Managing your Red Hat Enterprise Linux guests with RHN Satellite Brad Hinson: Sr. Support Engineer Lead on System z, Red Hat Shawn Wells: Lead, Linux on System z, Red Hat
Slide 1

Slide 2
Red Hat Network Red Hat’s modular, Webbased Linux management platform ● Highly scalable solution ● Integrates with existing platforms Modular approach ● Updates – Management – Provisioning – Monitoring
Slide 3
What is Red Hat Network? A systems management platform designed to provide complete lifecycle management of the operating system and applications. A single solution for lifecycle management of compute resources ● Installing and provisioning new system ● Updating systems ● Managing configuration files ● Monitoring performance ● Redeploying for a new purpose
Slide 4

Why use Red Hat Network? Red Hat Network makes Linux: Deployable ● Provision thousands of machines at once without touching them Scalable ● Expand IS/IT capabilities without expanding resources Manageable ● Update 1,000 systems as easily as 1 Consistent ● Ensure that security fixes and configuration changes are applied across your organization
Slide 5

Benefits of Red Hat Network Lower system administration costs ● Management tools let you maximize your hardware investment ● Complete installation takes only minutes (Hosted) to 12 days (Satellite) Increase productivity ● 410X system admin productivity, easily allowing 150+ systems/system admin ● Flexible architecture allows use of GUI, API, or CLI (scripted) interface ● All tasks automated allowing you to move beyond “guru bottleneck” Improve security ● Content stream comes directly & immediately from Red Hat ● Complete audit trail and various predefined reports ● Policies and permissions provide centrally managed rolebased administration
Slide 6

Example: Using Red Hat Network for adaptive infrastructure Many enterprises want to use hardware more efficiently ● ● Demand for externallyfacing services often shifts. In order to adapt to changing demand conditions, administrators need flexible systems It can take hours to manually redeploy a single system Detect when demand increases ● ● Red Hat Network can alert you when systems or applications reach defined levels of performance Allows you to take action before customers notice performance degradation Redeploy systems quickly ● ● ● Red Hat Network stores profiles that can include packages, custom applications, configuration files, and more Use the profiles to change underutilized systems to the type of system needed to meet current business needs In 2030 minutes, you can have hundreds of systems redeployed
Slide 7
Red Hat Network components Service Modules ● ● ● ● Update Management Provisioning Monitoring Architectures ● ● Hosted Satellite
Slide 8
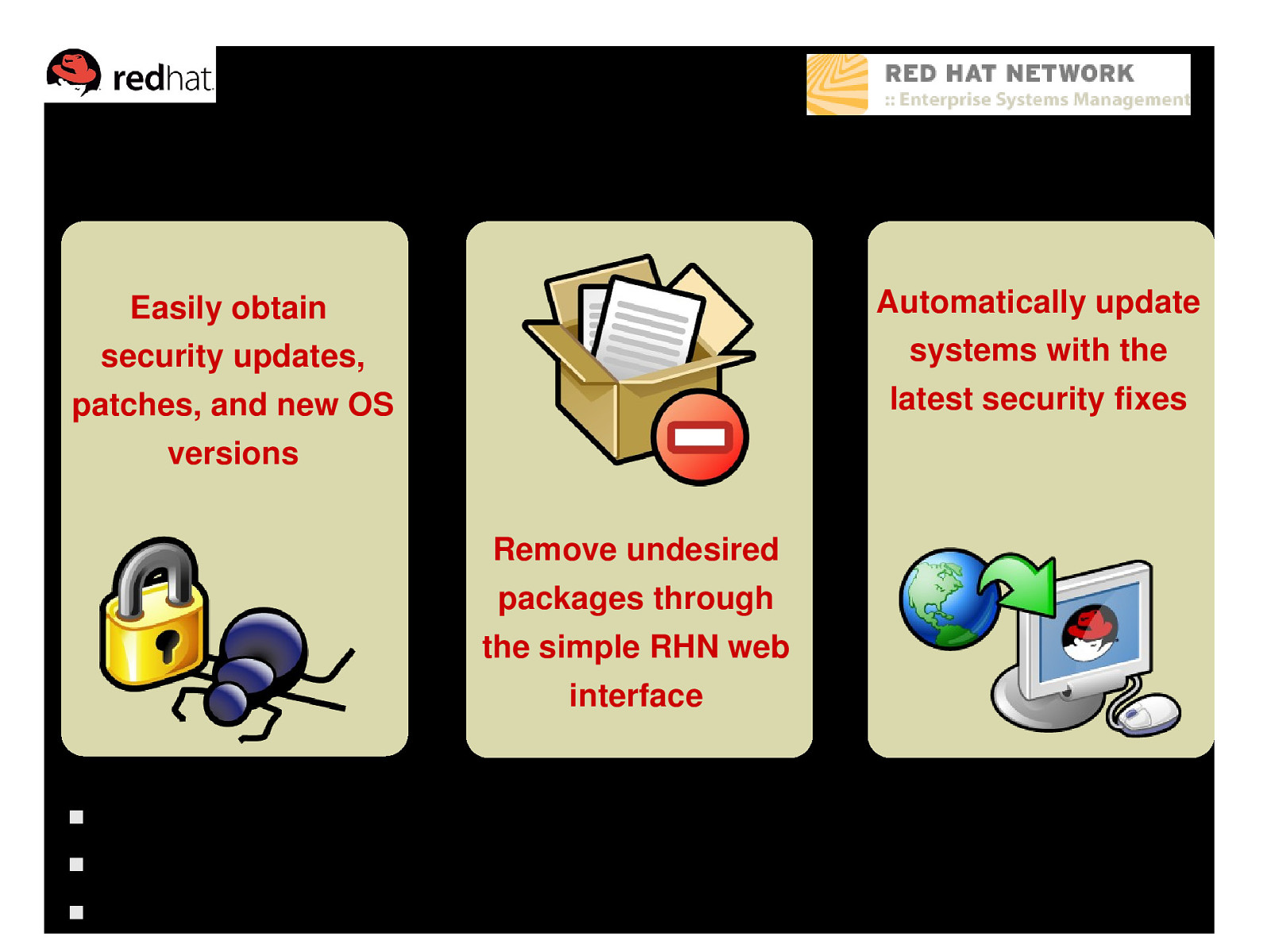
Update Module Automatically update Easily obtain systems with the security updates, latest security fixes patches, and new OS versions Remove undesired packages through the simple RHN web interface Included in every Enterprise Linux subscription All content is digitally signed for added security Full dependency checking ensures the integrity of your system
Slide 9
Management Module Easily obtain security updates, patches, and new OS versions Manage groups of systems as easily as a single system Assign permissions Assign permissions to administrators for to administrators for managing different managing different groups or roles groups or roles Remove undesired packages Schedule updates to occur during maintenance windows Powerful search capabilities let you identify systems based on packages, system information, and much more Compare package profiles between systems to quickly spot differences Manage both Enterprise Linux and Solaris systems within the same RHN interface
Slide 10
Provisioning Module Undo problematic Provision existing or changes with bare metal systems snapshots and using rollback predetermined profiles or system cloning Improve consistency by using RHN to manage and deploy configuration files Use Provisioning to deploy Enterprise Linux, other applications, and customized configuration files Kickstart writer lets you quickly create templates used for provisioning Issue remote commands to perform additional pre and postinstall instructions
Slide 11
Monitoring Module Group probes into suites for fast deployment Dozens of low impact probes can be set for each system Receive email or pager notices when a probe reaches a predefined warning or critical threshold Monitor systems, as well as applications from Oracle, BEA, Apache, and MySQL View reports and graphs of probe performance over time Temporarily disable notifications – helpful when performing system maintenance Monitoring Module requires a Satellite deployment model
Slide 12
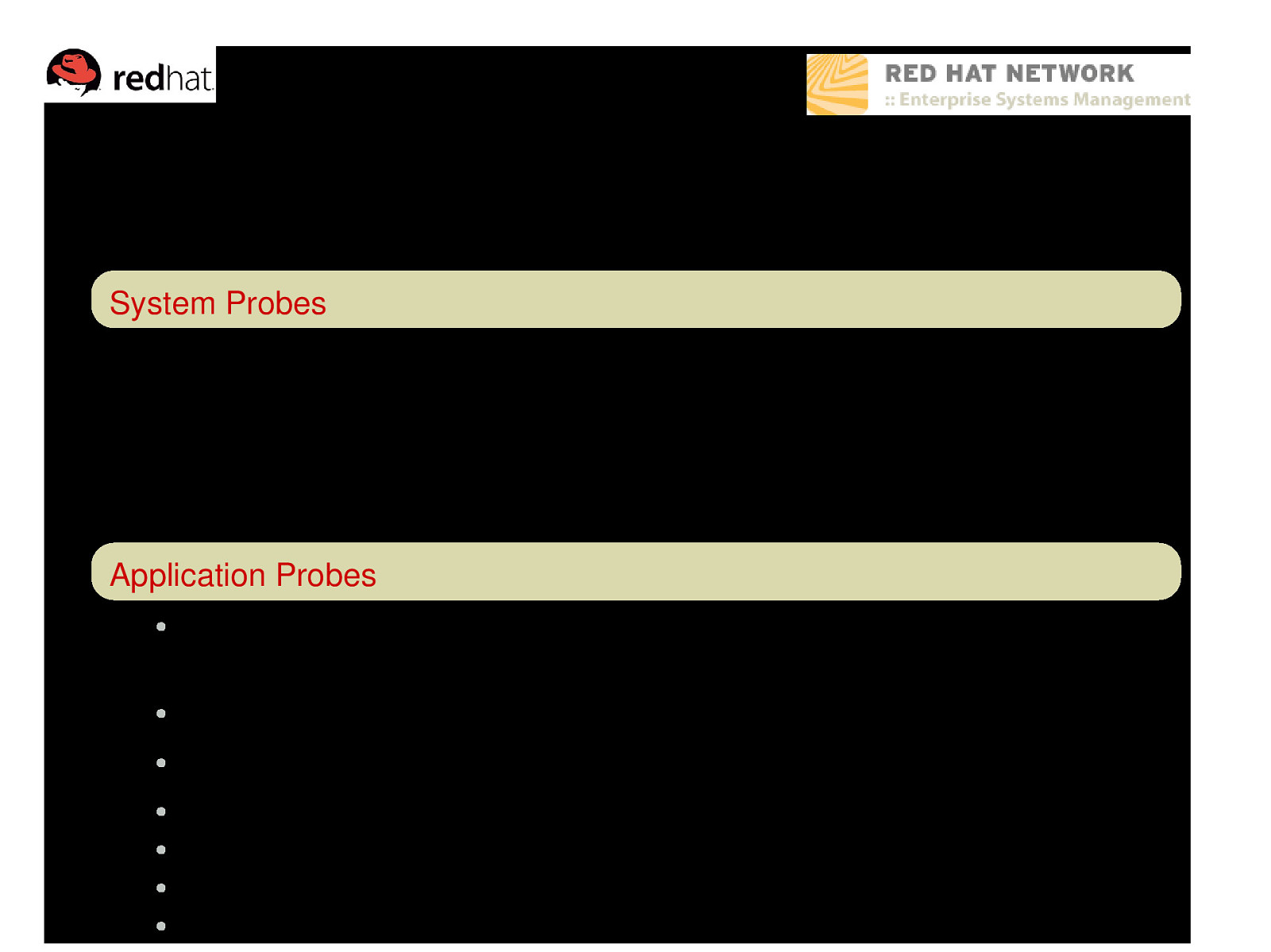
What can be monitored? System Probes Linux: CPU Usage, Disk I/O Throughput, Disk Usage, Interface Traffic, Load, Memory Usage, Process Health, … Network: FTP, HTTP, HTTPS, IMAP, Ping, POP, RPCService, SSH, SMTP, … Log Agent: Log Size, Pattern Matching, … Application Probes ● Oracle 8i/9i: Availability, Client Connectivity, Disk Sort Ratio, Index Extents, Locks, Sessions, Tablespace Usage, TNS Ping, … ● BEA Weblogic: Heap Free, JDBC Connection Pool, Server State, … ● Apache: Processes, Traffic, Uptime ● MySQL: Database Accessibility, Opened Tables, Query Rate, Threads Running ● ● ● You can also create your own probes using tools provided through Red Hat Network.
Slide 13
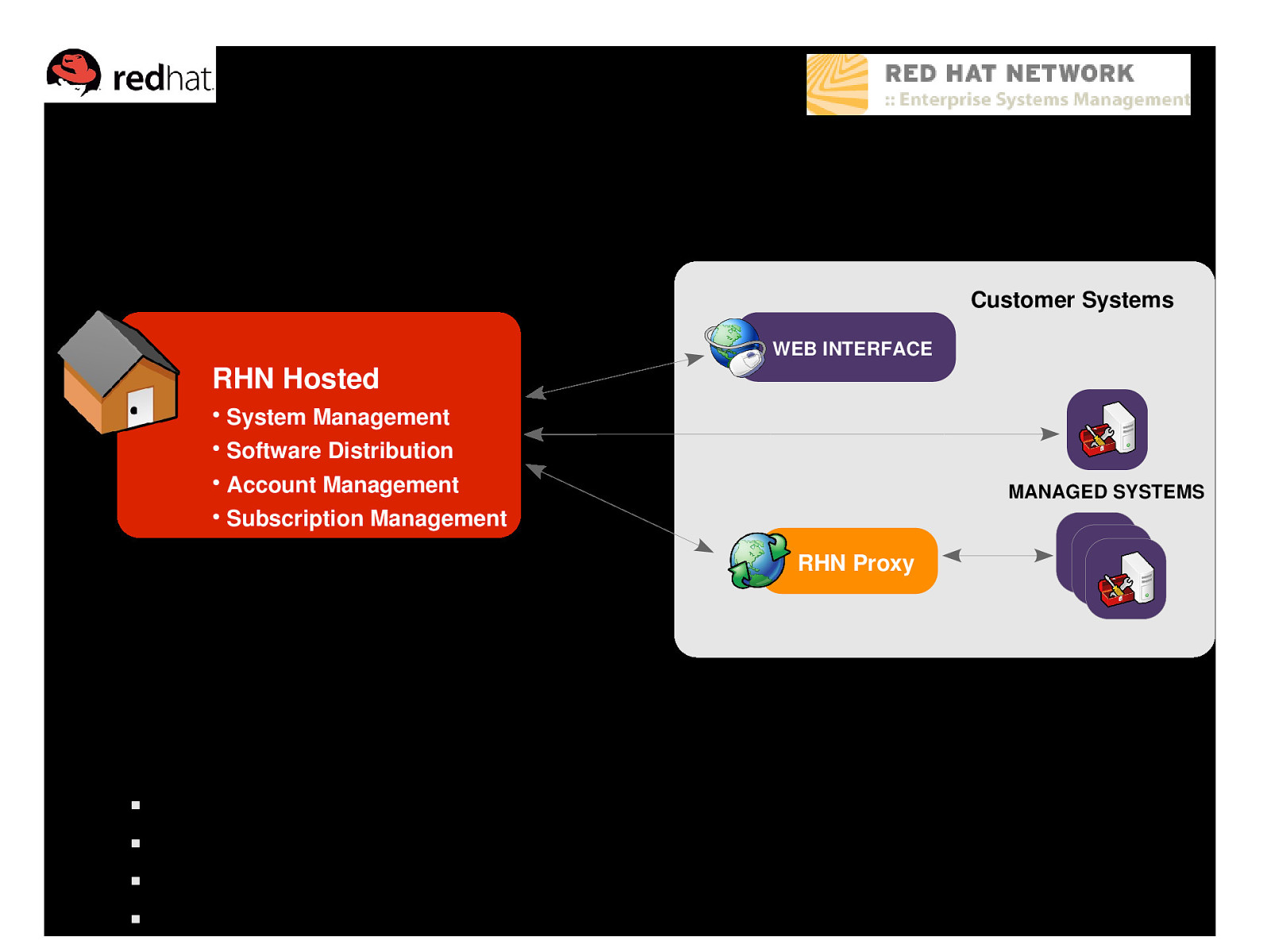
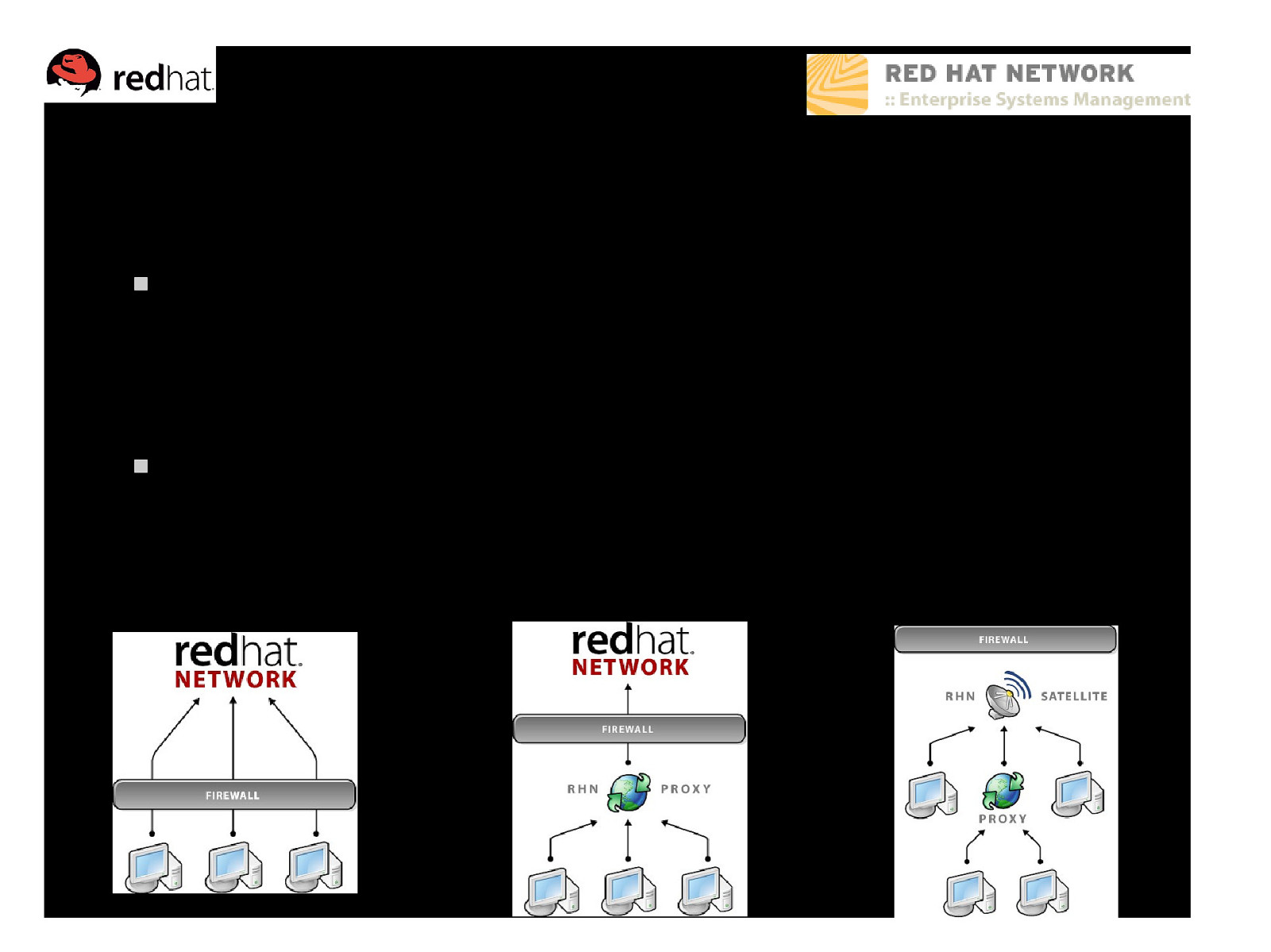
Hosted deployment model Customer Systems RHN Hosted ● System Management ● Software Distribution ● Account Management ● Subscription Management WEB INTERFACE MANAGED SYSTEMS RHN Proxy Quick setup is designed to enable management for small deployments All system information, profiles, and packages are stored in Red Hat’s servers Each managed system connects across the Internet for all managed actions RHN Proxy can be added to lower bandwidth use by caching packages locally
Slide 14
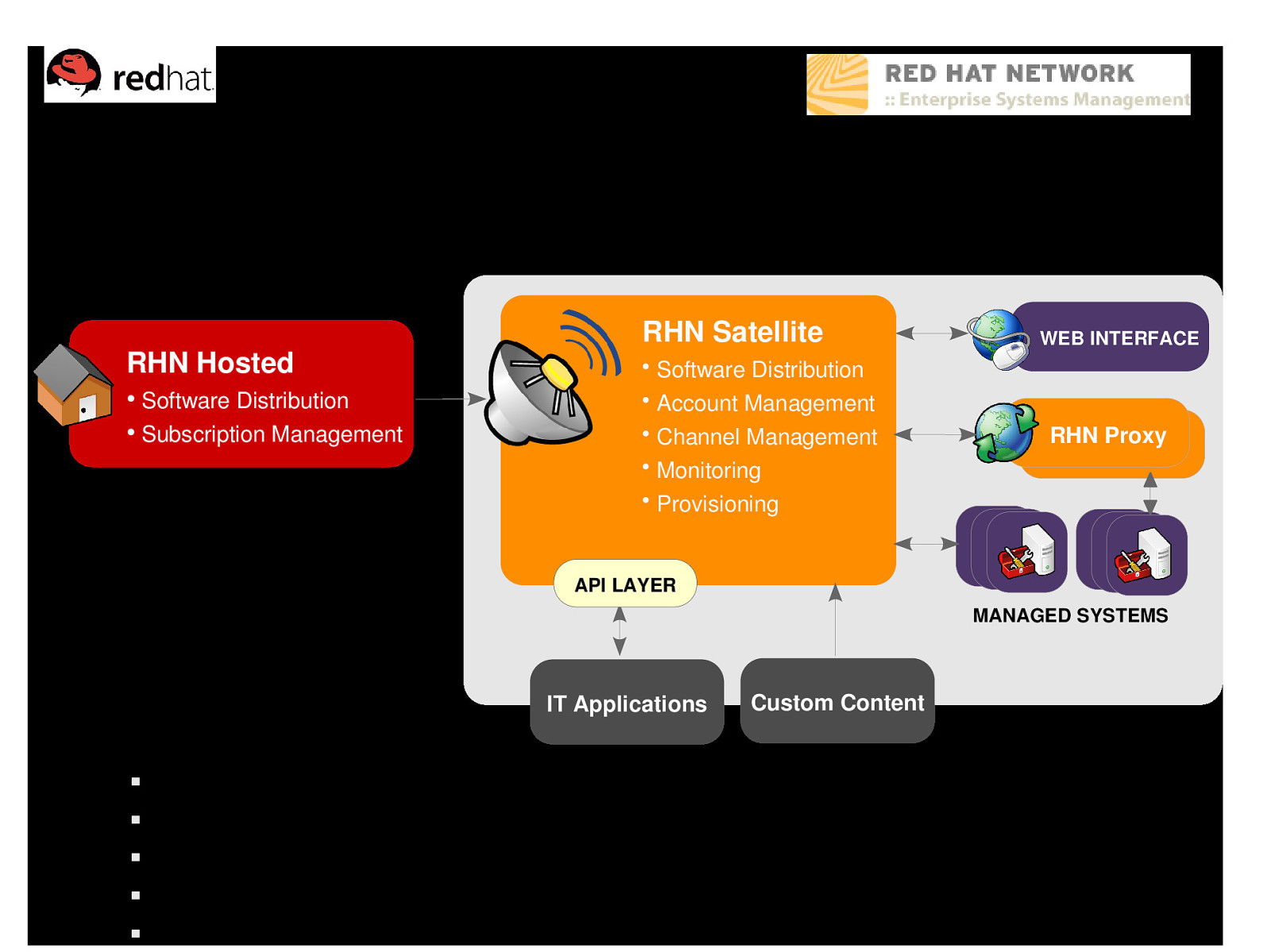
Satellite deployment model RHN Hosted Software Distribution ● Subscription Management ● RHN Satellite • Software Distribution • Account Management • Channel Management • Monitoring • Provisioning WEB INTERFACE RHN Proxy API LAYER MANAGED SYSTEMS IT Applications Custom Content Enterprise management solution – enhanced control Local database stores all packages, profiles, and system information Syncs content from RHN Hosted Custom content distribution Can run disconnected from the Internet
Slide 15

Why use a Satellite Server? Improved performance ● Systems connect to Satellite instead of each downloading content from Red Hat ● Satellite syncs with Red Hat to get the latest packages and errata ● Embedded Oracle database scales to thousands of connected systems Better control ● Satellite can run disconnected from the Internet for maximum security ● Use custom channels to distribute inhouse or 3rd party content ● Build around your processes – create cloned channels for staged environments Advanced functionality ● Monitoring and Solaris Management only available to Satellite users ● Satellite enables kickstarts with Provisioning Module ● Kickstart trees integrated into package repository for easy provisioning ● Store and deploy configuration files from the Satellite to improve consistency
Slide 16

Satellite terms to understand Channel: A list of software packages. There are two types of channels (base, child). Organization Administrator: User role with highest level of control. This user can add users, systems, and system groups. Channel Administrator: This user can create/clone/modify software channels. Red Hat Update Agent: Client application that connects to RHN/Satellite.
Slide 17

How it Works Database ● RHN Satellite Server ● Entry point for Red Hat Update Agent running on clients ● Apache HTTP server serving XMLRPC requests) RHN Satellite Web Interface ● Your existing database (standalone) or bundled (embedded Oracle 9i R2) Advanced system, system group, user, and channel management interface RPM Repository ● Package repository for Red Hat RPM packages as well as middleware/custom RPM packages.
Slide 18

How it Works Management Tools ● Database and file system syncrhonization tools ● RPM importing tools ● Channel maintenance tools (Web based) ● Errata management tools (Web based) ● User management tools (Web based) ● Client system and system grouping tools (Web based) ● Red Hat Update Agent on the client systems
Slide 19

Installation Requirements Software ● RHEL 4 (31bit or 64bit) ● @Base install Hardware ● 1 to 2 (virtual) IFLs ● 2 to 4 GB storage (memory) ● 1 GB swap (combination VDISK, disk) ● 1 x mod3 for OS install ● Estimated 12 GB disk space for embedded database ● 6 GB per channel (disk)
Slide 20

Infrastructure Requirements Network Ports ● (80, 443) outbound, unless running in disconnected mode ● (80, 443) inbound, for WebUI and client requests ● (4545) outbound, if monitoring is configured and probes are active on clients ● (5222) inbound, to push actions to client systems ● (5269) inbound, to push actions to RHN Proxy Server Other Requirements ● Red Hat Network account ● Entitlement Certificate
Slide 21

Example RHN Certificate (XML) ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● <rhn-cert version=”0.1”> <rhn-cert-field name=”product”>RHN-SATELLITE-001</rhn-cert-field> <rhn-cert-field name=”owner”>Clay’s Precious Satellite</rhn-cert-field> <rhn-cert-field name=”issued”>2005-01-11 00:00:00</rhn-cert-field> <rhn-cert-field name=”expires”>2005-03-11 00:00:00</rhn-cert-field> <rhn-cert-field name=”slots”>30</rhn-cert-field> <rhn-cert-field name=”provisioning-slots”>30</rhn-cert-field> <rhn-cert-field name=”nonlinux-slots”>30</rhn-cert-field> <rhn-cert-field name=”channel-families” quantity=”10” family=”rhel-cluster”/> <rhn-cert-field name=”channel-families” quantity=”30” family=”rhel-ws-extras”/> <rhn-cert-field name=”channel-families” quantity=”10” family=”rhel-es-extras”/> <rhn-cert-field name=”channel-families” quantity=”40” family=”rhel-as”/> <rhn-cert-field name=”channel-families” quantity=”30” family=”rhn-tools”/> <rhn-cert-field name=”satellite-version”>3.6</rhn-cert-field> <rhn-cert-field name=”generation”>2</rhn-cert-field> <rhn-cert-signature> ——-BEGIN PGP SIGNATURE——Version: Crypt::OpenPGP 1.03 ● ● ● ● ● ● ● iQBGBAARAwAGBQJCAG7yAAoJEJ5yna8GlHkysOkAn07qmlUrkGKs7/5yb8H/nboG mhHkAJ9wdmqOeKfcBa3IUDL53oNMEBP/dg== =0Kv7 ——-END PGP SIGNATURE——</rhn-cert-signature> </rhn-cert>
Slide 22
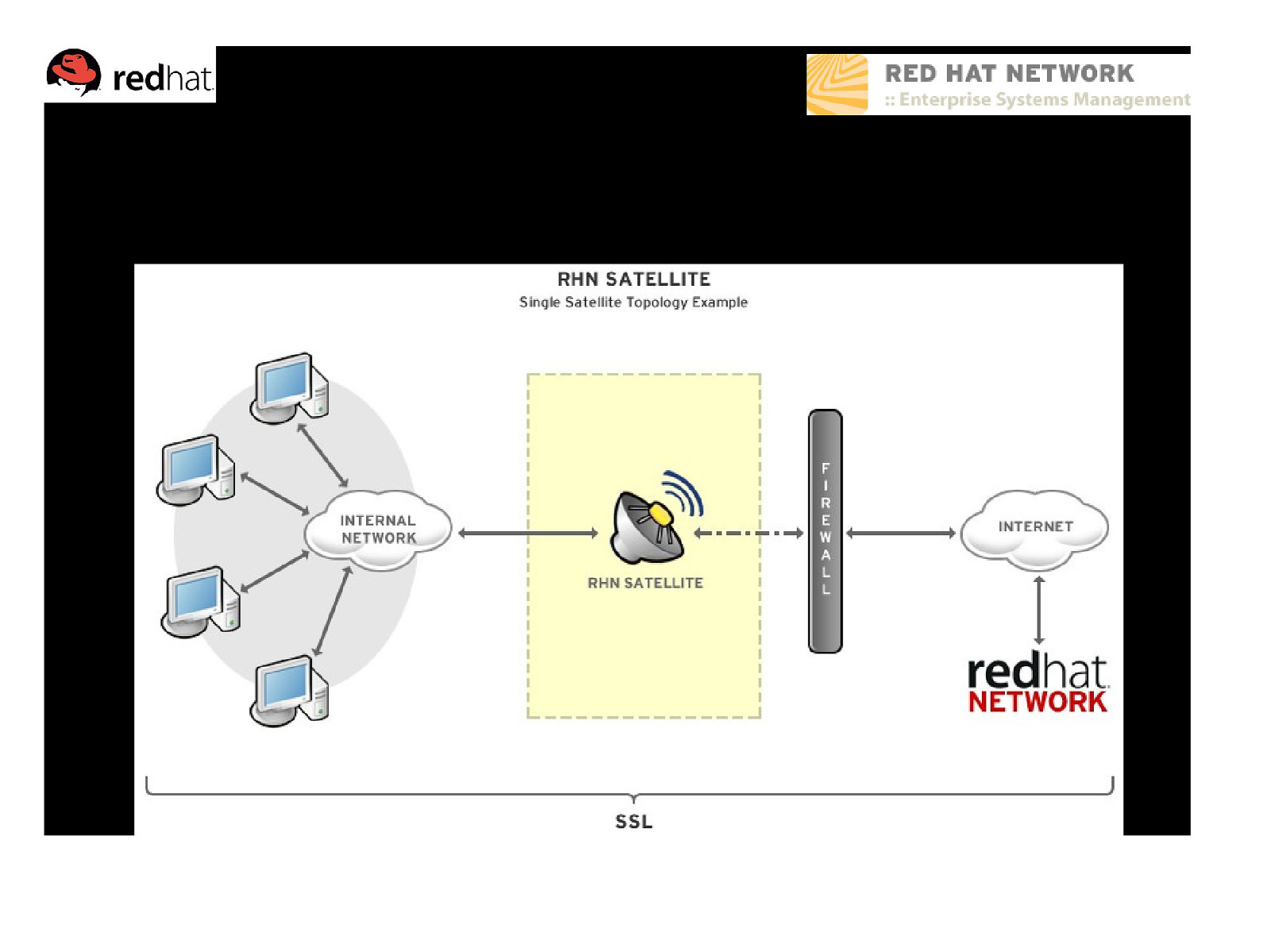
Example Topology – Single Satellite
Slide 23
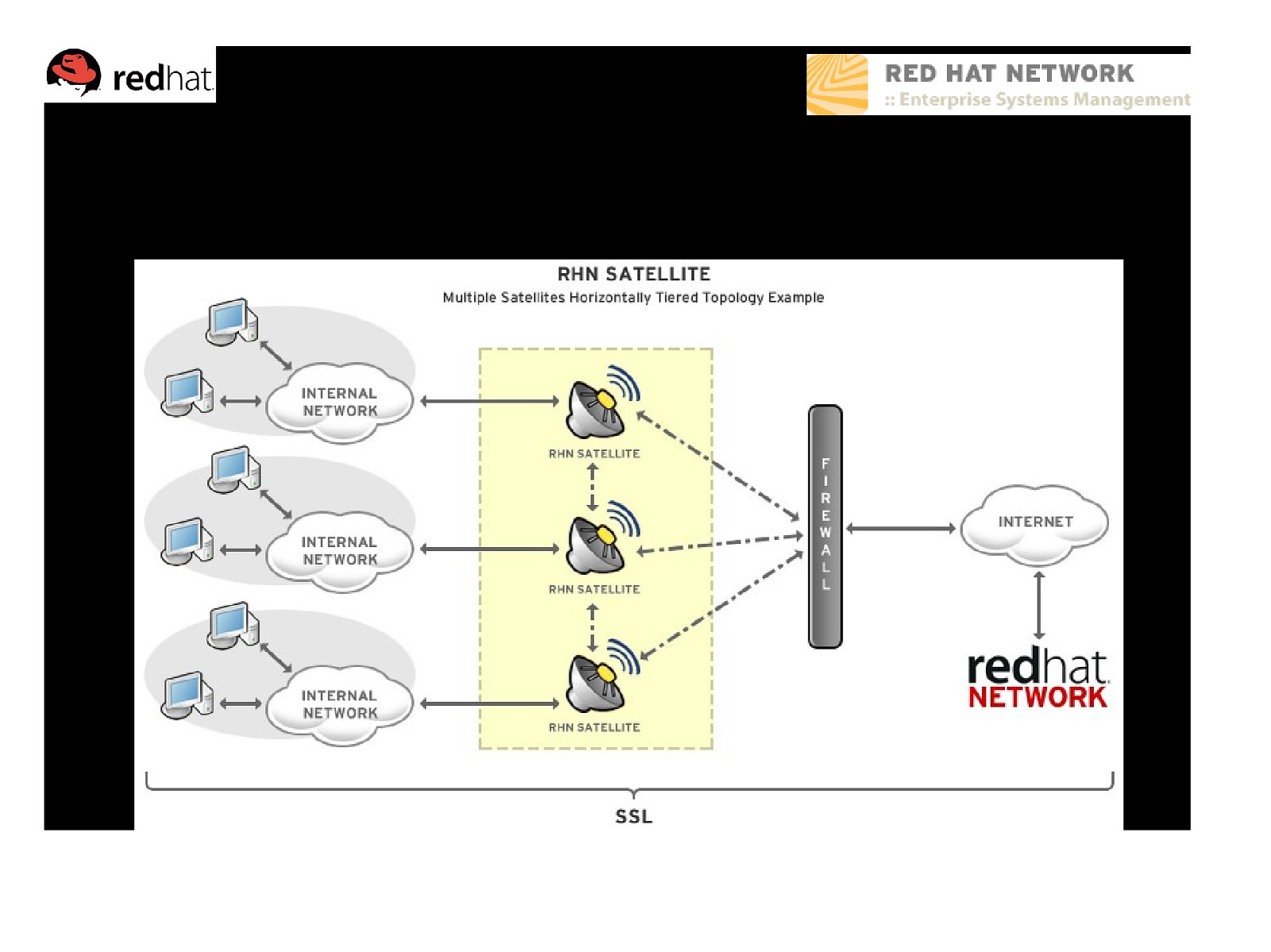
Example Topology – Multiple Tiered
Slide 24
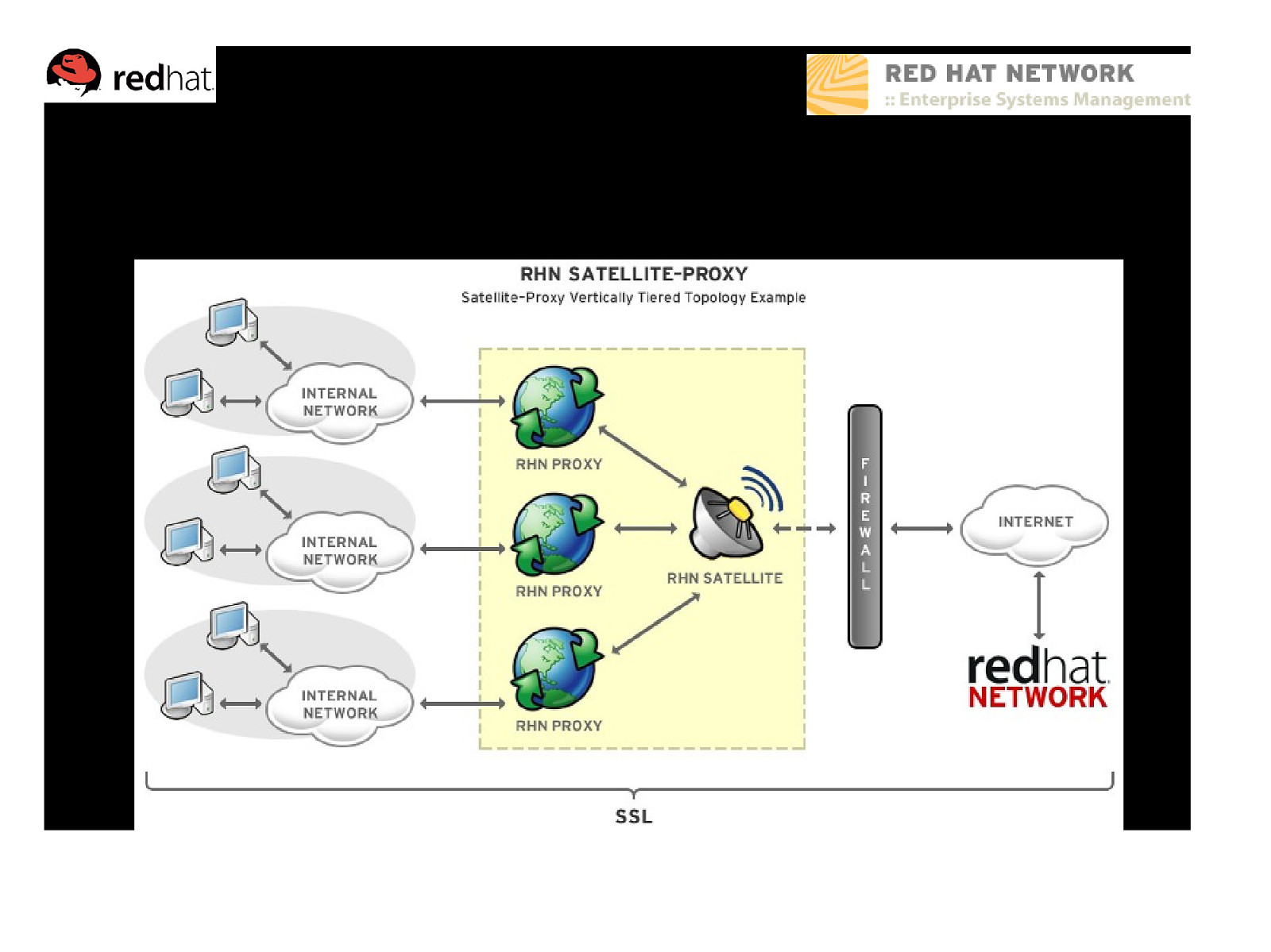
Example – Proxy Vertically Tiered
Slide 25
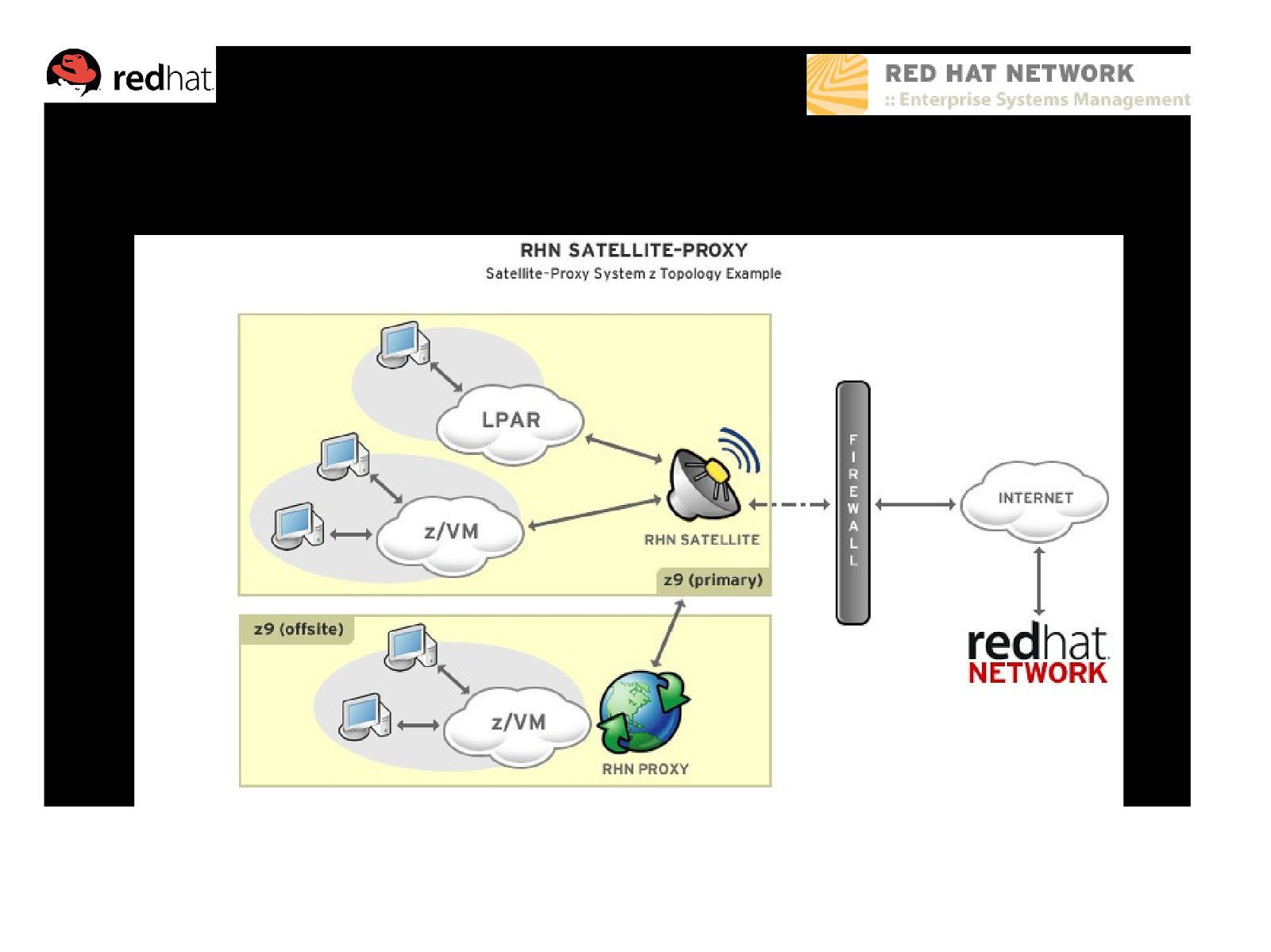
Example – System z (multiple site)
Slide 26

Installing RHN Satellite mount o loop iso_filename /media/ cd /media; ./install.pl ● ./install.pl help ● ./install.pl disconnected Installer steps ● Create database ● Import Satellite certificate ● Register/Activate Satellite ● Generate CA certificate for SSL traffic
Slide 27

Import Packages with satellitesync Synchronize metadata/packages with RHN ● Satellite connected to RHN Internal steps ● channelfamilies – Import/sync channel family (architecture) data ● channels – Import/sync channel data ● rpms – Import/sync RPMs ● packages – Import/sync full package data for RPMs retrieved successfully ● errata – Import/sync Errata information
Slide 28

Import Packages (Disconnected) Synchronize metadata/packages from Channel Content ISO ● Released shortly after each RHEL update on RHN, then in regular increments Use channel data from another Satellite ● rhnsatelliteexporter exports channel families, architectures, channel metadata, blacklists, RPMs, RPM metadata, errata, and kickstarts ● rhnsatelliteexporter dir=/var/satbackup/ ● scp r storage.example.com:/var/satbackup/* /var/rhnsatimport ● satellitesync listchannels mountpoint /var/rhnsatimport ● satellitesync c rhels390xas4 mountpoint /var/rhnsatimport ● Can specify multiple channels in one command. Estimate ~2 hours per channel.
Slide 29

Sources of further information Problem ● Where can I find further information on RHN Satellite? Solution ● Red Hat Knowledgebase ● ● RHN Documentation ● ● https://rhn.redhat.com/help/ RHN Satellite Users mailing list ● ● http://kbase.redhat.com/faq/ https://www.redhat.com/mailman/listinfo/rhnsatelliteusers RHN Satellite comes with 24/7 support ● https://www.redhat.com/apps/support/
Slide 30
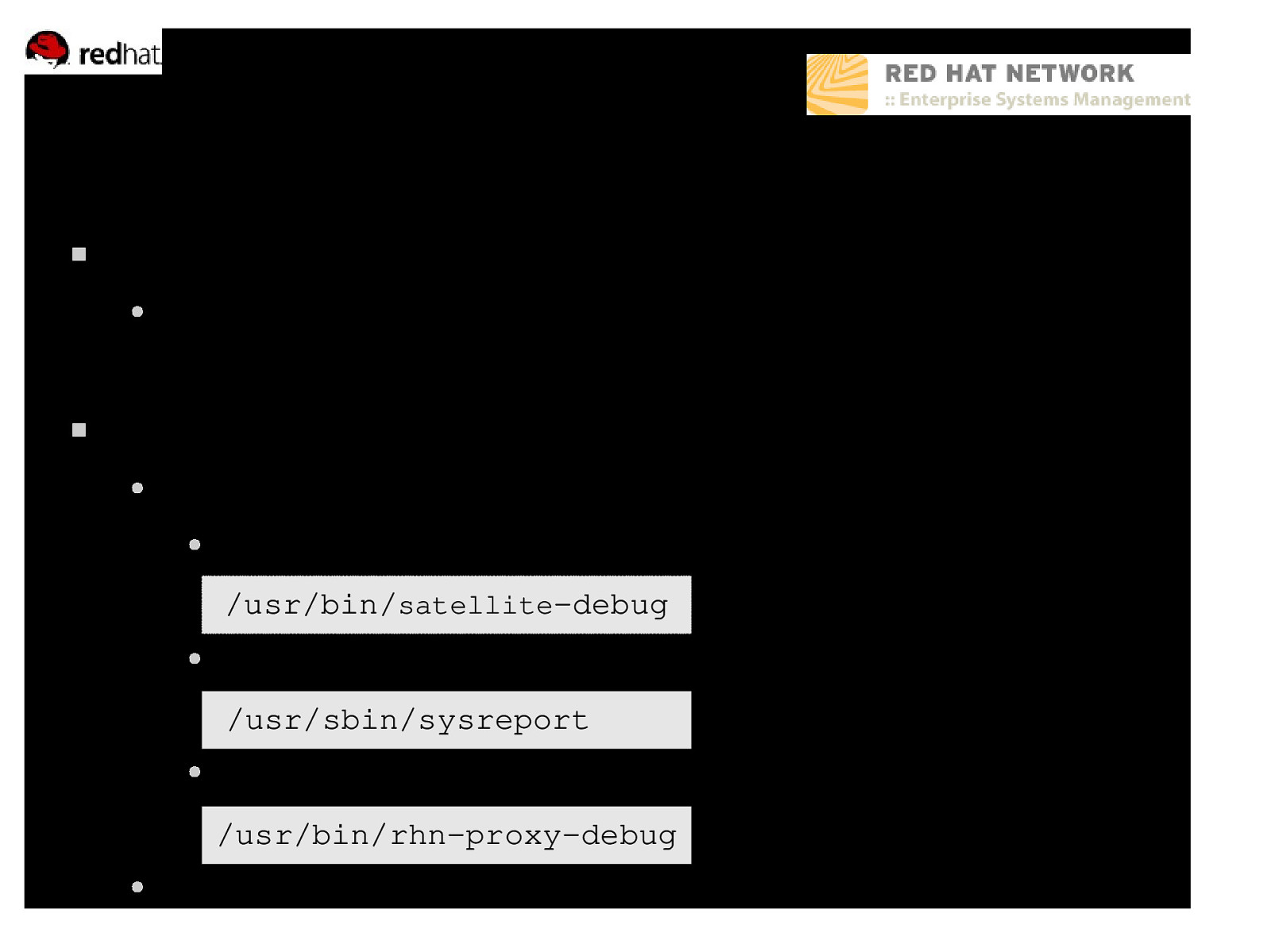
Contacting Red Hat Support Problem ● My Satellite is not working, what should I do? Solution ●
- Gather data, include ● RHN Satellite Debug /usr/bin/satellite-debug ● System Report /usr/sbin/sysreport ● RHN Proxy Debug (if needed) /usr/bin/rhn-proxy-debug ●
- Contact Red Hat Support with data
Slide 31

Appendix – Technical Data RHN Satellite Components Apache Java & RHN Push Monitoring Database & Taskomatic Misc data
Slide 32

RHN Satellite Components Web Server – Apache ● Satellite Web UI ● /XMLRPC ● /API Java – Tomcat (new) RHN Push – Jabber ● osadispatcher (server side) ● osad (client side) Monitoring Technology (new) ● Monitoring Backend ● Monitoring Scout Database Server – Oracle 9i Scheduled tasks – Taskomatic
Slide 33

RHN Satellite – Apache Apache processes within RHN Satellite handle multiple types of requests ● ● Satellite Web UI with perl and java components /XMLRPC, /API & /APPLET via python Main configuration files ● /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf ● /etc/httpd/conf/rhn/ ● /etc/rhn/rhn.conf Runs with standard httpd daemon on ports 80 and 443 Apache writes to various log files in the follow locations ● /var/log/rhn/ ● /var/log/httpd/ Misc files of note ● SSL Certificates used by Apache ● /etc/httpd/conf/ssl.key/server.key ● /etc/httpd/conf/ssl.crt/server.crt
Slide 34

RHN Satellite – Java & RHN Push Tomcat is communicated to via Apache for portions of the Java Web UI within RHN Satellite 4.0 Main configuration file ● /etc/tomcat5/tomcat5.conf ● /var/log/tomcat5/ Tomcat daemon listens to ports ● ● ● The jabber protocol is being used by RHN as a means of being able to push scheduled actions to systems. ● Main log directory ● 8005 8009 8080 Satellite connects to jabber (osa dispatcher) Clients connect to jabber (osad) Main configuration files for push technology ● /etc/jabberd/jabberd.cfg ● /etc/rhn/rhn.conf Main log files are ● /var/log/messages ● /var/log/rhn/osadispatcher.log
Slide 35

RHN Satellite – Monitoring Monitoring Backend Monitoring Scout ● Some of the monitoring configuration files ● /etc/rhn/rhn.conf ● /etc/rhn/cluster.ini ● /etc/NOCpulse.ini ● Scout can also be on the same server as the backend /etc/httpd/conf/rhn/rhn_monitoring .conf Specific to Scout ● /home/nocpulse/etc/SatCluster.ini Monitoring has one main nanny script which is gogo.pl Nearly all Monitoring logging is done within ● /home/nocpulse/var/ ● /opt/notification/var/
Slide 36

RHN Satellite – Database & Taskomatic RHN Satellite needs communication to an Oracle 9i Database Server ● ● /etc/tnsnames.ora ● /etc/rhn/rhn.conf /opt/apps/oracle/config/9.2.0/spfil erhnsat.ora Listener daemon (tnslsnr) runs localhost only on port 1290 Main log files for Oracle ● ● Taskomatic is a daemon that runs constantly on RHN Satellite. It is used to execute scheduled tasks which are queued in the database. Uses /etc/rhn/rhn.conf configuration file. Logs into /var/log/messages Embedded or External Oracle Main configuration files for database ● /var/log/rhn/rhn_database.log /rhnsat/admin/rhnsat/bdump/alert _rhnsat.log
Slide 37

Anything else I should know? The most important configuration file ● Two common general options of interest that can be changed ● ● /etc/rhn/rhn.conf traceback_mail – change the default email address alerts go to. Check this email address for traceback emails if something goes wrong debug default is 1, setting to 5 or 6 is enough for troubleshooting Restart RHN Satellite services using command ● service rhn-satellite restart ● This will run the following service scripts ● jabberd rhn-database osa-dispatcher taskomatic ● tomcat5 httpd Monitoring MonitoringScout
Slide 38

Questions?