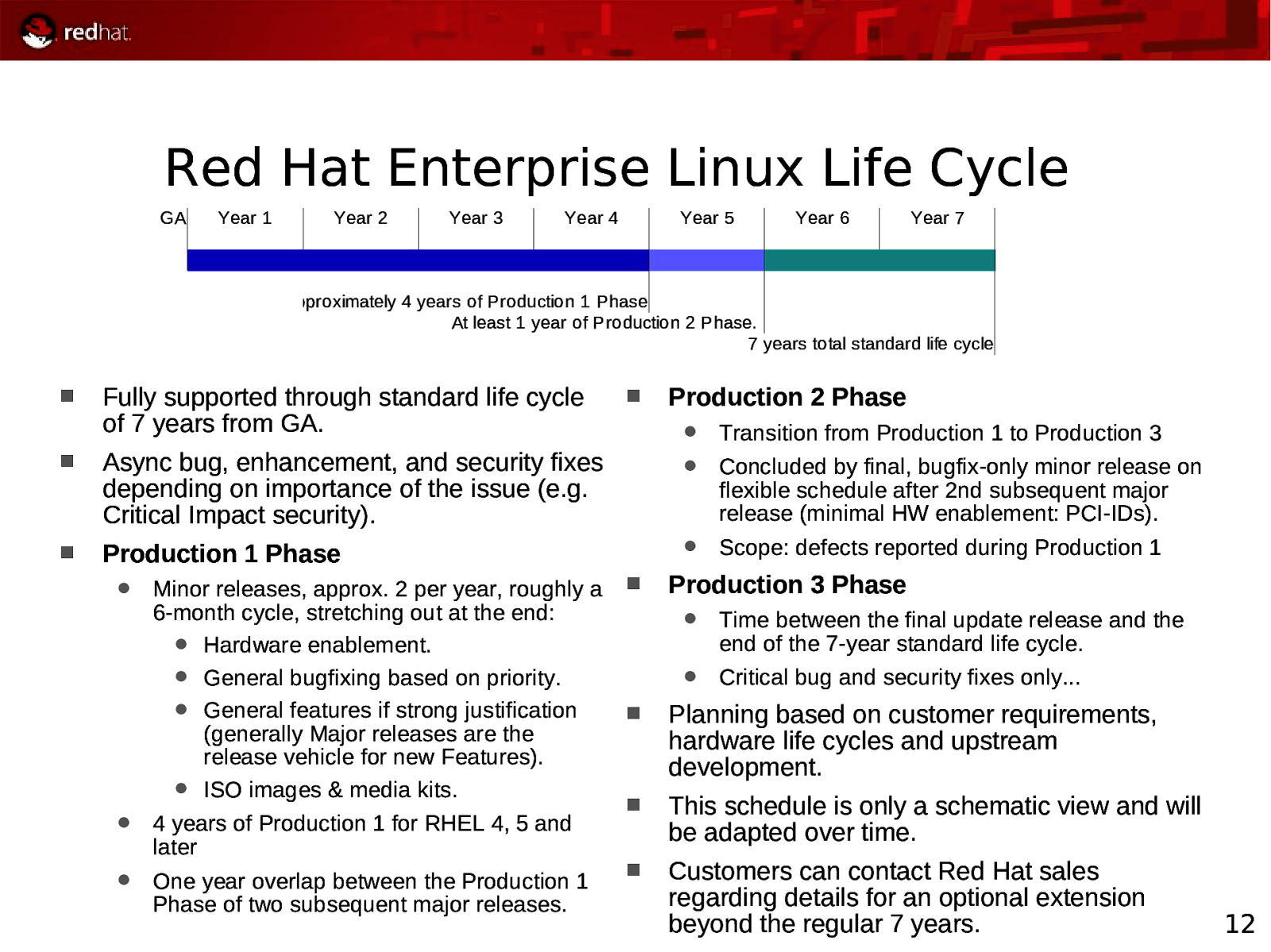
Red Hat Enterprise Linux Life Cycle GA Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Year 7 Approximately 4 years of Production 1 Phase At least 1 year of Production 2 Phase. 7 years total standard life cycle Fully supported through standard life cycle of 7 years from GA. Async bug, enhancement, and security fixes depending on importance of the issue (e.g. Critical Impact security). Production 1 Phase Minor releases, approx. 2 per year, roughly a 6-month cycle, stretching out at the end: Hardware enablement. General bugfixing based on priority. General features if strong justification (generally Major releases are the release vehicle for new Features). ISO images & media kits. 4 years of Production 1 for RHEL 4, 5 and later One year overlap between the Production 1 Phase of two subsequent major releases. Production 2 Phase Transition from Production 1 to Production 3 Concluded by final, bugfix-only minor release on flexible schedule after 2nd subsequent major release (minimal HW enablement: PCI-IDs). Scope: defects reported during Production 1 Production 3 Phase Time between the final update release and the end of the 7-year standard life cycle. Critical bug and security fixes only… Planning based on customer requirements, hardware life cycles and upstream development. This schedule is only a schematic view and will be adapted over time. Customers can contact Red Hat sales regarding details for an optional extension beyond the regular 7 years. 12
Slide 13
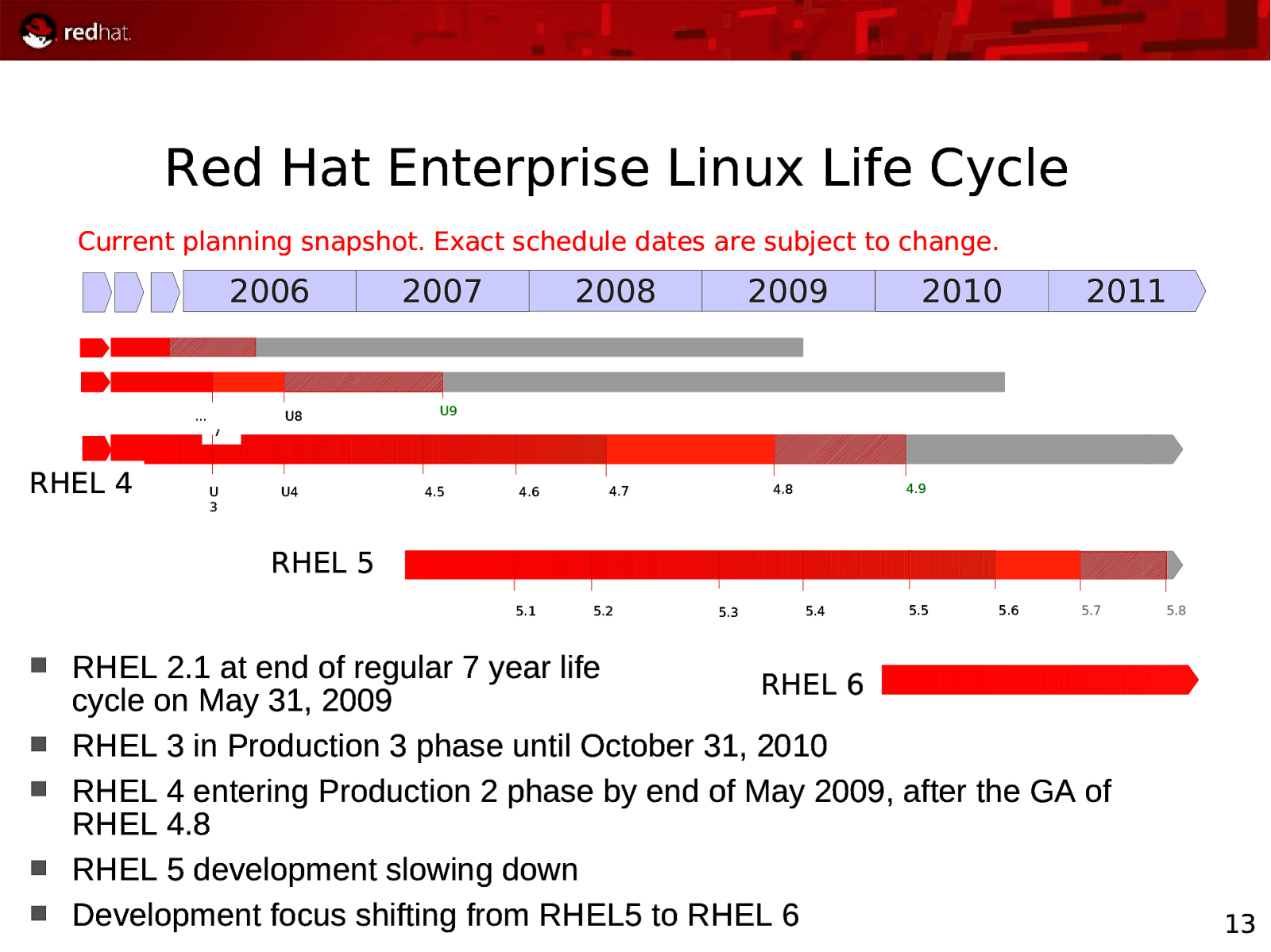
Red Hat Enterprise Linux Life Cycle Current planning snapshot. Exact schedule dates are subject to change. 2006 … U 7 RHEL 4 U 3 U8 U4 2008 2007 2009 2010 2011 U9 4.5 4.6 4.9 4.8 4.7 RHEL 5 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 RHEL 2.1 at end of regular 7 year life RHEL 6 cycle on May 31, 2009 RHEL 3 in Production 3 phase until October 31, 2010 RHEL 4 entering Production 2 phase by end of May 2009, after the GA of RHEL 4.8 RHEL 5 development slowing down Development focus shifting from RHEL5 to RHEL 6 5.8 13
Slide 14

RHEL 5.3 Current Technology
Slide 15
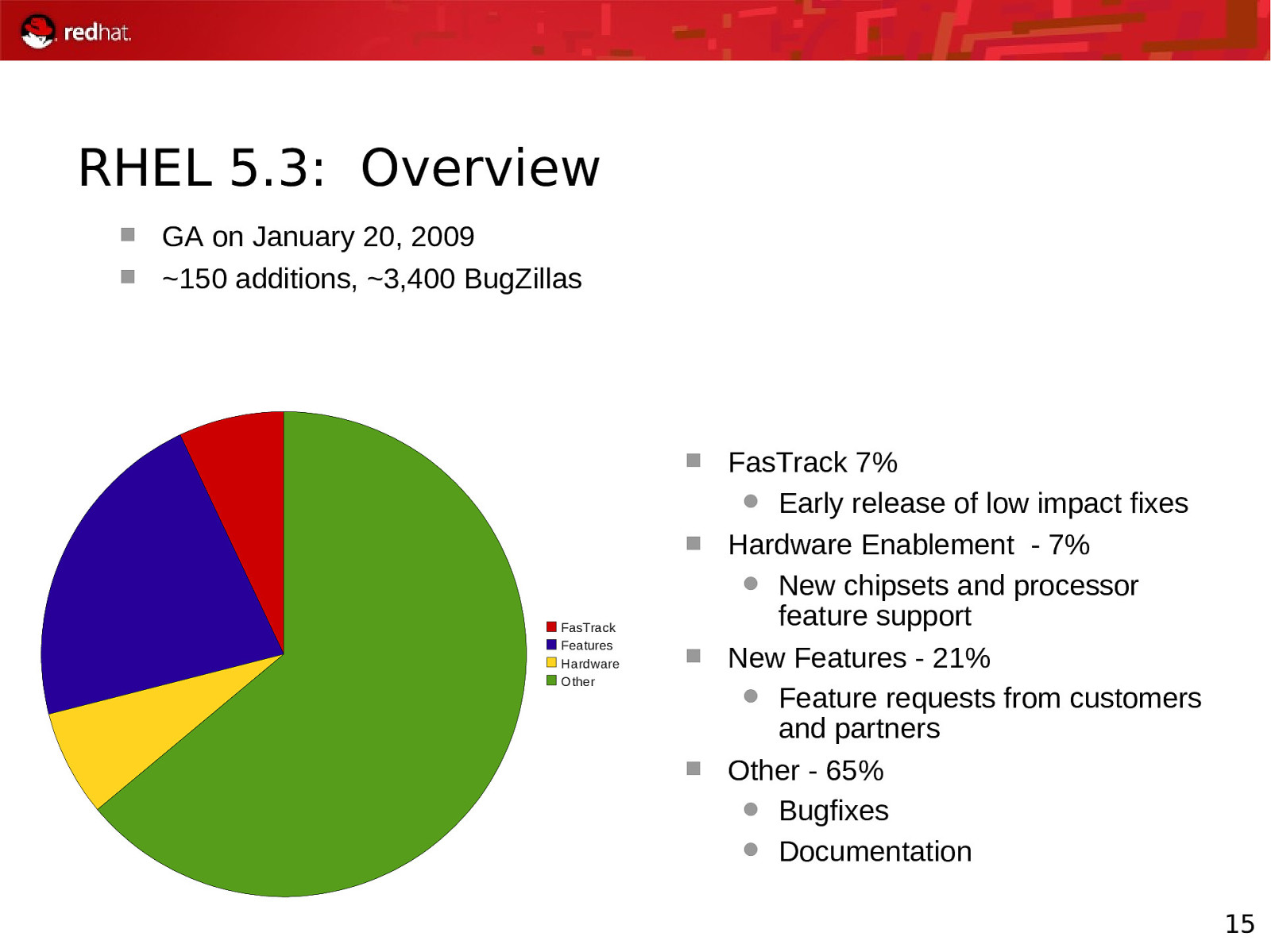
RHEL 5.3: Overview GA on January 20, 2009 ~150 additions, ~3,400 BugZillas FasTrack 7% Early release of low impact fixes Hardware Enablement - 7% New chipsets and processor feature support New Features - 21% Feature requests from customers and partners Other - 65% Bugfixes Documentation FasTrack Features Hardware Other 15
Slide 16

RHEL 5.3: Networking Provision of several selectable TCP congestion modules (2.6.13) Ref: http://lwn.net/Articles/128681/ IPV6 - Support several new sockopt / ancillary data in Advanced API (2.6.14) IPv4/IPv6: UFO (UDP Fragmentation Offload) (2.6.15) Offloads IP fragmentation functionality of large UDP datagram to hardware Improves performance Add nf_conntrack subsystem: (2.6.15) Common IPv4/IPv6 generic connection tracking subsystem Allows IPv6 to have a stateful firewall capability (not previously possible) Increased security Enables analysis of whole streams of packets, rather than only checking the headers of individual packets 16
Slide 17

RHEL 5.3: Networking IPv6 RFC 3484 compliant source address selection (2.6.15) Add support for Router Preference (RFC4191) (2.6.17) Add Router Reachability Probing (RFC4191) (2.6.17) Generic segmentation offload (GSO) (2.6.18) Available in place of TSO (TCP Segmentation Offload) Performance improvements for large packet transfers without hardware assistance SELinux per-packet access controls Replaces old packet controls Add Secmark support to core networking Allows security subsystems to place security markings on network packets (2.6.18) Inclusion of DCCPv6 – Datagram Congestion Control Protocol (2.6.16) 17
Slide 18

RHEL 5.3: Storage Management RAID 4/5/10 support added to dm-raid. Full support for software iSCSI target. Full support for LVM cluster mirror (cmirror). Add the ability to prioritize paths on HP MSA/HSV active/passive storage controllers. Reduce boot time by improving lvmcache, to reduce the amount of device scanning. Enhanced disk partition statistics 18
Slide 19

RHEL 5.3: File System / Storage Mgmt Block device encryption support, including support for /root partition, including configuration in anaconda installer. ext4 tech preview samba: rebased from 3.0.28 to 3.0.32 for bugfixes Now supports Windows Vista and 2008 fixes for DC functionality (interoperability with Citrix and Domain trusts) Ecryptfs fixes (tech preview) 19
Slide 20

RHEL 5.3: System Services Rebased version of CUPS print server, now fully Kerberized dhcpv6 support ktune, a service that sets several kernel tuning parameters to values suitable for specific system profiles. Currently, ktune provides a profile for large-memory systems running disk-intensive and network-intensive applications. New package, tech preview. Package upstream rebases to the following utilities: ksh, lm-sensors, lftp, net-snmp, openIPMI-tool, openldap, openmotif, pythonurlgrabber, openPegasus, VNC RPM to Fedora 9 version, which includes numerous bugfixes yum and yum-utils primarily for speed improvements totem, rb, and gstreamer rebased to enable modular codecs addition Numerous wireshark security fixes 20
Slide 21

RHEL 5.3: Security Enhancements pkinit clients can now be configured to use keys for client certificates which may not contain Kerberos-specific extensions & interoperability fixes nss_ldap now configured with support for paged results extension SELinux: enablement of New NetworkManager and Audit functionality. SELinux: Hundreds of AVC denial fixes. Improved Audit and Logging TTY input audit support Remote audit logging via unencrypted connection 21
Slide 22
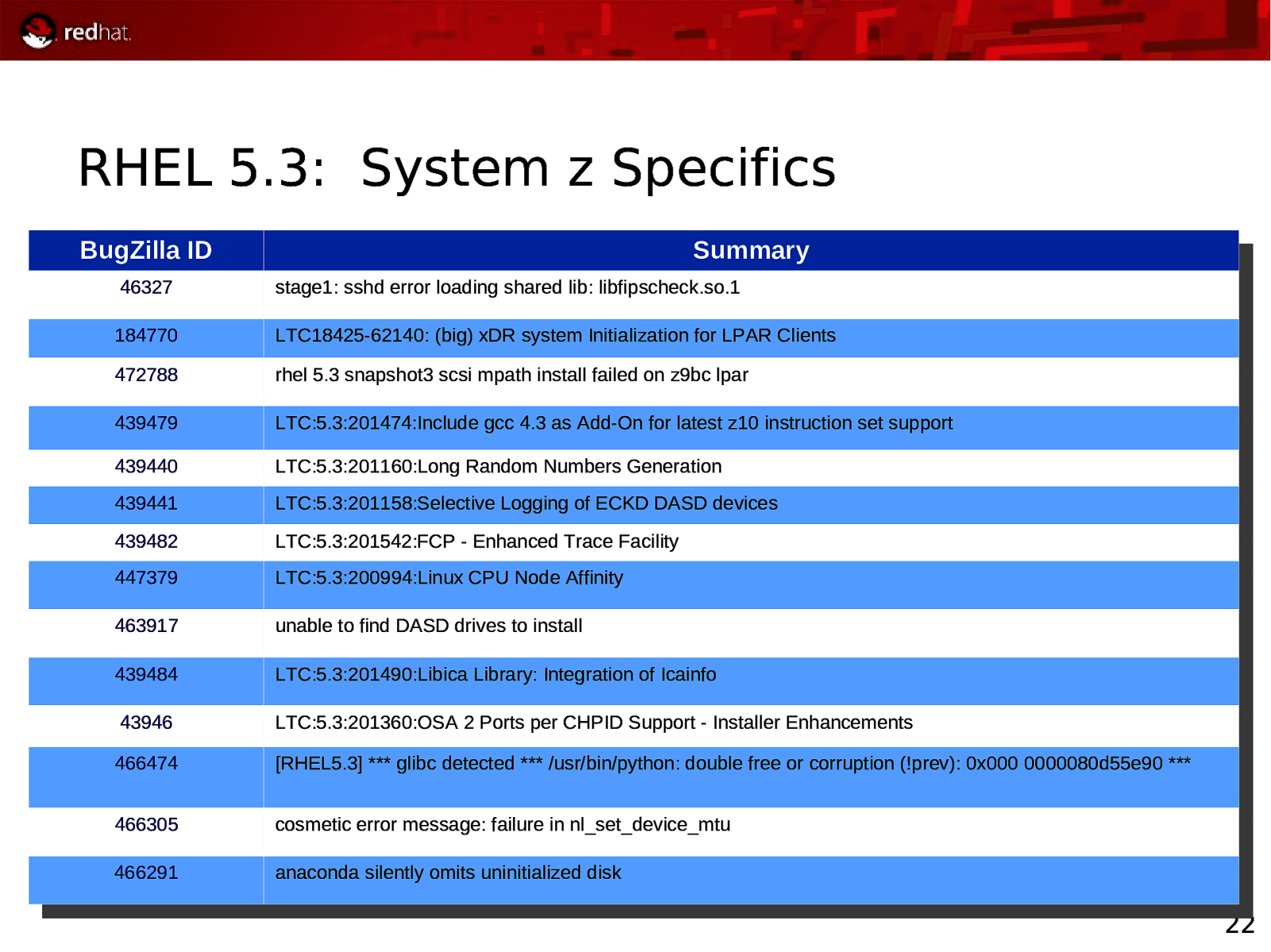
RHEL 5.3: System z Specifics BugZilla ID BugZilla ID Summary Summary 46327 46327 stage1: sshd error loading shared lib: libfipscheck.so.1 stage1: sshd error loading shared lib: libfipscheck.so.1 184770 184770 472788 472788 LTC18425-62140: (big) xDR system Initialization for LPAR Clients LTC18425-62140: (big) xDR system Initialization for LPAR Clients rhel 5.3 snapshot3 scsi mpath install failed on z9bc lpar rhel 5.3 snapshot3 scsi mpath install failed on z9bc lpar 439479 439479 LTC:5.3:201474:Include gcc 4.3 as Add-On for latest z10 instruction set support LTC:5.3:201474:Include gcc 4.3 as Add-On for latest z10 instruction set support 439440 439440 439441 439441 439482 439482 447379 447379 LTC:5.3:201160:Long Random Numbers Generation LTC:5.3:201160:Long Random Numbers Generation LTC:5.3:201158:Selective Logging of ECKD DASD devices LTC:5.3:201158:Selective Logging of ECKD DASD devices LTC:5.3:201542:FCP - Enhanced Trace Facility LTC:5.3:201542:FCP - Enhanced Trace Facility LTC:5.3:200994:Linux CPU Node Affinity LTC:5.3:200994:Linux CPU Node Affinity 463917 463917 unable to find DASD drives to install unable to find DASD drives to install 439484 439484 LTC:5.3:201490:Libica Library: Integration of Icainfo LTC:5.3:201490:Libica Library: Integration of Icainfo 43946 43946 466474 466474 LTC:5.3:201360:OSA 2 Ports per CHPID Support - Installer Enhancements LTC:5.3:201360:OSA 2 Ports per CHPID Support - Installer Enhancements [RHEL5.3] *** glibc detected *** /usr/bin/python: double free or corruption (!prev): 0x000 0000080d55e90 *** [RHEL5.3] *** glibc detected *** /usr/bin/python: double free or corruption (!prev): 0x000 0000080d55e90 *** 466305 466305 cosmetic error message: failure in nl_set_device_mtu cosmetic error message: failure in nl_set_device_mtu 466291 466291 anaconda silently omits uninitialized disk anaconda silently omits uninitialized disk 22
Slide 23

RHE 5.4
Slide 24

RHEL 5.4 : Overview The official GA release of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.4 (kernel-2.6.18-164.el5) was released on 02-Sep-2009 Generic (not s390 specific) updates include Virtualization: full support for the Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) hypervisor only on x86_64 while Xen only x86 & Power based virtualization is still available & supported Network: Kernel & Userspace update to support Generic Receive Offload (GRO) which increases the performance of inbound network connections by reducing the amount of processing done by the CPU. Furthermore Netfilter Framework & Bind Updates Storage: Support for the XFS file system has also been added to the kernel as a Technology Preview. Tools: SystemTap is now fully supported, and has been re-based to the latest upstream version. 24
Slide 25

RHEL 5.4: File System / Storage Mgmt Add integrity check to cryptsetup-luks, in order to meet FIPS-140 requirements. Ext4 - refreshed the backport for our tech preview to bring in bug fixes and support for delayed allocation. File system freeze/quiesce interface added to support hardware snapshots for file systems. Full support for FUSE and libfuse to allow end users to more easily install and use their own user space FUSE file systems. 25
Slide 26
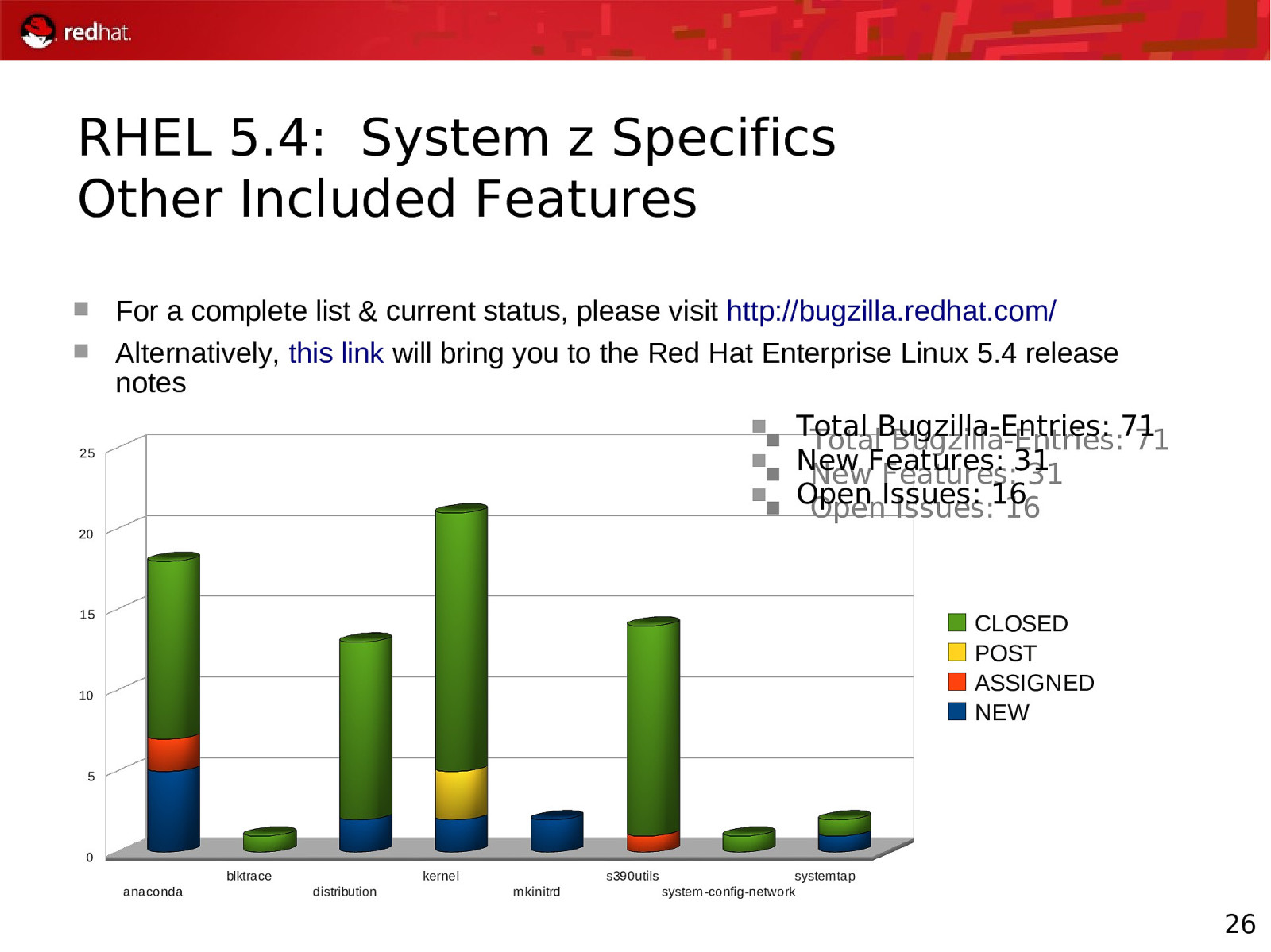
RHEL 5.4: System z Specifics Other Included Features For a complete list & current status, please visit http://bugzilla.redhat.com/ Alternatively, this link will bring you to the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.4 release notes Total Bugzilla-Entries: 71 Total Bugzilla-Entries: 71 25 New Features: 31 New Features: 31 Open Issues: 16 Open Issues: 16 20 15 CLOSED POST ASSIGNED NEW 10 5 0 blktrace anaconda kernel distribution s390utils m kinitrd system tap system -config-network 26
Slide 27

RHEL 5.4: System z Specifics BugZilla BugZillaID ID Summary Summary 475556 475556 475569 475569 461288 461288 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] DS8000 support: Large volume support (userspace) [201738] [LTC 5.4 FEAT] DS8000 support: Large volume support (userspace) [201738] [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Shutdown actions tools [201755] [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Shutdown actions tools [201755] [EMC 5.4 feat] Require kernel support to issue Control I/O to CKD dasd on EMC Symmetrix [EMC 5.4 feat] Require kernel support to issue Control I/O to CKD dasd on EMC Symmetrix arrays arrays [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Automatic IPL after dump (kernel) [201169] [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Automatic IPL after dump (kernel) [201169] [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Improve checking mechanisms and workflow of Linux on System z Anaconda [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Improve checking mechanisms and workflow of Linux on System z Anaconda install process [201676] install process [201676] [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Program directed IPL support - no XML in system dumper [200782] [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Program directed IPL support - no XML in system dumper [200782] [LTC 5.4 FEAT] FCP - Performance data reports [201730] [LTC 5.4 FEAT] FCP - Performance data reports [201730] [LTC 5.4 FEAT] 201173:Crypto Hardware Enablement Device Driver Support - toleration [LTC 5.4 FEAT] 201173:Crypto Hardware Enablement Device Driver Support - toleration [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Shutdown actions interface (userspace) [201748] [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Shutdown actions interface (userspace) [201748] [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Dynamic CPU hotplug daemon for System z [201132] [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Dynamic CPU hotplug daemon for System z [201132] [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Change list of Anaconda network alternatives to indicate supported devices [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Change list of Anaconda network alternatives to indicate supported devices on System z [201679] on System z [201679] [LTC 5.4 FEAT] TTY terminal server over IUCV (kernel) [201734] [LTC 5.4 FEAT] TTY terminal server over IUCV (kernel) [201734] 474688 474688 475346 475346 475670 475670 475552 475552 488496 488496 475564 475564 474679 474679 475345 475345 475551 475551 27
Slide 28
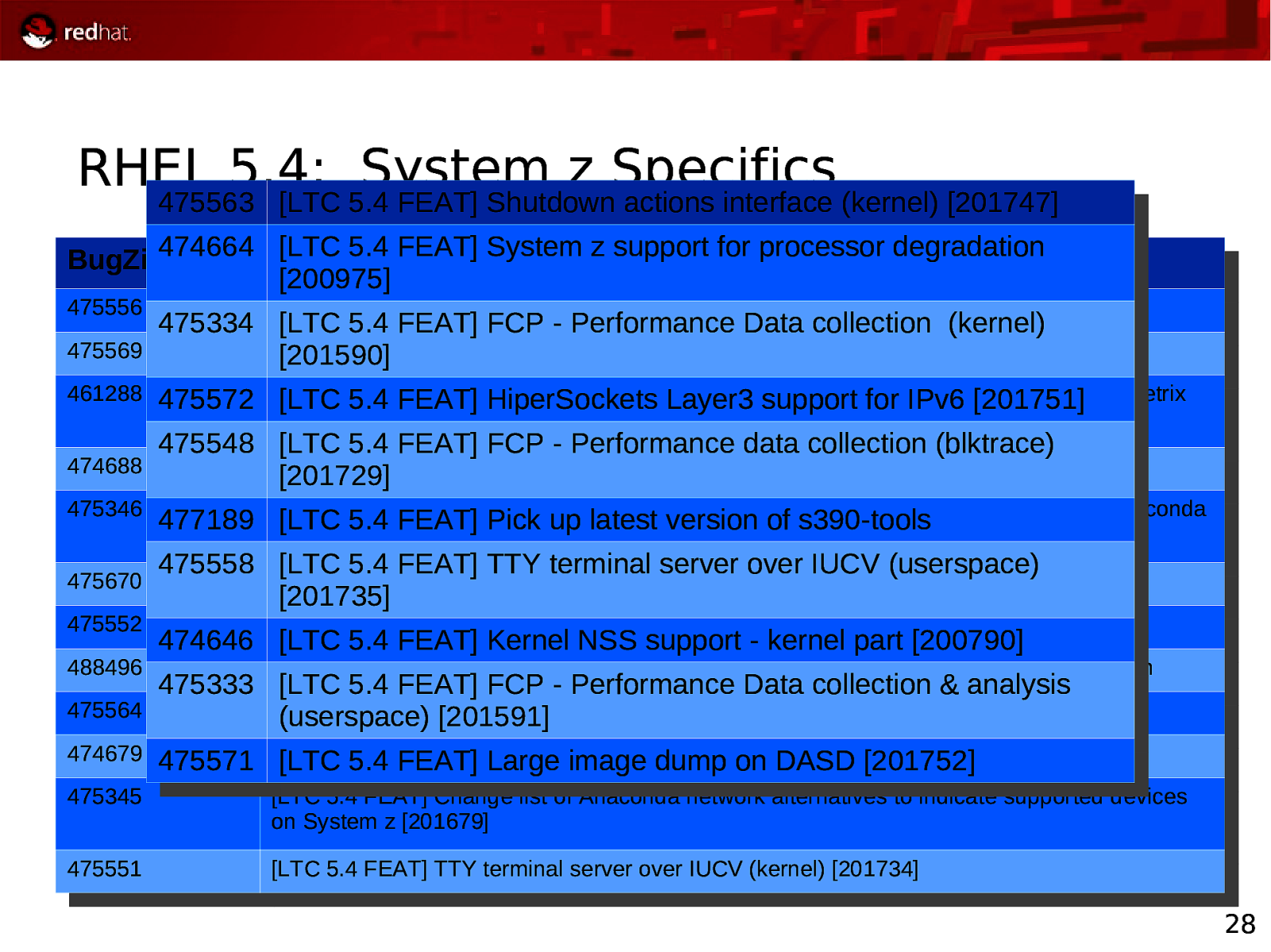
RHEL 5.4: System z Specifics 475563 475563 [LTC [LTC5.4 5.4FEAT] FEAT]Shutdown Shutdownactions actionsinterface interface(kernel) (kernel)[201747] [201747] 474664 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] System zzsupport for processor degradation BugZilla ID Summary 474664 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] System support for processor degradation BugZilla ID Summary [200975] [200975] 475556 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] DS8000 support: Large volume support (userspace) [201738] 475556 475334 [LTC [LTC 5.4 FEAT] DS8000 support: Large volume support (userspace) [201738] 5.4 FEAT] FCP - -Performance Data collection (kernel) 475334 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] FCP Performance Data collection (kernel) 475569 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Shutdown actions tools [201755] [201590] 475569 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Shutdown actions tools [201755] [201590] 461288 475572 [EMC 5.4 feat] Require kernel support toLayer3 issue Control I/O tofor CKD dasd on EMC Symmetrix 5.4 FEAT] HiperSockets support IPv6 [201751] 461288 475572 [LTC [EMC 5.4 feat] Require kernel support to issue Control I/O to CKD dasd on EMC Symmetrix [LTC 5.4 FEAT] HiperSockets Layer3 support for IPv6 [201751] arrays arrays 475548 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] FCP - Performance data collection [LTC FEAT] FCP Performance data collection(blktrace) (blktrace) 474688 475548 [LTC 5.4 5.4 FEAT] Automatic IPL- after dump (kernel) [201169] [201729] 474688 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Automatic IPL after dump (kernel) [201169] [201729] 475346 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Improve checking mechanisms and workflow of Linux on System z Anaconda 5.4 FEAT] Pickchecking up latest version and of s390-tools 475346 477189 [LTC [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Improve mechanisms workflow of Linux on System z Anaconda process [201676]Pick up latest version of s390-tools 477189 install [LTC 5.4 FEAT] install process [201676] 475558 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] TTY terminal server over IUCV (userspace) [LTC FEAT] TTY terminal server over (userspace) 475670 475558 [LTC 5.4 5.4 FEAT] Program directed IPL support - no XMLIUCV in system dumper [200782] 475670 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Program directed IPL support - no XML in system dumper [200782] [201735] [201735] 475552 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] FCP - Performance data reports [201730] 475552 474646 [LTC [LTC 5.4 FEAT] FCPKernel - Performance data reports [201730]part [200790] 5.4 FEAT] NSS support - -kernel 474646 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Kernel NSS support kernel part [200790] 488496 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] 201173:Crypto Hardware Enablement Device Driver Support - toleration 488496 475333 [LTC [LTC 5.4 FEAT] 201173:Crypto Hardware Enablement Device Driver Support - toleration 5.4 FEAT] FCP Performance Data collection & analysis 475333 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] FCP Performance Data collection & analysis 475564 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Shutdown actions interface (userspace) [201748] (userspace) [201591] 475564 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Shutdown (userspace) [201591]actions interface (userspace) [201748] 474679 475571 [LTC 5.45.4 FEAT] Dynamic CPUimage hotplugdump daemonon forDASD System [201752] z [201132] FEAT] Large 474679 475571 [LTC [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Dynamic CPU hotplug daemon for System z [201132] [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Large image dump on DASD [201752] 475345 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Change list of Anaconda network alternatives to indicate supported devices 475345 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Change list of Anaconda network alternatives to indicate supported devices on System z [201679] on System z [201679] 475551 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] TTY terminal server over IUCV (kernel) [201734] 475551 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] TTY terminal server over IUCV (kernel) [201734] 28
Slide 29
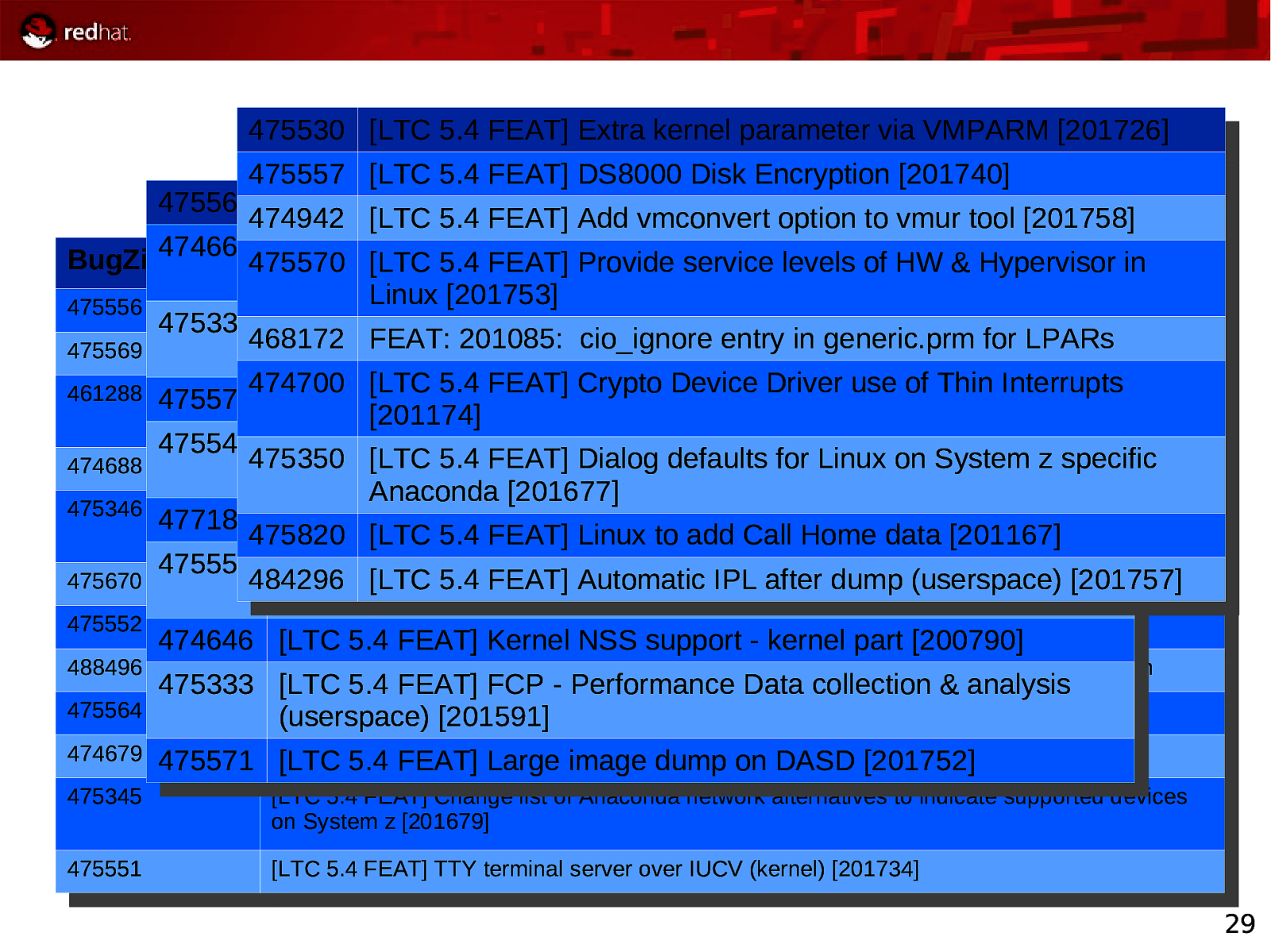
475530 475530 [LTC [LTC5.4 5.4FEAT] FEAT]Extra Extrakernel kernelparameter parametervia viaVMPARM VMPARM[201726] [201726] 475557 475557 [LTC [LTC5.4 5.4FEAT] FEAT]DS8000 DS8000Disk DiskEncryption Encryption[201740] [201740] 475563 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Shutdown actions interface (kernel) [201747] 475563 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Shutdown actions interface (kernel) [201747] 474942 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Add vmconvert option to vmur 474942 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Add vmconvert option to vmurtool tool[201758] [201758] 474664 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] System z support for processor degradation BugZilla ID Summary 474664 [LTC 5.4 FEAT]FEAT] System z support for processor degradation [LTC BugZilla ID 475570 Summary 475570 [LTC5.4 5.4 FEAT]Provide Provideservice servicelevels levelsofofHW HW&&Hypervisor Hypervisorinin [200975] [200975] Linux [201753] 475556 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] DS8000 support: Large volume support (userspace) [201738] Linux [201753] 475556 475334 [LTC [LTC 5.4 FEAT] DS8000 support: Large volume support (userspace) [201738] 5.4 FEAT] FCP - -Performance Data collection (kernel) 475334 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] FCP Performance Data collection (kernel) 468172 FEAT: 201085: cio_ignore entry in generic.prm for LPARs 475569 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Shutdown actions tools [201755] 468172 FEAT: 201085: cio_ignore entry in generic.prm for LPARs [201590] 475569 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Shutdown actions tools [201755] [201590] [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Crypto Device Driver ofofdasd Thin Interrupts 461288 475572474700 [EMC 5.4 feat] Require kernel support toLayer3 issue Control I/Ouse to CKD on EMC Symmetrix [LTC 5.4HiperSockets FEAT] Crypto Device Driver use Thin Interrupts [LTC 5.4 FEAT] support for IPv6 [201751] 461288 475572474700 [EMC 5.4 feat] Require kernel support to issue Control I/O to CKD dasd on EMC Symmetrix [LTC 5.4 FEAT] HiperSockets Layer3 support for IPv6 [201751] [201174] arrays [201174] arrays 475548 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] FCP - -Performance data collection (blktrace) [LTC 5.4 FEAT] FCP Performance data collection (blktrace) 475350 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Dialog defaults for Linux on System zzspecific 474688 475548 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Automatic IPL after dump (kernel) [201169] 475350 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Dialog defaults for Linux on System specific [201729] 474688 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Automatic IPL after dump (kernel) [201169] [201729] Anaconda [201677] Anaconda 475346 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Improve [201677] checking mechanisms and workflow of Linux on System z Anaconda 5.4 FEAT] Pick up latest version ofofs390-tools 475346 477189 [LTC [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Improve checking mechanisms and workflow of Linux on System z Anaconda install process [201676] 477189 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Pick up latest version s390-tools [201167] 475820 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Linux to add Call Home install process 475820 [LTC[201676] 5.4 FEAT] Linux to add Call Homedata data [201167] 475558 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] TTY terminal server over IUCV (userspace) [LTC FEAT] TTY terminal server over (userspace) 475670 475558 [LTC 5.4 5.4 FEAT] directed IPL support - no XMLIUCV in system dumper [200782] 484296 [LTC 5.4 Automatic IPL after dump (userspace) [201757] 475670 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Program directed IPL support - noafter XML dump in system dumper [200782] 484296 [LTCProgram 5.4FEAT] FEAT] Automatic IPL (userspace) [201757] [201735] [201735] 475552 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] FCP - Performance data reports [201730] 475552 474646 [LTC [LTC 5.4 FEAT] FCP - Performance data reports [201730]part [200790] 474646 [LTC5.4 5.4FEAT] FEAT]Kernel KernelNSS NSSsupport support- -kernel kernel part [200790] 488496 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] 201173:Crypto Hardware Enablement Device Driver Support - toleration 488496 475333 [LTC [LTC 5.4 FEAT] 201173:Crypto Hardware Enablement Device Driver Support - toleration 5.4 FEAT] FCP - -Performance Data collection &&analysis 475333 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] FCP Performance Data collection analysis 475564 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Shutdown actions interface (userspace) [201748] (userspace) [201591] 475564 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Shutdown (userspace) [201591]actions interface (userspace) [201748] 474679 475571 [LTC 5.45.4 FEAT] Dynamic CPUimage hotplugdump daemonon forDASD System [201752] z [201132] FEAT] Large 474679 475571 [LTC [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Dynamic CPU hotplug daemon for System z [201132] [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Large image dump on DASD [201752] 475345 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Change list of Anaconda network alternatives to indicate supported devices 475345 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] Change list of Anaconda network alternatives to indicate supported devices on System z [201679] on System z [201679] 475551 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] TTY terminal server over IUCV (kernel) [201734] 475551 [LTC 5.4 FEAT] TTY terminal server over IUCV (kernel) [201734] 29
Slide 30

S390-tools package rebased to Version 1.8.1 The s390utils package has been rebased to version 1.8.1. This package provides the essential tool chain for Linux on System z. It contains everything from the boot loader to dump related tools for a system crash analysis . News Features (excerpt) DASD related tools: Add Large Volume Support for ECKD DASDs Ipl_tools: Can be used to change the reipl & shutdown behaviour ziomon tools: Set of tools to collect data for zfcp performance analysis. lsluns: List available SCSI LUNs depending on adapter or port. lszcrypt: Show information about zcrypt devices and configuration. chzcrypt: Modify zcrypt configuration. cpuplugd: Daemon that manages CPU- and memory-resources based on a set of rules. Depending on the workload CPUs can be enabled or disabled. The amount of memory can be increased or decreased exploiting the Cooperative Memory Management (CMM1) feature. chchp: Tool to modify channel-path states lschp: Tool to list information about available channel-paths. mon_procd: Daemon that writes process information data to the z/VM monitor stream. vmur: Tool to work with z/VM spool file queues (reader, punch, printer). zfcpdump_v2: Version 2 of the zfcpdump tool. Now based on the upstream Linux kernel 2.6.23. 30 Plus various bug fixes
Slide 31
Kernel Control Program Identification (CPI) If your RHEL5.4 Linux instance runs in LPAR mode, you can now use the extended control program identification (CPI) module, sclp_cpi and the sysfs interface /sys/firmware/cpi to assign names to your Linux instance The names are used, for example, to identify the Linux instance on the HMC. This feature is only available while running in LPAR Extra kernel parameter via VMPARM Modify the IPL records to append extra parameters specified with the z/VM VMPARM option to the kernel command line. Support for processor degradation Adds support for processor degradation, which allows processor speed to be reduced in some circumstances (i.e. system overheating). This new feature allows automation software to observe the machine state. TTY terminal server over IUCV Provide central access to the Linux console for the different guests of a z/VM. The terminal server connects to the different guests over IUCV. The IUCV based console is ASCII based. Fullscreen applications like vi are usable on the console. 31
Slide 32
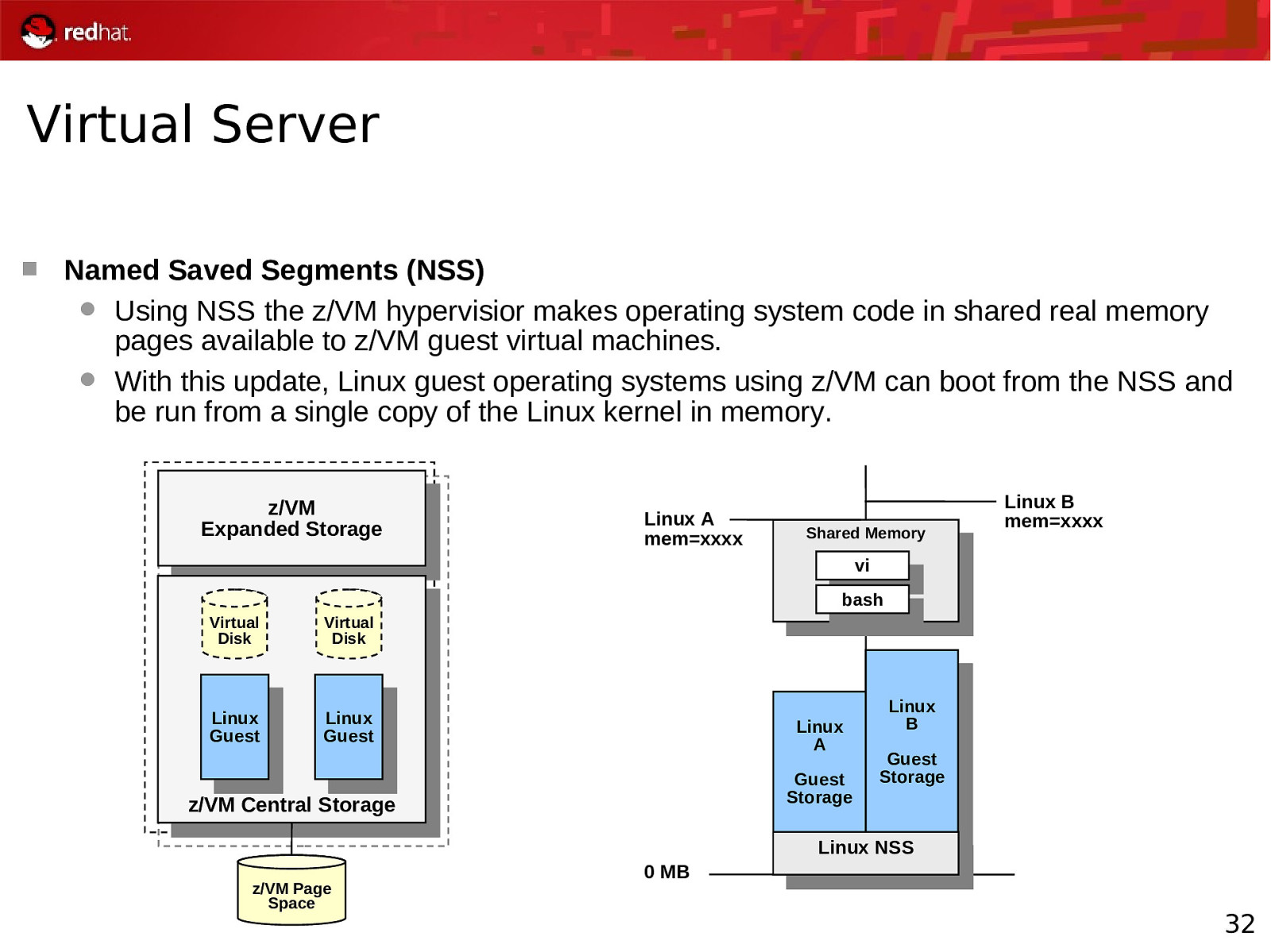
Virtual Server Named Saved Segments (NSS) Using NSS the z/VM hypervisior makes operating system code in shared real memory pages available to z/VM guest virtual machines. With this update, Linux guest operating systems using z/VM can boot from the NSS and be run from a single copy of the Linux kernel in memory. z/VM Expanded Storage Linux A mem=xxxx Shared Memory Linux B mem=xxxx vi bash Virtual Disk Virtual Disk Linux Guest Linux Guest Linux A Guest Storage z/VM Central Storage Linux B Guest Storage Linux NSS z/VM Page Space 0 MB 32
Slide 33

Networking HiperSockets Layer3 Support for IPv6 How IPv6 support for HiperSockets devices running in layer 3 mode is available IPv6 is supported on: Ethernet interfaces of the OSA-Express adapter running in QDIO mode. HiperSockets layer 2 and layer 3 interfaces z/VM guest LAN interfaces running in QDIO mode. IPv6 is not supported on the OSA-Express Token Ring and ATM features. 33
Slide 34

RAS Multi volume dump support for DASDs Added the ability to dump on multiple ECKD DASD devices, which can be necessary, if the system memory size is larger than the size of a single DASD device. Service Levels of Hardware & Hypervisor A new Interface which provides service levels of hardware and z/VM service-levels to the Linux userspace. Interface: /proc/service_levels Lstape support for SCSI Tapes With this feature it is now possible to list installed FCP-attached tape devices (SCSI tapes) besides channel attached tapes using the lstape command Shutdown Actions Interface The new shutdown actions interface allows to specify for each shutdown trigger (halt, power off, reboot, panic) one of the five available shutdown actions (stop, ipl, reipl, dump, vmcmd). A sysfs interface under /sys/firmware is provided for that purpose. Possible use cases are e.g. to specify that a vmdump should be automatically triggered in case of a kernel panic or the z/VM logoff command should be executed on halt. Automatic IPL after dump The new shutdown action dump_reipl is introduced. It combines the actions dump and 34 re-ipl, first a dump is taken, then a re-ipl of the system is triggered
Slide 35
Storage FCP performance data collection & reports: Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP) performance data can now be measured. Metrics that are collected and reported on include: Performance relevant data on stack components such as Linux devices, Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) Logical Unit Numbers (LUNs) and Host Bus Adapter (HBA) storage controller information. Per stack component: current values of relevant measurements such as throughput, utilization and other applicable measurements. Statistical aggregations (minimum, maximum, averages and histogram) of data associated with I/O requests including size, latency per component and totals. DS8K Encryption Support This feature enhances s390-tools to be able to display if the Storage has its disk encrypted or not. Kernel support to issue Control I/O to dasd on EMC Symmetrix arrays Support has been added to the kernel to issue EMC Symmetrix Control I/O. This update provides the ability to manage EMC Symmetrix storage arrays. 35
Slide 36

Future Linux on System z Technology
Slide 37
Advanced Virtualization Dynamic Memory Add/Remove (kernel 2.6.27) Enable to attach and use standby memory that is configured for a logical partition or z/VM guest. Memory Attach & Detach requires running Linux on System z as a VM-guest requires z/VM 5.4 plus the PTF for APAR VM64524. Standby CPU activation/deactivation (kernel 2.6.25) Allow standby CPUs to be activated / deactivated Suspend / Resume (kernel 2.6.31) With suspend and resume support, you can stop a running Linux on System z instance and later continue operations. When Linux is suspended, data is written to a swap partition. The resume process uses this data to make Linux continue from where it left off when it was suspended. A suspended Linux instance does not require memory or processor cycles. 37
Slide 38
Storage Support HyperPav (kernel 2.6.25) HyperPav is addressing the need to access more data with good performance and high availability! This feature, which required a IBM DS8000™ disk storage system in average leads to a higher utilization, resulting in I/O transfer rates. Activated automatically when the necessary prerequisites are there (DS8000 with HyperPAV LIC, z/VM 5.3). Transparent for the Linux on System z guest DASD Large Volume Support (> kernel 2.6.29) Large Volume Support is a feature that allows to use ECKD devices with more than 65520 cylinders. This features is available with DS8000 R4.0 High Performance FICON (HPF) (kernel 2.6.29) Added HPF support to the DASD Device Driver HPF is an extension to the FICON architecture and is designed to improve the execution of small block I/O requests. HPF streamlines the FICON architecture and reduces the overhead on the channel processors, control unit ports, switch ports, and links by improving the way channel programs are written and processed. 38
Slide 39

Usability & Serviceability Automatic IPL After Dump (kernel 2.6.30) Extension to the shutdown action interface which combines the actions dump and reipl, first a dump is taken, then a re-ipl of the system is triggered Compiler Improvements (gcc 4.3/4.4) – The latest compiler enhancements allow a customer to recompile existing applications which can be optimized for the latest hardware generation without any changes to the source code. – This can lead up to a > 10 % performance improvement. Large Page Support (kernel 2.6.25) – Support for a new access method to allocate larger chunks of memory, resulting in performance improvements, especially in Java based environments – This feature exploits z10 hardware features and provides a software emulation for older systems. 39
Slide 40

Miscellaneous STP/ETR Support (kernel 2.6.27) Support for clock synchronization using the server time protocol (STP) or an external time reference (ETR). Kernel vdso support (kernel 2.6.29) Kernel provided shared library to speed up a few system calls (gettimeofday, clock_getres, clock_gettime) 40
Slide 41

Q&A
Slide 42

Contact Shawn D. Wells W/W System z Sales, Strategy, Marketing sdw@redhat.com Cell: (+1) 443-534-0130 (US EST) Hans J. Picht Linux on System z RedHat Liaison hans@de.ibm.com Cell (+49) 175-1629-201 (CET) 42